How sustainable agriculture practices reduce climate change impacts
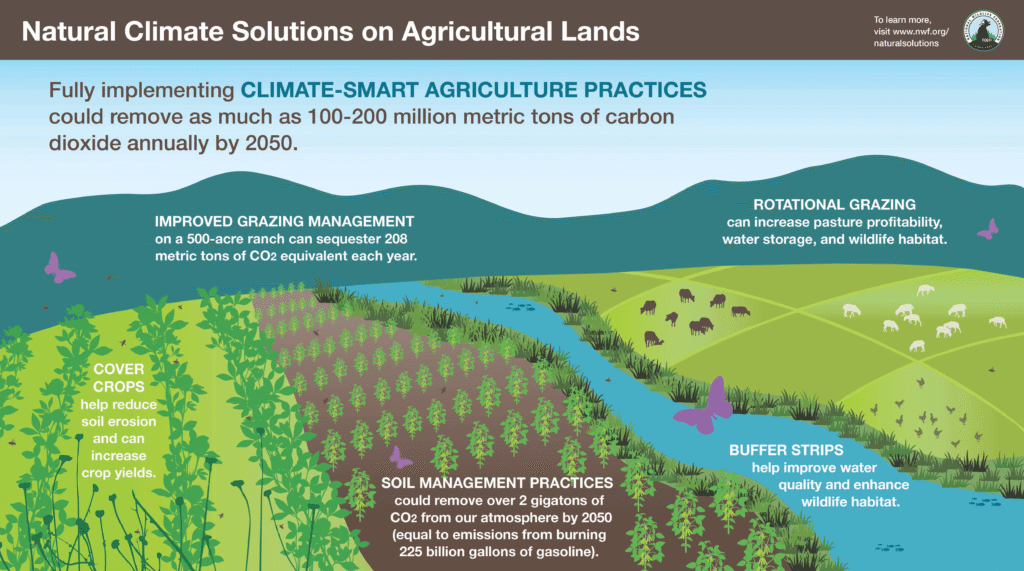
The global agricultural sector is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and environmental degradation, exacerbating climate change. However, by adopting sustainable agriculture practices, farmers and producers can reduce their environmental footprint, mitigate climate change impacts, and promote ecosystem resilience. Sustainable agriculture involves a range of techniques, from conservation tillage and agroforestry to organic farming and regenerative agriculture, that prioritize soil health, biodiversity, and efficient water use. By transitioning to more sustainable practices, the agricultural sector can play a crucial role in reducing its contribution to climate change.
- Mitigating Climate Change through Sustainable Agriculture
-
Mitigating Climate Change: The Role of Sustainable Agriculture Practices
- 'How does sustainable agriculture mitigate the effects of climate change?'
- Soil Conservation and Carbon Sequestration
- Water Management and Efficient Use
- Biodiversity Conservation and Ecosystem Services
- What role does sustainable agriculture play in mitigating environmental degradation?
- Soil Conservation and Health
- Biodiversity Conservation
- Water Conservation
- 'How do sustainable agricultural methods mitigate the effects of climate change?'
- Soil Conservation and Carbon Sequestration
- Climate-Resilient Crop and Animal Management
- Water Conservation and Efficient Use
- What sustainable agricultural methods can effectively reduce the impacts of climate change?
- Soil Conservation and Health
- Agroforestry and Biodiversity Conservation
- Climate-Smart Agriculture Practices
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is sustainable agriculture and how does it help mitigate climate change?
- How do sustainable agriculture practices reduce synthetic fertilizer use?
- Can sustainable agriculture practices help sequester carbon in soils?
- How does sustainable agriculture support biodiversity and climate change mitigation?
Mitigating Climate Change through Sustainable Agriculture
Sustainable agriculture plays a crucial role in reducing the impacts of climate change by implementing practices that minimize environmental degradation, promote eco-friendly farming methods, and support biodiversity. By adopting these practices, farmers can significantly lower their carbon footprint, improve soil health, and contribute to a more resilient food system.
Soil Conservation and Carbon Sequestration
Sustainable agriculture practices such as no-till or reduced-till farming, cover cropping, and organic amendments help to enhance soil health and promote carbon sequestration. By minimizing soil disturbance and increasing soil organic matter, farmers can reduce soil erosion, improve water retention, and create a sink for carbon dioxide. This not only mitigates climate change but also improves soil fertility and structure.
