How warming oceans affect marine ecosystems and fisheries
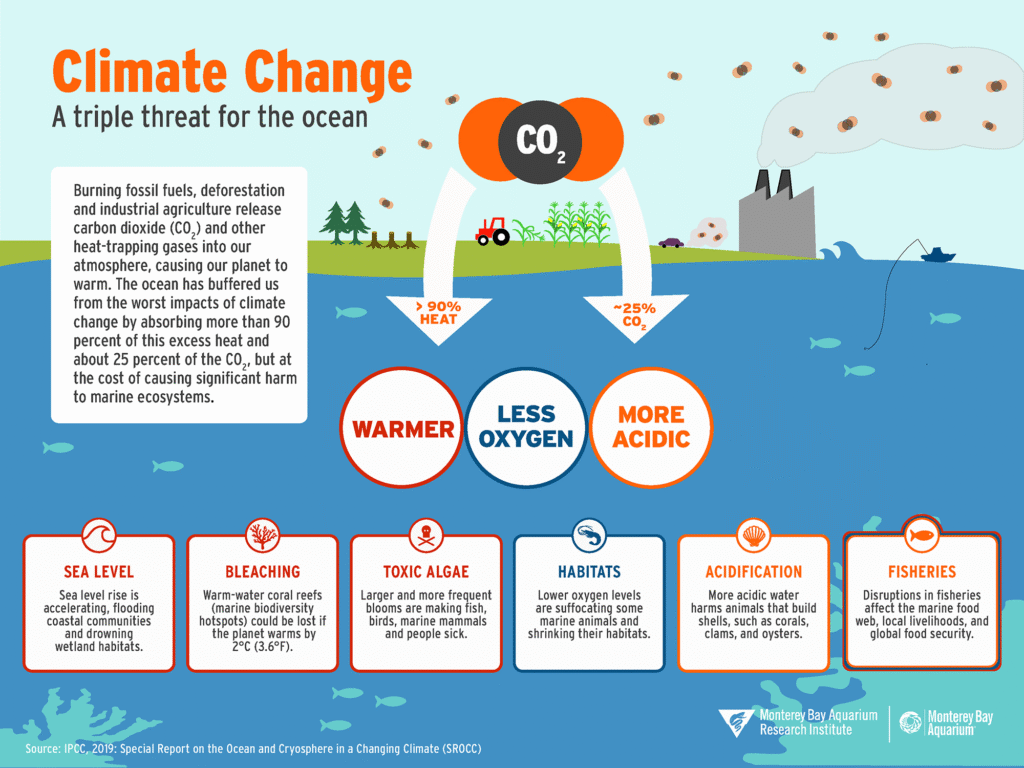
The world's oceans are facing an unprecedented crisis as a result of climate change, with rising temperatures having a profound impact on marine ecosystems and fisheries. As the planet continues to warm, the oceans are absorbing a significant portion of the excess heat, leading to a steady increase in ocean temperatures. This warming is having far-reaching consequences for marine life, from the simplest plankton to the largest predators, and the fisheries that depend on them. Understanding the effects of warming oceans is crucial to mitigating these impacts and ensuring the long-term health of marine ecosystems.
- Impact of Rising Ocean Temperatures on Marine Life and Fisheries
-
Understanding the Impact of Rising Ocean Temperatures on Marine Life and Fisheries
- What is the impact of rising ocean temperatures on marine ecosystems and the fishing industry?
- Changes in Species Distribution and Phenology
- Impacts on Fisheries and the Fishing Industry
- Consequences for Marine Biodiversity
- What is the impact of rising ocean temperatures on marine biodiversity?
- Changes in Species Distribution
- Impacts on Marine Ecosystems
- Consequences for Marine Fisheries
- What is the impact of rising ocean temperatures on marine biodiversity and fisheries productivity?
- Shifts in Species Distributions
- Impacts on Fisheries Productivity
- Consequences for Ecosystem Function
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the impact of warming oceans on marine biodiversity?
- How do warming oceans influence fisheries and fish populations?
- What are the consequences of ocean warming on coral reefs and associated ecosystems?
- Can warming oceans lead to changes in the distribution of marine species towards the poles?
Impact of Rising Ocean Temperatures on Marine Life and Fisheries
The warming of the world's oceans is having a profound impact on marine ecosystems and fisheries. As the planet continues to warm due to climate change, the consequences for marine life are far-reaching and multifaceted. Rising ocean temperatures are altering the distribution, behavior, and productivity of marine species, with significant implications for the health of marine ecosystems and the industries that depend on them.
