How sustainable urban planning mitigates heat waves risks
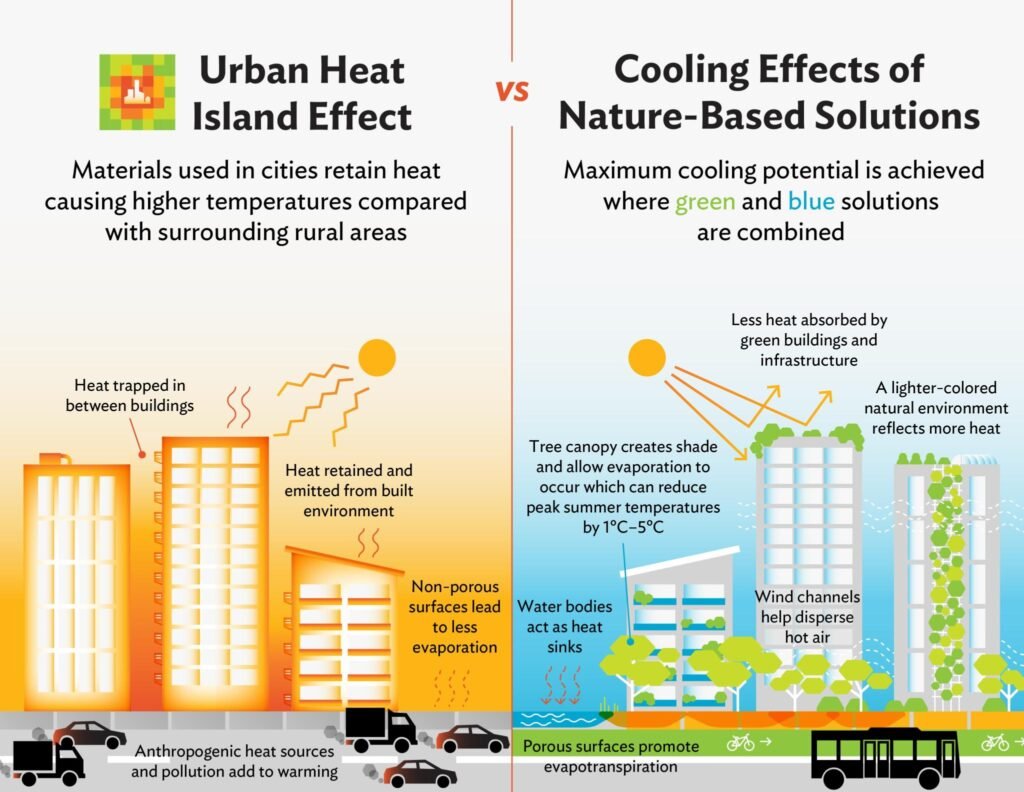
Cities worldwide are experiencing increasingly severe heat waves due to climate change, posing significant health risks to their inhabitants. Sustainable urban planning plays a crucial role in mitigating these risks by incorporating design elements that reduce the urban heat island effect. Effective planning can help to lower temperatures, improve air quality, and enhance residents' overall well-being. By integrating green spaces, optimizing building layouts, and utilizing cool materials, cities can develop resilience to heat waves. This article explores the strategies and benefits of sustainable urban planning in reducing the impacts of heat waves on urban populations.
- Mitigating Heat Waves through Sustainable Urban Planning Strategies
-
Mitigating Heat Wave Risks through Sustainable Urban Design Principles
- What role does urban planning play in reducing the effects of urban heat islands?
- Green Infrastructure
- Cool Pavements and Materials
- Urban Design and Configuration
- 'How can sustainable urban planning and design help mitigate the impact of heat waves?'
- Green Infrastructure and Urban Forestry
- Cool Roofs and Pavements
- Water-Sensitive Urban Design
- What role does sustainable urban planning play in reducing the impact of climate change and enhancing city resilience to extreme weather events like heatwaves?