Reducing Synthetic Fertilizers and Promoting Agroecology
The use of synthetic fertilizers is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions in agriculture. Sustainable agriculture practices promote the use of organic and natural fertilizers, such as compost and manure, which reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers. Additionally, agroecological practices like crop rotation, intercropping, and integrating livestock into farming systems enhance biodiversity, promote ecosystem services, and reduce the reliance on external inputs.
Climate-Resilient Agriculture and Water Management
Sustainable agriculture practices also focus on building resilience to climate change by promoting climate-resilient crop and animal varieties, agroforestry, and conservation agriculture. Furthermore, efficient water management practices, such as drip irrigation and mulching, help farmers to conserve water, reduce waste, and mitigate the impacts of droughts and floods.
| Sustainable Agriculture Practice | Climate Change Mitigation Benefit |
|---|---|
| No-till or reduced-till farming | Reduces soil disturbance, promotes carbon sequestration |
| Cover cropping | Enhances soil health, reduces erosion, and promotes biodiversity |
| Organic amendments | Improves soil fertility, structure, and water retention |
| Agroecological practices | Promotes ecosystem services, reduces reliance on external inputs |
Mitigating Climate Change: The Role of Sustainable Agriculture Practices
'How does sustainable agriculture mitigate the effects of climate change?'
Sustainable agriculture is a farming practice that prioritizes environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and economic viability. It plays a crucial role in mitigating the effects of climate change by adopting practices that reduce greenhouse gas emissions, promote soil health, and conserve natural resources.
Soil Conservation and Carbon Sequestration
Sustainable agriculture promotes soil conservation through techniques like no-till or reduced-till farming, cover cropping, and crop rotation. These methods help to reduce soil erosion, improve soil organic matter, and promote soil biota. As a result, soils become more effective at sequestering carbon from the atmosphere, thus reducing the amount of greenhouse gases.
- Improved soil structure and fertility
- Increased soil water retention
- Enhanced soil biodiversity
Water Management and Efficient Use
Sustainable agriculture also focuses on efficient water use and management. Practices such as drip irrigation, mulching, and conservation agriculture help to minimize water waste and reduce the environmental impact of farming. By using water more efficiently, farmers can reduce their reliance on non-renewable water sources and minimize the energy needed to pump and treat water.
- Reduced water pollution from agricultural runoff
- Increased crop yields with less water
- Improved drought resilience
Biodiversity Conservation and Ecosystem Services