Shifts in Species Distribution and Abundance
As ocean temperatures rise, many marine species are shifting their ranges poleward or to deeper waters in search of cooler temperatures. This can lead to changes in the composition of marine communities, with some species becoming more abundant while others decline. For example, warm-water fish such as sardines and anchovies are moving northward, while cold-water species like cod and haddock are declining in abundance. This can have significant implications for fisheries and the communities that depend on them.
| Species | Current Distribution | Projected Shift |
|---|---|---|
| Atlantic Cod | Northern Atlantic | Northward |
| Sardines | Temperate and tropical waters | Expanding to higher latitudes |
Impacts on Phytoplankton and the Marine Food Web
Phytoplankton, the microscopic plants that form the base of the marine food web, are also being affected by warming oceans. As temperatures rise, phytoplankton growth rates and productivity can change, with potential cascading effects on the entire food web. Changes in phytoplankton communities can impact the availability of food for zooplankton, fish, and other marine species. This, in turn, can have significant implications for the health of marine ecosystems and the fisheries that depend on them.
| Phytoplankton Group | Response to Warming | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Dinoflagellates | Increasing growth rates | Potential increase in harmful algal blooms |
| Coccolithophores | Decreasing calcification | Impacts on ocean carbon sequestration |
Consequences for Fisheries and Coastal Communities
The impacts of warming oceans on marine ecosystems and fisheries can have significant consequences for the industries and communities that depend on them. Fisheries management will need to adapt to changing species distributions and productivity to ensure the long-term sustainability of fisheries. Additionally, coastal communities may need to develop new livelihood strategies in response to changes in fisheries and the marine ecosystem.
| Region | Fisheries Impact | Community Response |
|---|---|---|
| North Atlantic | Decline of cod and other groundfish | Shift to alternative fisheries or industries |
| Tropical Pacific | Changes in tuna and other pelagic fisheries | Development of ecotourism and other alternative livelihoods |
Understanding the Impact of Rising Ocean Temperatures on Marine Life and Fisheries
What is the impact of rising ocean temperatures on marine ecosystems and the fishing industry?

The impact of rising ocean temperatures on marine ecosystems and the fishing industry is a complex and multifaceted issue. Rising ocean temperatures are altering the delicate balance of marine ecosystems, leading to changes in species distribution, behavior, and extinction risk. As the ocean warms, many marine species are shifting their ranges poleward or to deeper waters in search of cooler habitats, disrupting the intricate web of relationships within ecosystems.
Changes in Species Distribution and Phenology
Rising ocean temperatures are driving changes in species distribution and phenology, with many marine species altering their migration patterns, breeding times, and feeding behaviors in response to changing environmental conditions. This can have cascading effects on ecosystems, as changes in one species can impact others that depend on them for food or habitat.
- Changes in phytoplankton blooms can impact the timing of zooplankton grazing, affecting the productivity of fisheries.
- Shifts in fish distributions can alter the composition of fish communities, impacting fisheries and the livelihoods of people who depend on them.
- Changes in species phenology can disrupt the synchronization of predator-prey interactions, leading to mismatches between predators and their prey.
Impacts on Fisheries and the Fishing Industry
The fishing industry is also being impacted by rising ocean temperatures, as changes in fish distributions and productivity affect the availability of fish for commercial and recreational fisheries. As fish populations shift in response to changing ocean conditions, fisheries may need to adapt by changing their fishing practices, targeting different species, or moving to new fishing grounds.
- Fisheries that are unable to adapt to changes in fish distributions may experience declines in catch and revenue.
- Changes in fish populations can also impact the livelihoods of people who depend on fishing and seafood processing for their income.
- The impacts of climate change on fisheries can also have flow-on effects to food security, as seafood is an important source of protein for many communities around the world.
Consequences for Marine Biodiversity
Rising ocean temperatures are also having significant consequences for marine biodiversity, as many marine species are pushed towards the limits of their tolerance or beyond. As a result, some species are facing increased extinction risk, with potential cascading effects on ecosystems.
- Corals are particularly vulnerable to warming, with mass bleaching events becoming increasingly common.
- Polar ecosystems are also being impacted, as warming waters alter the distribution of sea ice and the species that depend on it.
- The loss of biodiversity can have significant ecosystem consequences, including reduced ecosystem resilience and altered ecosystem processes.
What is the impact of rising ocean temperatures on marine biodiversity?

The impact of rising ocean temperatures on marine biodiversity is a pressing concern, as it can have far-reaching consequences for the delicate balance of marine ecosystems. Rising ocean temperatures are altering the distribution, behavior, and physiology of marine species, leading to changes in the composition of marine communities.
Changes in Species Distribution
Rising ocean temperatures are causing many marine species to shift their ranges poleward or to deeper waters in search of cooler temperatures. This can lead to changes in the composition of marine communities, as some species may not be able to adapt to the changing conditions.
