How sustainable forestry supports carbon capture and storage
Sustainable forestry practices play a crucial role in the global effort to mitigate climate change by capturing and storing carbon dioxide. As the world grapples with the challenges of rising temperatures and environmental degradation, the importance of forests as carbon sinks has gained significant attention. By adopting responsible forestry management techniques, forests can be maintained and enhanced to absorb more carbon from the atmosphere, thereby supporting global climate goals. The connection between sustainable forestry and carbon capture is multifaceted, involving various ecological and managerial strategies that contribute to a more stable climate.
- How Sustainable Forestry Plays a Crucial Role in Carbon Capture and Storage
-
The Role of Sustainable Forestry in Enhancing Carbon Sequestration and Mitigating Climate Change
- What role do forests play in capturing and storing carbon through sustainable forestry practices?
- Carbon Sequestration Mechanisms
- Impact of Sustainable Forestry Practices
- Benefits of Forest Carbon Sequestration
- How does sustainable forestry contribute to effective carbon sequestration?
- Maintaining Forest Health and Productivity
- Enhancing Carbon Sequestration through Forest Management
- Monitoring and Verifying Carbon Sequestration
- 'How do forests contribute to carbon sequestration and storage in the context of sustainable forestry practices?'
- Carbon Sequestration Mechanisms
- Sustainable Forestry Practices for Carbon Storage
- Forest Management for Enhanced Carbon Sequestration
- Can sustainable forestry practices enhance the effectiveness of carbon capture and storage initiatives?
- Role of Sustainable Forestry in Carbon Sequestration
- Integration with Carbon Capture and Storage Technologies
- Economic and Social Benefits
- Frequently Asked Questions
How Sustainable Forestry Plays a Crucial Role in Carbon Capture and Storage
Sustainable forestry is vital for maintaining the health of our planet, and one of its key benefits is its role in carbon capture and storage. Forests act as massive carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through the process of photosynthesis and storing it in trees, soil, and other organic matter. By adopting sustainable forestry practices, we can enhance this natural process, contributing significantly to the global effort to mitigate climate change.
The Role of Trees in Carbon Sequestration
Trees are the backbone of carbon sequestration in forestry. Through photosynthesis, they absorb CO2 from the atmosphere and store carbon in their biomass and soil. Different tree species have varying capacities for carbon sequestration, with some, like conifers and broadleaves, being particularly effective. Sustainable forestry management involves selecting the right species for the local climate and soil conditions, thereby maximizing carbon capture.
Sustainable Forestry Practices for Enhanced Carbon Storage
Implementing sustainable forestry practices is crucial for maximizing carbon storage. This includes methods like reforestation, where new trees are planted in areas where forests have been depleted, and afforestation, which involves creating new forests in areas that were not previously forested. Additionally, practices such as thinning and selective logging can help maintain forest health and promote the growth of remaining trees, thereby enhancing their carbon sequestration potential.
Measuring the Impact of Sustainable Forestry on Carbon Capture
To understand the effectiveness of sustainable forestry in carbon capture and storage, it's essential to measure its impact. This involves assessing the carbon footprint of forestry operations and monitoring the carbon sequestration rates of different forest ecosystems. By using advanced technologies and modeling techniques, forest managers can estimate the amount of carbon stored in forests and identify areas for improvement.
| Forest Management Practice | Carbon Sequestration Benefit |
|---|---|
| Reforestation | Restores forest ecosystems, enhancing carbon capture |
| Sustainable Logging | Maintains forest health, promoting continued carbon sequestration |
| Afforestation | Creates new carbon sinks, increasing overall carbon storage |
The Role of Sustainable Forestry in Enhancing Carbon Sequestration and Mitigating Climate Change
What role do forests play in capturing and storing carbon through sustainable forestry practices?