Sustainable agriculture promotes biodiversity by maintaining ecological balance and conserving ecosystem services. By planting diverse crops, maintaining ecological corridors, and conserving natural habitats, farmers can support a wide range of plant and animal species. This biodiversity helps to maintain ecosystem services like pollination, pest control, and nutrient cycling, which are essential for long-term agricultural productivity.
- Enhanced ecosystem resilience to climate change
- Improved pollination services
- Increased pest and disease resistance
What role does sustainable agriculture play in mitigating environmental degradation?
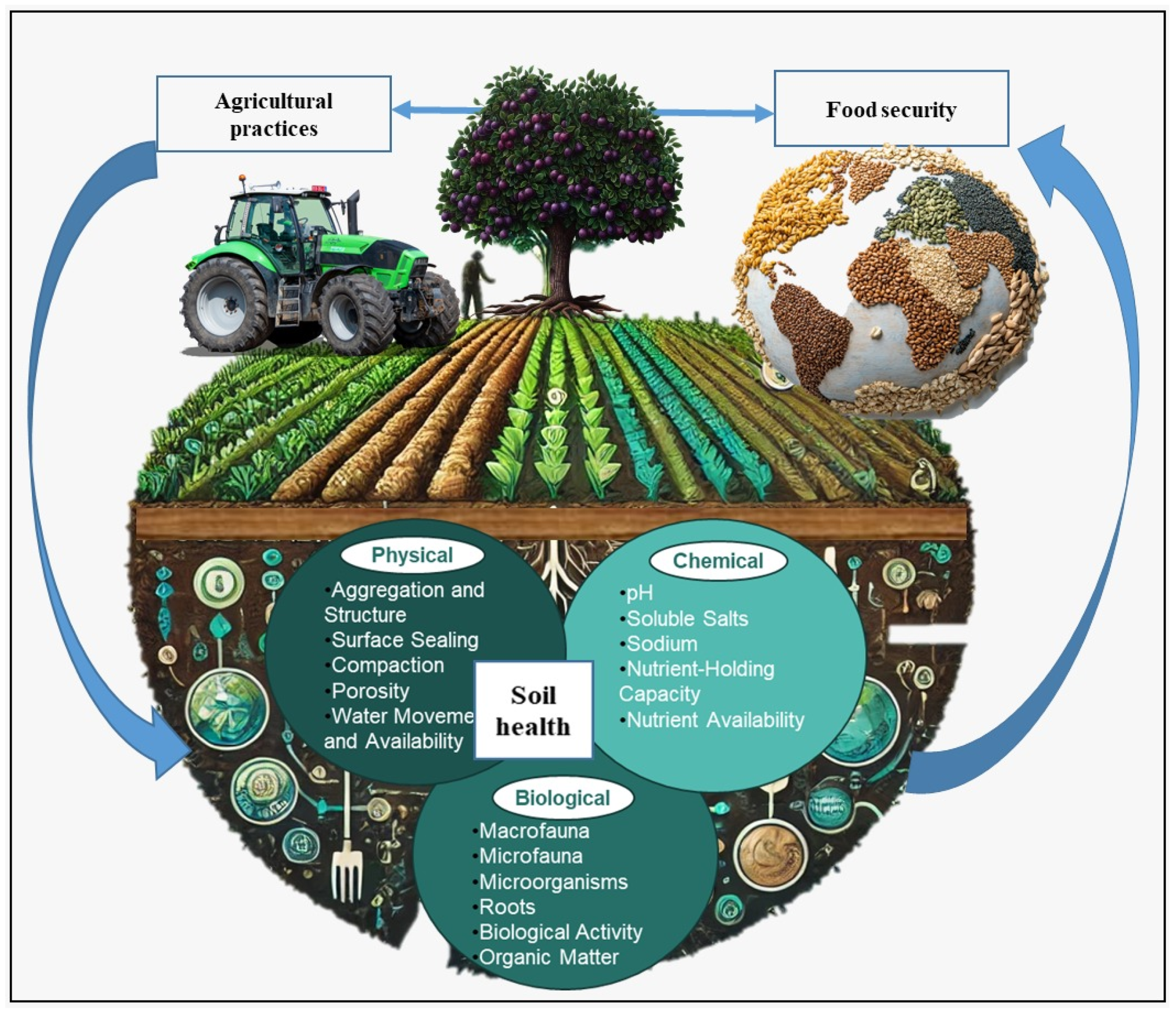
Sustainable agriculture plays a crucial role in mitigating environmental degradation by promoting farming practices that prioritize soil health, biodiversity, and efficient water use. This approach helps to reduce the environmental impact of farming, which is a significant contributor to global environmental degradation. By adopting sustainable agriculture practices, farmers can reduce their reliance on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, minimize soil erosion, and promote ecosystem services.
Soil Conservation and Health
Sustainable agriculture emphasizes the importance of maintaining soil health through techniques such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and organic amendments. These practices help to improve soil structure, increase soil organic matter, and promote soil biota. As a result, soil erosion is reduced, and soil fertility is maintained or improved. Some of the key strategies for promoting soil conservation and health include:
- Using cover crops to protect soil from erosion and improve soil health
- Implementing conservation tillage or no-till practices to reduce soil disturbance
- Incorporating organic amendments, such as compost or manure, to improve soil fertility
Biodiversity Conservation
Sustainable agriculture also plays a critical role in conserving biodiversity by promoting ecosystem services and protecting natural habitats. By maintaining ecological balance, farmers can reduce the need for external inputs, such as pesticides and fertilizers, and create a more resilient farming system. Some of the key strategies for promoting biodiversity conservation include:
- Planting a diverse range of crops to promote ecosystem services and reduce pest and disease pressure
- Maintaining ecological corridors and natural habitats to support pollinators and other beneficial organisms
- Using integrated pest management (IPM) practices to minimize the use of chemical pesticides
Water Conservation
Sustainable agriculture also helps to conserve water by promoting efficient irrigation practices and reducing water waste. By adopting techniques such as drip irrigation and mulching, farmers can reduce their water usage and minimize the environmental impact of their farming operations. Some of the key strategies for promoting water conservation include:
- Using drip irrigation or other efficient irrigation systems to reduce water loss
- Implementing conservation agriculture practices, such as mulching or cover cropping, to reduce soil moisture loss
- Monitoring soil moisture levels to optimize irrigation scheduling
'How do sustainable agricultural methods mitigate the effects of climate change?'