- Some species are shifting their ranges at a rate of up to 100 km per decade.
- Changes in species distribution can have cascading effects on ecosystems, leading to changes in predator-prey dynamics and nutrient cycling.
- This can also lead to the loss of biodiversity, as some species may not be able to adapt to the changing conditions.
Impacts on Marine Ecosystems
Rising ocean temperatures can have significant impacts on marine ecosystems, including coral bleaching, changes in phytoplankton productivity, and shifts in the distribution of marine algae. These changes can have cascading effects on the entire ecosystem, leading to changes in the provision of ecosystem services.
- Coral bleaching is a major consequence of rising ocean temperatures, with mass bleaching events becoming more frequent and severe.
- Changes in phytoplankton productivity can have impacts on the entire food web, as phytoplankton are the base of many marine food webs.
- Shifts in the distribution of marine algae can also have impacts on the biodiversity of marine ecosystems.
Consequences for Marine Fisheries
Rising ocean temperatures can also have significant impacts on marine fisheries, as changes in species distribution and abundance can affect the productivity and sustainability of fisheries. This can have significant economic and social impacts on communities that depend on fishing and seafood production.
- Changes in species distribution can lead to changes in the composition of fish catches, with some species becoming more or less abundant.
- Rising ocean temperatures can also lead to changes in the productivity of fisheries, as changes in ocean conditions affect the growth and survival of fish.
- This can have significant economic impacts on the fishing industry, as well as on the food security of communities that depend on seafood.
What is the impact of rising ocean temperatures on marine biodiversity and fisheries productivity?
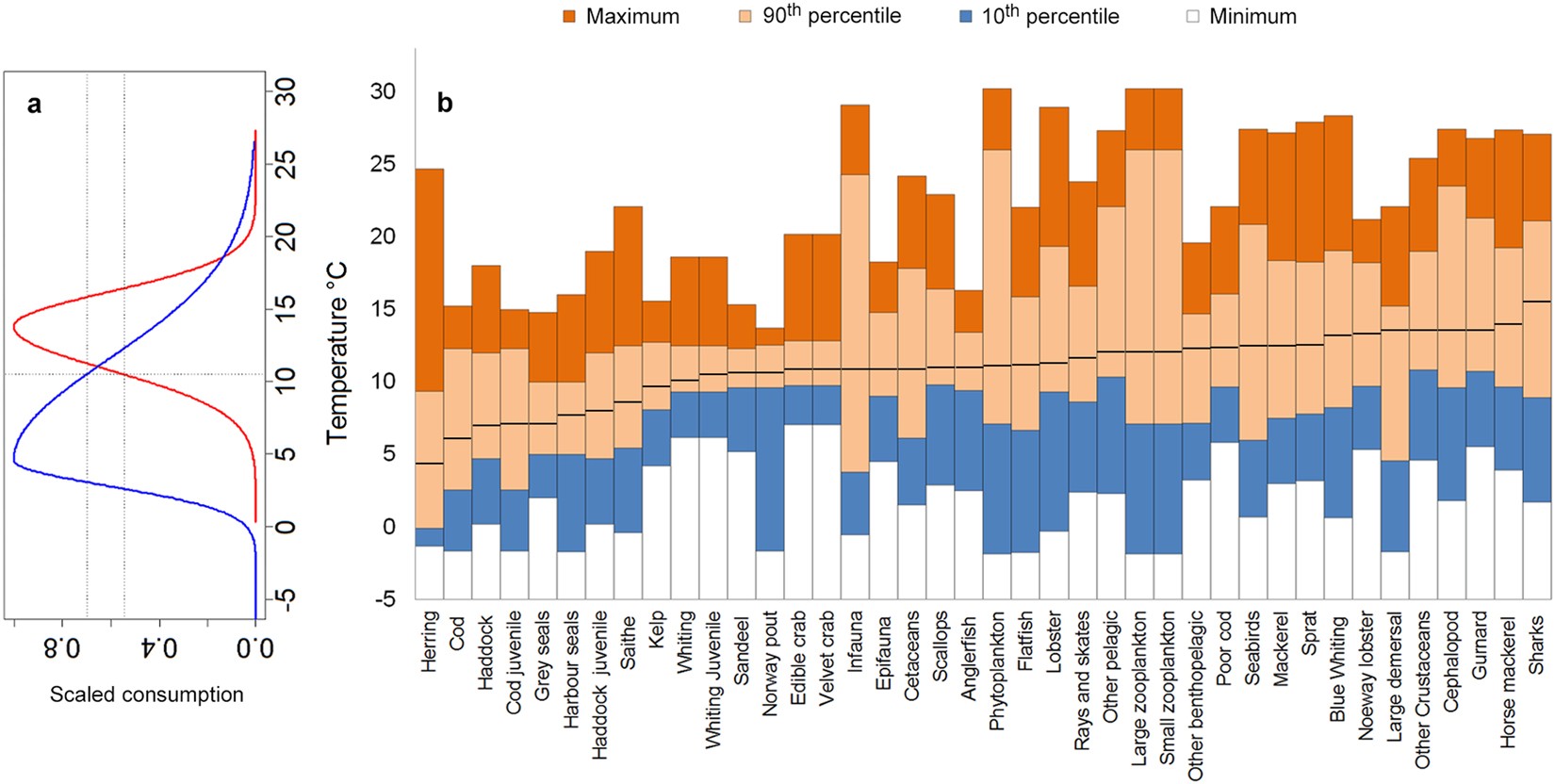
Rising ocean temperatures are having a profound impact on marine biodiversity and fisheries productivity. The warming of the ocean is causing a range of effects, from changes in species distributions and behaviors to impacts on the productivity of fisheries. As the ocean continues to warm, these impacts are likely to become more pronounced, with potentially significant consequences for the health of marine ecosystems and the communities that depend on them.