- Green Infrastructure and Urban Heat Island Mitigation
- Climate-Resilient Urban Design
- Policies and Regulations for Climate Change Mitigation
- 'Optimizing Urban Green Spaces to Mitigate Urban Heat Island Effects Across Diverse Climatic Contexts'
- Urban Green Space Design Considerations
- Climate-Sensitive Green Space Planning
- Integrating Green Infrastructure with Urban Planning
- Frequently Asked Questions
Mitigating Heat Waves through Sustainable Urban Planning Strategies
Sustainable urban planning plays a crucial role in mitigating the risks associated with heat waves. As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change, cities are increasingly becoming hotspots for heat-related illnesses and mortality due to the urban heat island effect. This phenomenon occurs when built-up areas, such as cities, experience warmer temperatures than their surrounding rural areas due to the concentration of heat-absorbing surfaces like pavement and buildings. By incorporating sustainable design principles and green infrastructure, cities can reduce the impact of heat waves on their residents.
Green Infrastructure and Cooling Effects
Green infrastructure, such as parks, gardens, and green roofs, can significantly mitigate the urban heat island effect by providing shade, cooling the air through evapotranspiration, and reducing the amount of heat-absorbing surfaces. For instance, a study found that increasing the tree canopy cover in a city can lower the air temperature by up to 3°C during heat waves. Moreover, green roofs can reduce the temperature of rooftops by up to 20°C compared to traditional roofing materials.
| Type of Green Infrastructure | Cooling Effect |
|---|---|
| Parks and Gardens | Reduces air temperature by up to 3°C |
| Green Roofs | Reduces rooftop temperature by up to 20°C |
| Urban Trees | Provides shade and reduces air temperature by up to 2°C |
Urban Design and Heat Wave Mitigation
Urban design plays a critical role in mitigating the effects of heat waves. By designing cities with narrow streets, shaded walkways, and building orientations that minimize direct sun exposure, cities can reduce the amount of heat absorbed and retained. Additionally, incorporating cool pavements and reflective building materials can also help to mitigate the urban heat island effect.
| Urban Design Feature | Heat Wave Mitigation Benefit |
|---|---|
| Narrow Streets | Reduces direct sun exposure and heat absorption |
| Shaded Walkways | Provides shade and reduces heat stress |
| Cool Pavements | Reduces surface temperature by up to 10°C |
Policy and Planning Frameworks for Heat Wave Mitigation
Effective policy and planning frameworks are essential for implementing sustainable urban planning strategies that mitigate the risks associated with heat waves. Cities can develop heat wave action plans that outline strategies for reducing heat-related illnesses and mortality. Additionally, cities can incorporate climate-resilient design principles into their urban planning frameworks to ensure that new developments are designed with heat wave mitigation in mind.
| Policy/Planning Framework | Heat Wave Mitigation Benefit |
|---|---|
| Heat Wave Action Plans | Outlines strategies for reducing heat-related illnesses and mortality |
| Climate-Resilient Design Principles | Ensures new developments are designed with heat wave mitigation in mind |
| Green Infrastructure Standards | Requires incorporation of green infrastructure into urban design |
Mitigating Heat Wave Risks through Sustainable Urban Design Principles
What role does urban planning play in reducing the effects of urban heat islands?