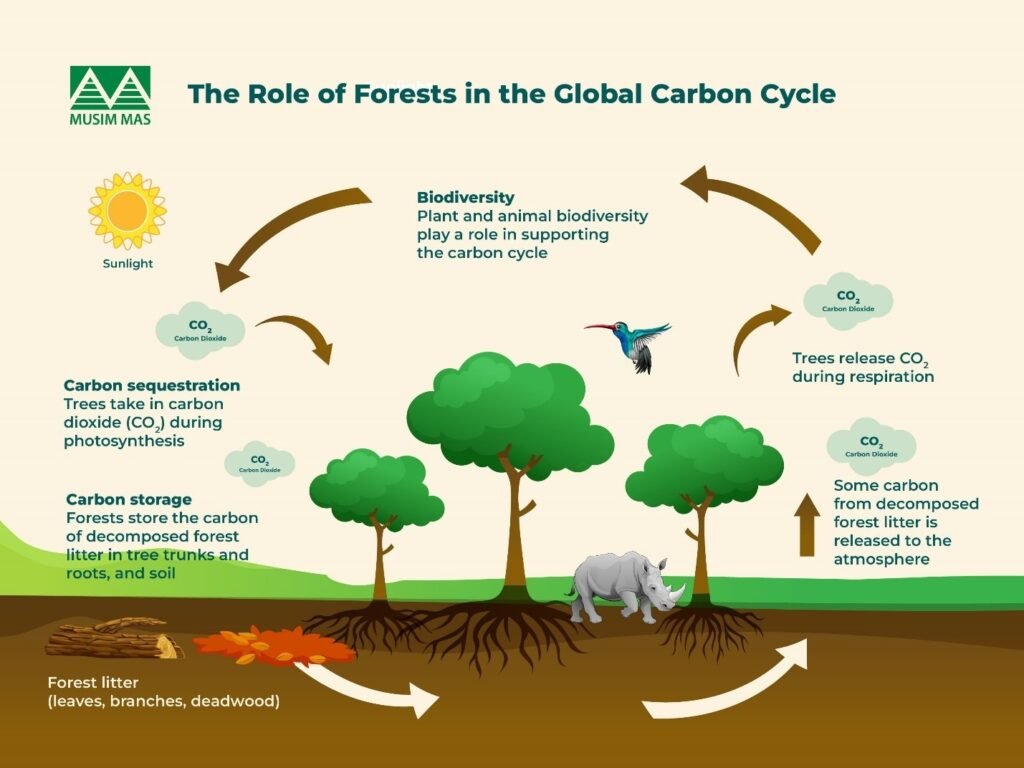
Forests play a significant role in capturing and storing carbon through sustainable forestry practices. They act as massive carbon sinks by absorbing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere through the process of photosynthesis and storing it in trees, soil, and other organic matter. Sustainable forestry practices are crucial for maintaining and enhancing this carbon sequestration capacity.
Carbon Sequestration Mechanisms
Forests sequester carbon through various mechanisms. The primary method is through the growth of trees, which absorb CO2 from the atmosphere and store it in biomass and soil. The carbon is stored in different forest components, including trunks, branches, roots, and soil. Sustainable forestry practices like reforestation, afforestation, and selective logging help maintain the health and productivity of forests, thereby enhancing their carbon sequestration potential.
- Photosynthesis: Trees absorb CO2 from the atmosphere and release oxygen.
- Carbon storage in biomass: Trees store carbon in their trunks, branches, and roots.
- Soil carbon storage: Soil acts as a significant carbon sink, storing carbon in organic matter.
Impact of Sustainable Forestry Practices
Sustainable forestry practices are essential for maintaining the health of forests and their ability to sequester carbon. Practices such as selective logging, reforestation, and protection of old-growth forests help ensure that forests continue to act as effective carbon sinks. By managing forests sustainably, the risk of deforestation and degradation is minimized, preserving the carbon stored in forests.
- Reforestation and afforestation: Planting new trees in areas where forests have been degraded or cleared.
- Selective logging: Harvesting trees in a way that minimizes damage to the remaining forest ecosystem.
- Protection of old-growth forests: Preserving forests that have been untouched for long periods, as they store significant amounts of carbon.
Benefits of Forest Carbon Sequestration
The benefits of forest carbon sequestration extend beyond climate change mitigation. Forests provide numerous ecosystem services, including biodiversity conservation, water regulation, and soil protection. By maintaining healthy forests through sustainable forestry practices, these benefits can be preserved and enhanced, contributing to overall environmental sustainability.
- Biodiversity conservation: Forests provide habitats for a wide range of plant and animal species.
- Water regulation: Forests play a crucial role in regulating water cycles and maintaining water quality.
- Soil protection: Tree roots help hold soil in place, preventing erosion and landslides.
How does sustainable forestry contribute to effective carbon sequestration?