Shifts in Species Distributions
As ocean temperatures rise, many marine species are being forced to shift their distributions poleward or to deeper waters in search of cooler temperatures. This can have significant impacts on the composition of marine ecosystems, as some species are able to adapt to the changing conditions while others are not. The consequences of these shifts can be far-reaching, with impacts on the structure and function of ecosystems. Some of the key effects of shifts in species distributions include:
- Changes in predator-prey dynamics, as some species are able to take advantage of new prey populations while others lose access to their traditional prey.
- Altered competition for resources, as new species move into an area and compete with existing species for food and habitat.
- Loss of biodiversity, as some species are unable to adapt to the changing conditions and are pushed to the edge of their range or even to extinction.
Impacts on Fisheries Productivity
Rising ocean temperatures are also having significant impacts on fisheries productivity. As the ocean warms, the productivity of some fisheries is declining, while others are experiencing changes in the distribution and abundance of target species. This can have significant economic and social impacts on the communities that depend on these fisheries. Some of the key effects of rising ocean temperatures on fisheries productivity include:
- Changes in the distribution and abundance of target species, as some species move to new areas or become more or less abundant.
- Impacts on the productivity of fisheries, as warming waters affect the growth rates and survival of fish and other marine species.
- Shifts in the timing of seasonal events, such as migrations and spawning, which can have cascading effects on the entire ecosystem.
Consequences for Ecosystem Function
The impacts of rising ocean temperatures on marine biodiversity and fisheries productivity are also having significant consequences for ecosystem function. As species distributions shift and fisheries productivity changes, the functioning of ecosystems is being altered. This can have far-reaching impacts on the health and resilience of marine ecosystems. Some of the key effects of rising ocean temperatures on ecosystem function include:
- Changes in nutrient cycling, as the composition of phytoplankton and other microorganisms is altered.
- Impacts on the structure of food webs, as changes in predator-prey dynamics and competition for resources affect the flow of energy through ecosystems.
- Loss of ecosystem services, as the degradation of ecosystems reduces their ability to provide important services such as coastal protection and water filtration.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the impact of warming oceans on marine biodiversity?
Warming oceans affect marine biodiversity by altering species distribution, behavior, and physiology. Rising temperatures can lead to changes in phytoplankton productivity, which cascades through the food web, impacting the entire ecosystem. This can result in local extinctions, changes in community composition, and loss of ecosystem function, ultimately threatening the resilience of marine ecosystems.
How do warming oceans influence fisheries and fish populations?
Warming oceans impact fisheries and fish populations by altering the distribution, abundance, and productivity of fish species. Changes in ocean temperature and chemistry affect the growth, migration, and survival of fish, leading to shifts in the composition of fish communities. This can result in reduced fish catches, economic losses for fishing industries, and food insecurity for communities dependent on fisheries.
What are the consequences of ocean warming on coral reefs and associated ecosystems?
Ocean warming has devastating consequences for coral reefs, causing mass bleaching events, reduced coral cover, and changes in associated fish communities. Rising temperatures also impact other ecosystems, such as seagrass beds and mangroves, which provide essential habitat for many marine species. The loss of these ecosystems can have cascading effects on biodiversity, fisheries, and coastal protection.
Can warming oceans lead to changes in the distribution of marine species towards the poles?
Yes, warming oceans can lead to changes in the distribution of marine species towards the poles. As temperatures rise, many species shift their ranges poleward in search of cooler waters, altering the composition of ecosystems and potentially leading to invasions of non-native species. This can result in changes to ecosystem function, biodiversity, and the distribution of fisheries, with potential impacts on food security and human communities.

Leave a Reply