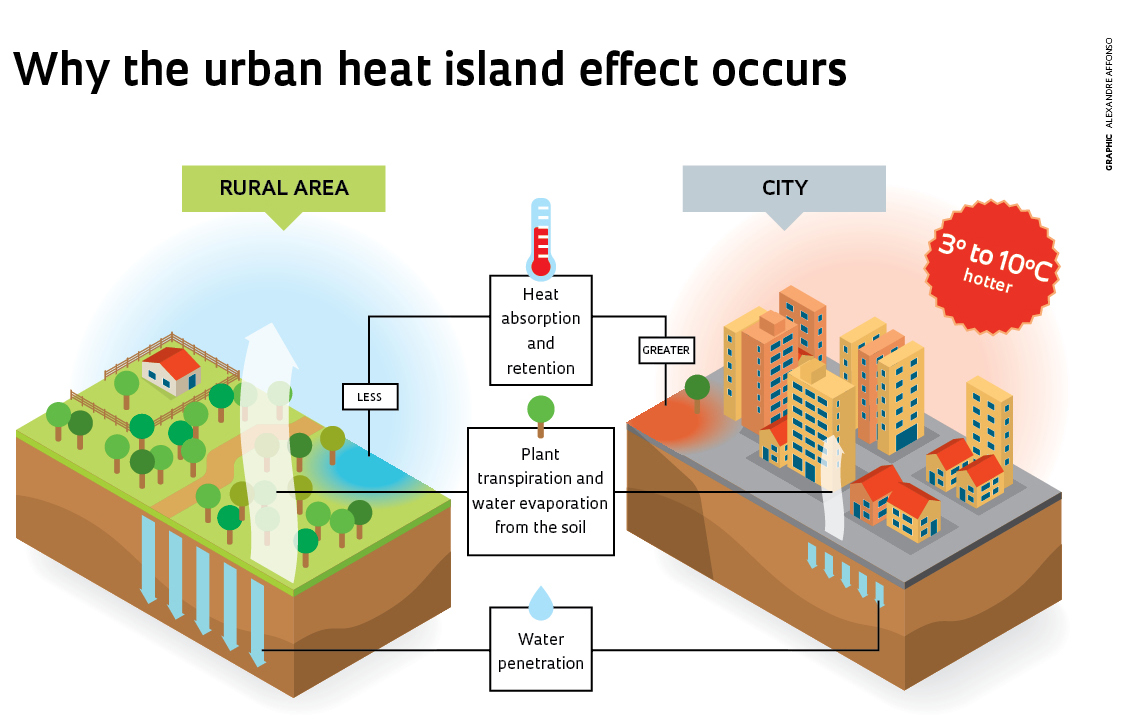
Urban planning plays a crucial role in reducing the effects of urban heat islands by incorporating various strategies to mitigate the urban heat island effect. Urban heat islands occur when built-up areas, such as cities and towns, experience warmer temperatures than their surrounding rural areas due to the concentration of heat-absorbing surfaces like pavement, buildings, and infrastructure. Effective urban planning can help alleviate this issue by designing cities in a way that minimizes heat absorption and promotes heat dissipation.
Green Infrastructure
One of the key strategies in reducing urban heat islands is the incorporation of green infrastructure. This involves integrating green spaces, such as parks, gardens, and green roofs, into urban design. Green infrastructure helps to mitigate the urban heat island effect by providing shade, cooling the air through evapotranspiration, and reducing the amount of heat-absorbing surfaces. Some ways to implement green infrastructure include:
- Creating urban parks and gardens to provide green spaces and reduce the urban heat island effect
- Incorporating green roofs and walls into building design to provide insulation and reduce heat absorption
- Implementing urban forestry initiatives to increase the number of trees in urban areas
Cool Pavements and Materials
Another important aspect of urban planning in reducing urban heat islands is the use of cool pavements and materials. Cool pavements and materials are designed to reflect more sunlight and absorb less heat, thereby reducing the amount of heat that is stored and released in urban areas. Some strategies for implementing cool pavements and materials include:
- Using light-colored pavements and materials to increase albedo and reduce heat absorption
- Implementing permeable pavements to reduce stormwater runoff and increase cooling through evaporation
- Using materials with high thermal mass to absorb and release heat slowly
Urban Design and Configuration
Urban design and configuration also play a significant role in mitigating the urban heat island effect. By designing cities in a way that promotes airflow, reduces the amount of heat-absorbing surfaces, and incorporates shading devices, urban planners can help to reduce the urban heat island effect. Some strategies for effective urban design and configuration include:
- Designing cities with narrow streets and closely spaced buildings to reduce the amount of direct sunlight that is absorbed
- Creating pedestrian-friendly spaces with shading devices, such as canopies and awnings
- Incorporating water features, such as lakes or rivers, into urban design to provide cooling through evaporation
'How can sustainable urban planning and design help mitigate the impact of heat waves?'