Sustainable agricultural methods play a crucial role in mitigating the effects of climate change by adopting practices that reduce greenhouse gas emissions, promote soil health, and conserve water. These methods help to minimize the environmental impact of farming while maintaining productivity and ensuring food security.
Soil Conservation and Carbon Sequestration
Sustainable agricultural practices like no-till or reduced-till farming, cover cropping, and incorporating organic amendments help to improve soil health and promote carbon sequestration. Healthy soils with high organic matter content can store more carbon, reducing atmospheric CO2 levels.
- Improved soil structure and aeration
- Increased soil water-holding capacity
- Enhanced soil biota and biodiversity
Climate-Resilient Crop and Animal Management
Sustainable agriculture involves the use of climate-resilient crop and animal varieties, as well as practices that promote ecological balance and minimize the use of external inputs. This includes the use of agroforestry, crop rotation, and integrated pest management. By adopting these practices, farmers can reduce their reliance on chemical inputs and promote ecosystem services.
- Diversification of crop and animal species
- Use of locally adapted and climate-resilient varieties
- Integration of trees into farming landscapes
Water Conservation and Efficient Use
Sustainable agricultural practices also focus on conserving water and reducing waste. Techniques like drip irrigation, mulching, and conservation agriculture help to minimize water loss and retain soil moisture. This not only reduces the environmental impact of farming but also enhances crop productivity and resilience to drought.
- Improved irrigation management
- Soil conservation and mulching
- Use of drought-tolerant crop varieties
What sustainable agricultural methods can effectively reduce the impacts of climate change?
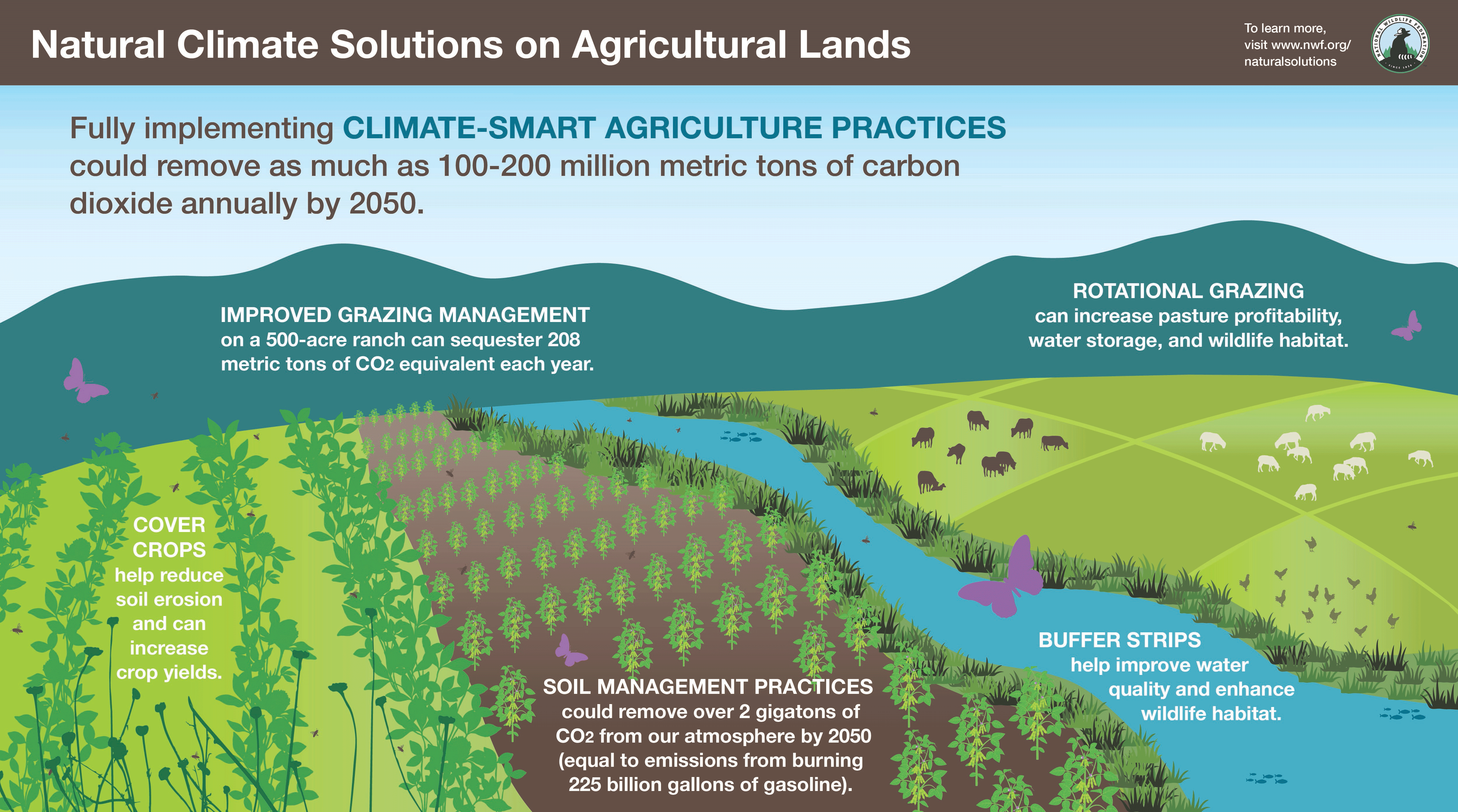
Sustainable agricultural methods are crucial in reducing the impacts of climate change. These methods not only help in mitigating climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions but also help farmers adapt to the changing climate. Some of the effective sustainable agricultural methods include practices that enhance soil health, conserve water, and promote biodiversity.
Soil Conservation and Health
Soil conservation and health are critical components of sustainable agriculture. Practices that enhance soil health not only improve its fertility and structure but also increase its carbon sequestration potential. This can be achieved through various methods. Some key strategies include:
- Using cover crops to protect the soil from erosion and enhance its organic matter content.
- Adopting conservation tillage or no-till farming to minimize soil disturbance.
- Incorporating organic amendments like compost or manure to improve soil fertility and structure.
Agroforestry and Biodiversity Conservation
Agroforestry, which involves integrating trees into agricultural landscapes, is another effective method for reducing the impacts of climate change. This practice not only helps in sequestering carbon but also promotes biodiversity and can improve farmers' resilience to climate change. Key aspects of agroforestry and biodiversity conservation include:
- Planting trees among crops or livestock to enhance ecological interactions and synergies.
- Conserving and restoring natural habitats within agricultural landscapes.
- Promoting the use of diverse crop and animal varieties to enhance resilience.
Climate-Smart Agriculture Practices
Climate-smart agriculture involves practices that help farmers adapt to climate change, improve agricultural productivity, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. These practices are tailored to the specific needs of farmers and are based on local conditions. Some of the key climate-smart agriculture practices include:
- Implementing irrigation management practices to conserve water and reduce the risk of water scarcity.
- Using climate-resilient crop and animal varieties that can withstand projected climate changes.
- Adopting integrated pest management practices to minimize the use of chemical pesticides and maintain ecosystem services.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is sustainable agriculture and how does it help mitigate climate change?
Sustainable agriculture refers to farming practices that prioritize soil health, biodiversity, and efficient water use. By adopting these practices, farmers can reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve soil carbon sequestration, and promote ecosystem services. This approach helps mitigate climate change by decreasing synthetic fertilizer use, conserving water, and enhancing soil's ability to absorb carbon dioxide.
How do sustainable agriculture practices reduce synthetic fertilizer use?
Sustainable agriculture practices reduce synthetic fertilizer use by promoting the use of natural amendments, such as compost and manure. This approach improves soil fertility, structure, and overall health, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers. By minimizing synthetic fertilizer application, farmers can decrease nitrous oxide emissions, a potent greenhouse gas, and lower the environmental impact of their operations.
Can sustainable agriculture practices help sequester carbon in soils?
Yes, sustainable agriculture practices can help sequester carbon in soils. Techniques like no-till or reduced-till farming, cover cropping, and incorporating organic amendments promote soil carbon sequestration. By improving soil health and structure, these practices enable soils to absorb and store more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, mitigating climate change. This approach also enhances soil fertility and overall ecosystem resilience.
How does sustainable agriculture support biodiversity and climate change mitigation?
Sustainable agriculture supports biodiversity by promoting agroecological practices that conserve and restore ecosystem services. By maintaining diverse crop rotations, conserving natural habitats, and reducing chemical use, farmers can protect and enhance biodiversity. This, in turn, helps build resilience to climate change by maintaining ecosystem functions, improving soil health, and supporting pollinators and other beneficial organisms.


Leave a Reply