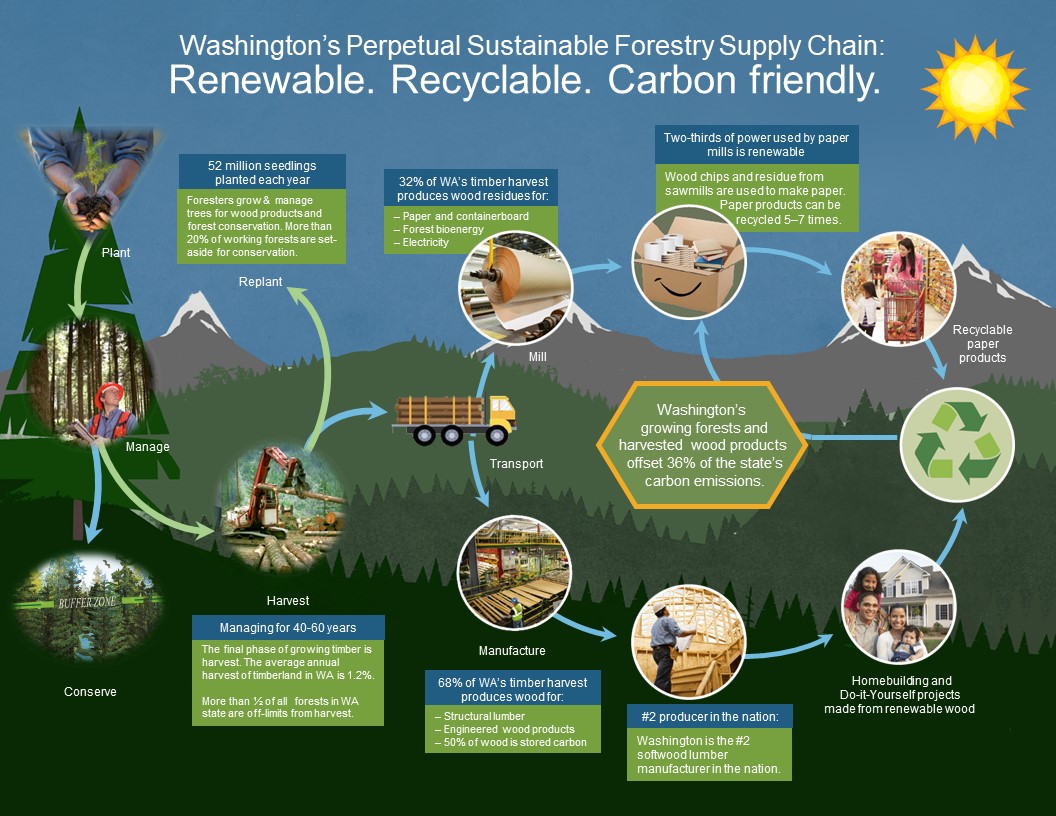
Sustainable forestry plays a significant role in effective carbon sequestration by adopting practices that maintain the health and productivity of forests while minimizing their impact on the environment. Forests act as massive carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through the process of photosynthesis and storing it in trees, soil, and other organic matter. When forests are managed sustainably, they can continue to sequester carbon for long periods, making them a valuable tool in the fight against climate change.
Maintaining Forest Health and Productivity
Maintaining the health and productivity of forests is crucial for effective carbon sequestration. This involves implementing practices such as selective logging, reforestation, and afforestation. By adopting these practices, forest managers can ensure that forests continue to thrive and sequester carbon over time. Some key strategies for maintaining forest health and productivity include:
- Implementing sustainable harvesting practices that minimize damage to the forest ecosystem
- Replanting harvested areas with native species that are well-suited to the local climate and soil conditions
- Protecting forests from pests, diseases, and wildfires through proactive management practices
Enhancing Carbon Sequestration through Forest Management
Effective forest management is critical for enhancing carbon sequestration in forests. This involves adopting practices that promote the growth of trees and other vegetation, while also minimizing the release of stored carbon into the atmosphere. Some key strategies for enhancing carbon sequestration through forest management include:
- Thinning and pruning trees to promote healthy growth and reduce competition for resources
- Protecting old-growth forests, which tend to store more carbon than younger forests
- Restoring degraded forests through reforestation and afforestation efforts
Monitoring and Verifying Carbon Sequestration
Monitoring and verifying carbon sequestration is essential for ensuring that forests are effectively removing carbon from the atmosphere. This involves tracking changes in forest biomass, soil carbon, and other relevant metrics over time. Some key strategies for monitoring and verifying carbon sequestration include:
- Conducting regular forest inventories to track changes in forest biomass and structure
- Using remote sensing technologies, such as satellite imagery, to monitor forest health and productivity
- Implementing robust verification protocols to ensure the accuracy of carbon sequestration estimates
'How do forests contribute to carbon sequestration and storage in the context of sustainable forestry practices?'