Sustainable urban planning and design can play a crucial role in mitigating the impact of heat waves by incorporating various strategies that reduce the urban heat island effect, improve air quality, and enhance the overall livability of cities. By adopting a holistic approach to urban planning, cities can reduce the risks associated with heat waves and create more resilient and sustainable environments for their residents.
Green Infrastructure and Urban Forestry
Green infrastructure and urban forestry are critical components of sustainable urban planning that can help mitigate the impact of heat waves. By incorporating green spaces, parks, and gardens into urban design, cities can reduce the urban heat island effect, improve air quality, and provide residents with cooler spaces to escape the heat. Some of the benefits of green infrastructure and urban forestry include:
- Reducing the amount of impervious surfaces that absorb and retain heat
- Providing shade and cooling through evapotranspiration
- Improving air quality by absorbing pollutants and particulate matter
Cool Roofs and Pavements
Cool roofs and pavements are another strategy that can be employed to mitigate the impact of heat waves. By using materials with high albedo (solar reflectance) or applying cool coatings to roofs and pavements, cities can reduce the amount of heat absorbed and retained by urban surfaces. Some of the benefits of cool roofs and pavements include:
- Reducing the urban heat island effect by minimizing heat absorption
- Lowering the temperature of urban surfaces, making them more comfortable for residents
- Reducing energy consumption by decreasing the need for air conditioning
Water-Sensitive Urban Design
Water-sensitive urban design is an approach to urban planning that incorporates water management into the design of cities. By incorporating features such as rain gardens, green roofs, and permeable pavements, cities can reduce the risk of flooding, improve water quality, and mitigate the impact of heat waves. Some of the benefits of water-sensitive urban design include:
- Reducing the amount of stormwater runoff that can contribute to flooding
- Providing insulation and cooling through the use of water features
- Improving air quality by reducing the amount of pollutants in stormwater runoff
What role does sustainable urban planning play in reducing the impact of climate change and enhancing city resilience to extreme weather events like heatwaves?

Sustainable urban planning plays a crucial role in reducing the impact of climate change and enhancing city resilience to extreme weather events like heatwaves. By incorporating green infrastructure, designing cities with climate resilience in mind, and implementing policies that reduce greenhouse gas emissions, cities can mitigate the effects of climate change.
Green Infrastructure and Urban Heat Island Mitigation
Green infrastructure, such as parks, gardens, and green roofs, can help mitigate the urban heat island effect, which occurs when built-up areas absorb and retain heat, making cities warmer than surrounding rural areas. By incorporating more green spaces, cities can reduce the temperature and improve air quality. Some ways to achieve this include:
- Creating urban parks and gardens to provide shading and evaporative cooling
- Implementing green roofs and walls to reduce heat absorption and improve insulation
- Increasing the use of vegetation in urban design to mitigate the urban heat island effect
Climate-Resilient Urban Design
Climate-resilient urban design involves designing cities to withstand and adapt to the impacts of climate change, including extreme weather events like heatwaves. This can be achieved through a range of strategies, including designing cities with compact and connected neighborhoods, incorporating climate-resilient water management systems, and using materials and building designs that can withstand extreme weather conditions. Some key considerations include:
- Designing cities with narrow streets and tall buildings to reduce the urban heat island effect
- Incorporating water-sensitive urban design to manage stormwater runoff and reduce the risk of flooding
- Using climate-resilient materials and building designs to withstand extreme weather conditions
Policies and Regulations for Climate Change Mitigation
Policies and regulations can play a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing city resilience to climate change. Cities can implement policies such as building codes, zoning regulations, and transportation policies that promote sustainable development and reduce emissions. Some effective policies include:
- Implementing building codes that require energy-efficient design and construction
- Zoning regulations that promote mixed-use development and reduce the need for lengthy commutes
- Transportation policies that promote the use of public transportation, walking, and cycling
'Optimizing Urban Green Spaces to Mitigate Urban Heat Island Effects Across Diverse Climatic Contexts'

Optimizing urban green spaces is a crucial strategy to mitigate the urban heat island (UHI) effect, which is a significant concern in urban areas worldwide. The UHI effect occurs when built-up areas, such as cities and urban agglomerations, experience warmer temperatures than their surrounding rural areas due to the absorption and retention of heat by urban infrastructure, such as pavement, buildings, and other infrastructure. Urban green spaces, including parks, gardens, and green roofs, can help alleviate the UHI effect by providing shade, cooling the air through evapotranspiration, and reducing the amount of heat-absorbing surfaces.