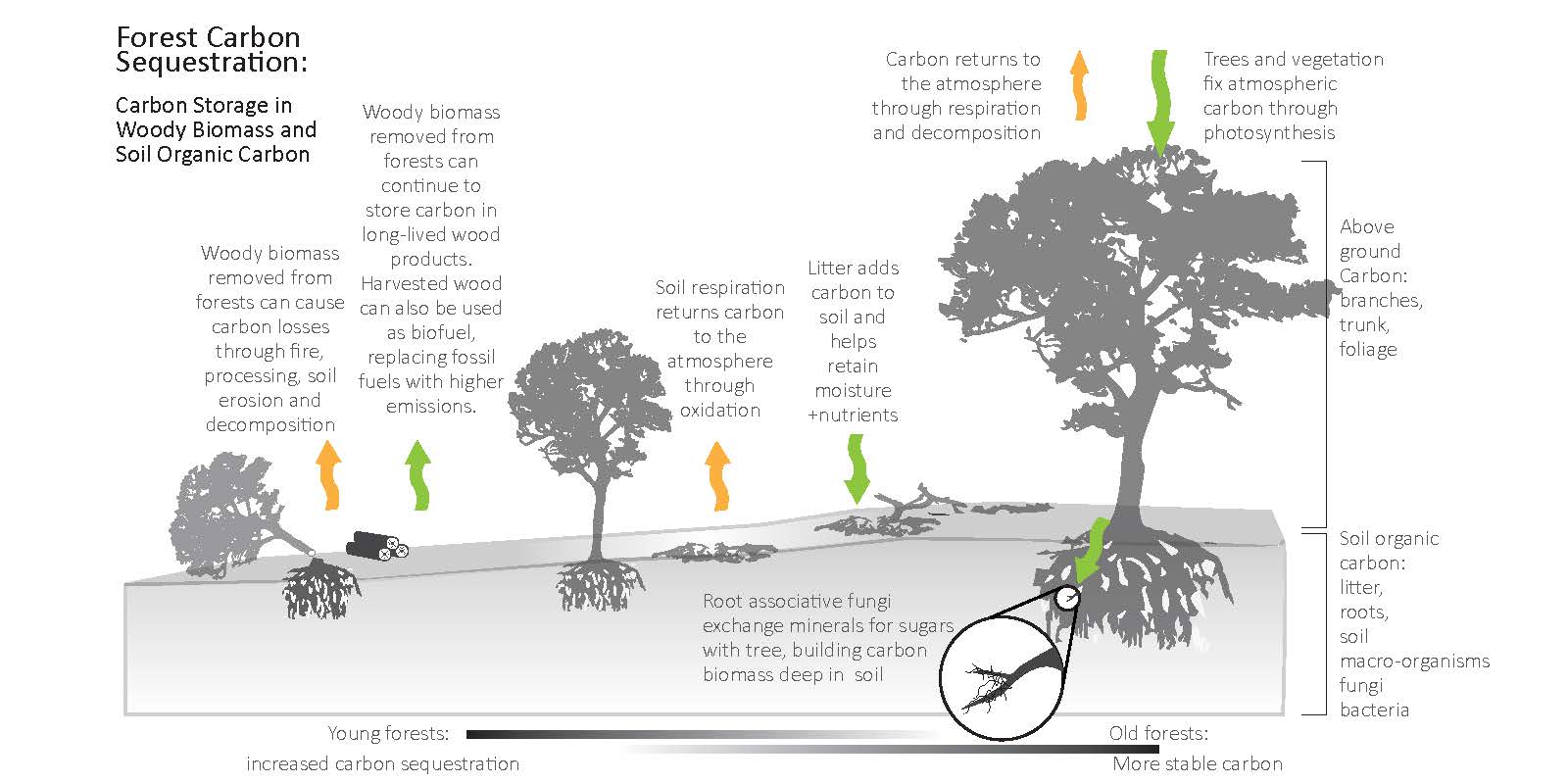
Forests play a crucial role in carbon sequestration and storage, and their importance cannot be overstated in the context of sustainable forestry practices. Trees absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through the process of photosynthesis, storing it in their biomass, soil, and dead organic matter. This natural process helps to mitigate climate change by reducing the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
Carbon Sequestration Mechanisms
Forests sequester carbon through various mechanisms, primarily through the growth of trees and other vegetation. As trees grow, they absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it in their biomass, including trunks, branches, roots, and leaves. The carbon is also stored in the soil through root growth and litter fall.