Urban Green Space Design Considerations
Urban green space design is a critical factor in determining the effectiveness of these areas in mitigating the UHI effect. Effective design considerations include the selection of vegetation species, the layout and configuration of green spaces, and the incorporation of water features.
- Vegetation species selection should be based on their evapotranspiration rates, shading capabilities, and adaptability to local climate conditions.
- The layout and configuration of green spaces should prioritize maximizing shade provision and minimizing the urban canyon effect.
- Incorporating water features, such as ponds or fountains, can enhance the cooling effect of green spaces through evaporation.
Climate-Sensitive Green Space Planning
The design and planning of urban green spaces must be sensitive to the local climate context to maximize their effectiveness in mitigating the UHI effect. In hot and dry climates, for example, green spaces should prioritize shading and evapotranspiration, while in temperate climates, they may focus on providing insulation and reducing wind speeds.
- In tropical climates, green spaces should incorporate dense vegetation to provide maximum shading and cooling.
- In arid climates, drought-tolerant vegetation should be used to minimize water consumption while maintaining cooling benefits.
- In temperate climates, green spaces can be designed to provide seasonal variation in shading and cooling.
Integrating Green Infrastructure with Urban Planning
The integration of green infrastructure with urban planning is essential to optimize the benefits of urban green spaces in mitigating the UHI effect. This can involve incorporating green spaces into urban design, using green roofs and walls, and creating green corridors to connect fragmented green spaces.
- Urban planning policies can support the creation and maintenance of green spaces through zoning regulations and incentives.
- Green infrastructure can be integrated with other urban systems, such as transportation and drainage, to maximize benefits.
- Community engagement and participation are crucial in ensuring that green spaces meet local needs and are maintained over time.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of green spaces in mitigating heat waves in urban areas?
Green spaces play a crucial role in mitigating heat waves in urban areas by providing shade, cooling the air through evapotranspiration, and reducing the urban heat island effect. Parks, gardens, and green roofs can help to lower temperatures, improve air quality, and create habitats for wildlife. By incorporating green spaces into urban design, cities can reduce the impact of heat waves on residents.
How does urban density affect heat wave risk?
Urban density can exacerbate heat wave risk by increasing the urban heat island effect, where built-up areas absorb and retain heat. Higher density areas with more pavement, buildings, and human activity tend to be warmer than less dense areas. However, well-planned dense cities with green infrastructure and cool roofs can mitigate this effect, reducing the risk of heat-related illnesses and mortality.
Can urban planning reduce the health impacts of heat waves?
Yes, urban planning can reduce the health impacts of heat waves by designing cities that minimize heat exposure. This can be achieved through strategies such as creating cool corridors, promoting green infrastructure, and designing buildings with heat mitigation features. By prioritizing heat resilience in urban planning, cities can protect vulnerable populations, such as the elderly and young children, from heat-related illnesses.
What are some effective strategies for heat wave mitigation in urban planning?
Effective strategies for heat wave mitigation in urban planning include incorporating green infrastructure, such as parks and green roofs, and using cool materials for pavements and buildings. Urban design strategies, like narrow streets and shaded public spaces, can also help to reduce heat exposure. Additionally, cities can implement heat wave early warning systems and emergency response plans to protect residents from extreme heat events.

Leave a Reply