- Photosynthesis: the process by which trees and other vegetation absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
- Biomass accumulation: the storage of carbon in the biomass of trees and other vegetation.
- Soil carbon storage: the storage of carbon in soils through root growth and litter fall.
Sustainable Forestry Practices for Carbon Storage
Sustainable forestry practices are essential for maintaining and enhancing the carbon sequestration potential of forests. Practices such as selective logging, reforestation, and afforestation can help to maintain forest ecosystems while also promoting carbon storage.
- Selective logging: harvesting trees in a way that minimizes damage to the remaining forest ecosystem.
- Reforestation: re-establishing forests on lands that were previously forested.
- Afforestation: establishing forests on lands that were not previously forested.
Forest Management for Enhanced Carbon Sequestration
Effective forest management is critical for enhancing carbon sequestration in forests. This can be achieved through practices such as extending rotation lengths, protecting old-growth forests, and promoting the growth of tree species with high carbon storage potential.
- Extending rotation lengths: allowing trees to grow for longer periods to increase biomass accumulation.
- Protecting old-growth forests: preserving forests with high carbon storage potential.
- Promoting tree species with high carbon storage potential: selecting tree species that are known to store more carbon.
Can sustainable forestry practices enhance the effectiveness of carbon capture and storage initiatives?
Sustainable forestry practices can play a crucial role in enhancing the effectiveness of carbon capture and storage initiatives. By adopting sustainable forestry practices, forests can be managed in a way that maintains their health, productivity, and ecological integrity, while also maximizing their carbon sequestration potential. This can be achieved through a variety of methods, including reforestation, afforestation, and selective logging.
Role of Sustainable Forestry in Carbon Sequestration
Sustainable forestry practices are essential for maintaining the carbon sequestration potential of forests. When forests are managed sustainably, they can continue to absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, storing it in trees, soil, and other organic matter. This not only helps to mitigate climate change but also maintains the health and biodiversity of forest ecosystems. Some of the ways sustainable forestry practices can enhance carbon sequestration include:
- Maintaining forest cover and promoting regeneration
- Improving forest management practices to increase carbon storage
- Protecting forests from degradation and conversion to other land uses
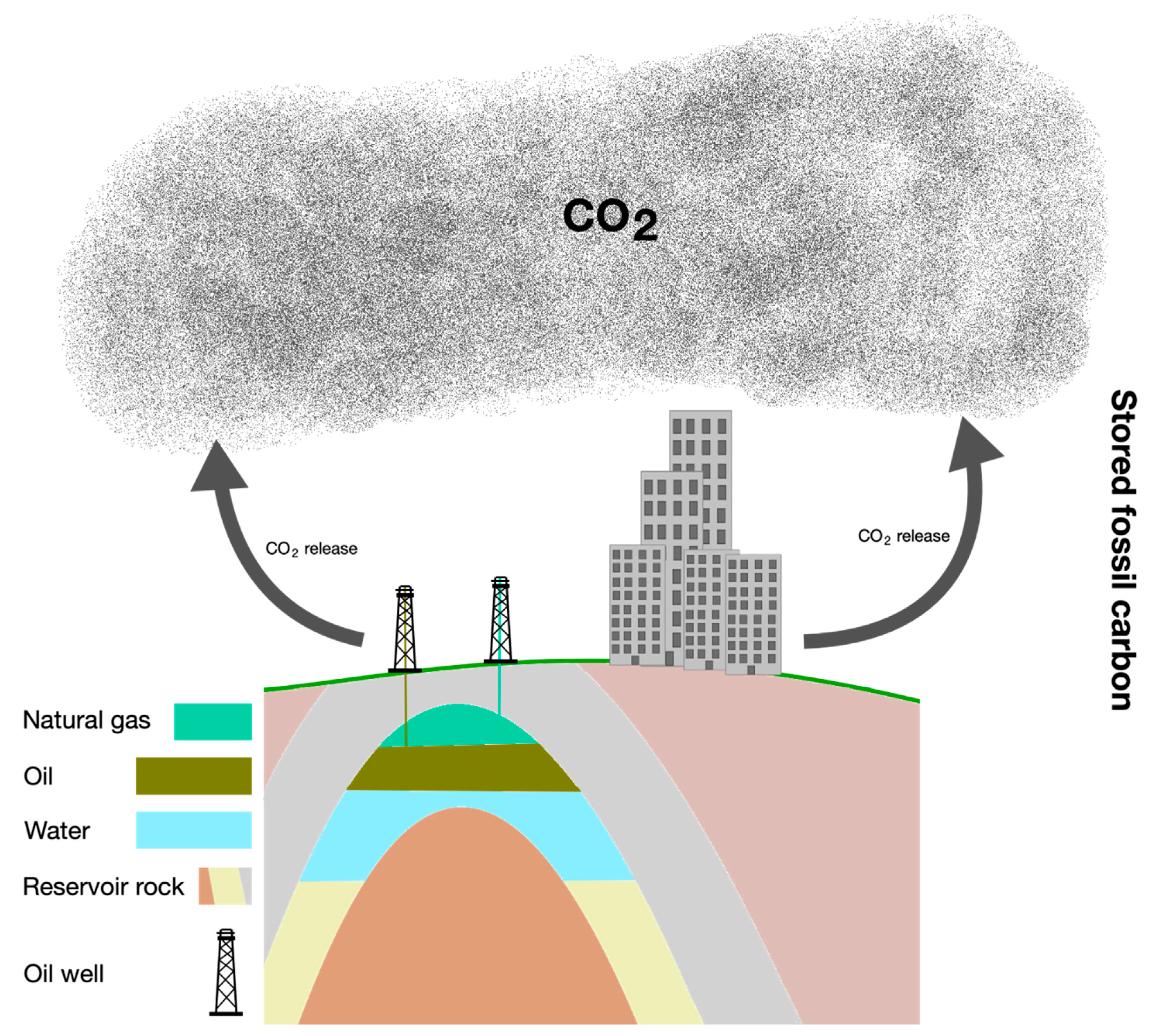
Integration with Carbon Capture and Storage Technologies
Sustainable forestry practices can be integrated with carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies to enhance their effectiveness. For example, biomass from sustainably managed forests can be used as a feedstock for bioenergy with CCS (BECCS), which can remove more CO2 from the atmosphere than it emits. Additionally, sustainable forestry practices can help to maintain the integrity of geological storage sites by reducing the risk of leakage or other environmental impacts. Some of the ways sustainable forestry practices can be integrated with CCS include:
- Producing biomass for BECCS
- Enhancing soil carbon storage through sustainable forest management
- Maintaining forest ecosystems that support CCS infrastructure
Sustainable forestry practices can also provide economic and social benefits that complement carbon capture and storage initiatives. For example, sustainable forestry can create jobs and stimulate local economies, while also providing ecosystem services such as clean water and air. Additionally, sustainable forestry practices can help to maintain the cultural and spiritual values of forests, which are important for many communities. Some of the economic and social benefits of sustainable forestry practices include:
- Creating employment opportunities in forestry and related industries
- Supporting local economies through sustainable forest products
- Maintaining ecosystem services that benefit local communities
Frequently Asked Questions
What is sustainable forestry and how does it relate to carbon capture?
Sustainable forestry involves managing forests to maintain their ecological integrity while providing wood and other forest products. This approach helps forests absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through photosynthesis, storing it in trees, soil, and dead wood. By adopting sustainable forestry practices, we can enhance carbon sequestration and reduce the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, mitigating climate change.
How does sustainable forestry support carbon storage?
Sustainable forestry supports carbon storage by promoting practices like reforestation, afforestation, and selective logging. These practices help maintain or increase forest carbon stocks. Trees absorb carbon dioxide during growth, storing it in biomass and soil. When harvested, wood products continue to store carbon. Sustainable forestry ensures that forests remain a net carbon sink, offsetting emissions from other sectors and contributing to a more stable climate.
Can sustainable forestry alone solve the climate crisis?
While sustainable forestry is crucial for carbon capture and storage, it is not a standalone solution to the climate crisis. It is one of many strategies needed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Sustainable forestry can complement efforts to transition to renewable energy, increase energy efficiency, and adopt climate-resilient practices. Together, these actions can help mitigate climate change.
How can consumers support sustainable forestry and carbon capture?
Consumers can support sustainable forestry by choosing products certified by organizations that ensure responsible forestry practices. Buying products made from sustainably sourced wood, supporting reforestation efforts, and advocating for policies that protect forests are effective ways to promote carbon capture and storage. By making informed choices, consumers can contribute to a more sustainable future.

Leave a Reply