How industrial emissions alter global atmospheric carbon balance
The global atmospheric carbon balance is a complex and dynamic system that plays a crucial role in regulating Earth's climate. Human activities, particularly industrial processes, have significantly impacted this delicate balance. Industrial emissions, including carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases, have increased substantially over the past century, contributing to climate change. The effects of these emissions on the global carbon balance are multifaceted and far-reaching, with significant implications for the environment, human health, and the economy. Understanding the mechanisms by which industrial emissions alter the global atmospheric carbon balance is essential for developing effective mitigation strategies.
- Impact of Industrial Emissions on the Global Atmospheric Carbon Balance
-
Understanding the Impact of Industrial Emissions on Global Atmospheric Carbon Balance
- What is the impact of industrial carbon emissions on the global atmospheric carbon balance?
- Effects on Atmospheric CO2 Concentrations
- Consequences for Global Carbon Sinks
- Mitigation Strategies and Challenges
- What is the impact of industrial emissions on the global atmospheric carbon balance?
- Effects on Atmospheric CO2 Concentration
- Influence on Climate Change Mitigation Efforts
- Global Response and Cooperation
- What impact has the Industrial Revolution had on atmospheric carbon levels?
- Increase in CO2 Emissions
- Impact on Global Carbon Cycle
- Consequences for Climate Change
- Frequently Asked Questions
Impact of Industrial Emissions on the Global Atmospheric Carbon Balance
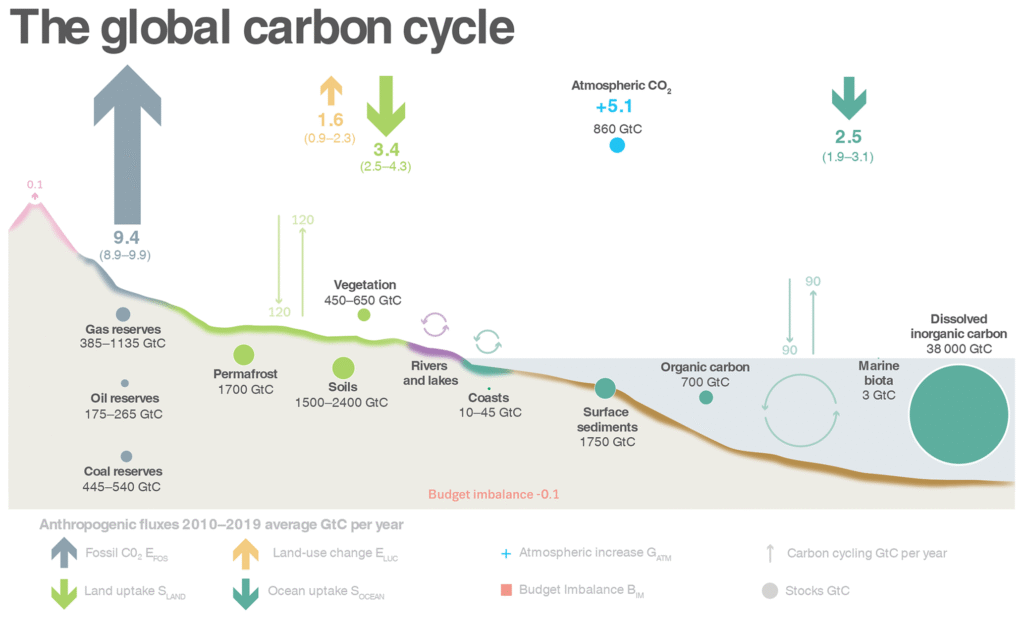
Industrial emissions have significantly altered the global atmospheric carbon balance, leading to a substantial increase in carbon dioxide (CO2) levels. The burning of fossil fuels and various industrial processes release large amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere, contributing to the greenhouse effect and global warming. This alteration in the carbon balance has severe implications for the environment, including climate change, ocean acidification, and biodiversity loss.
Sources of Industrial Emissions
The primary sources of industrial emissions include the burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas for energy production, as well as various industrial processes like cement production and steel manufacturing. These activities release significant amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere, contributing to the overall increase in greenhouse gas emissions. The extraction, processing, and transportation of fossil fuels also lead to emissions of methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O), further exacerbating the problem.
Effects on Atmospheric Carbon Balance
The increased levels of CO2 in the atmosphere due to industrial emissions disrupt the natural carbon cycle, leading to an imbalance in the global atmospheric carbon balance. The excess CO2 is absorbed by the oceans, causing ocean acidification, and by terrestrial ecosystems, affecting forest health and soil carbon storage. This, in turn, has cascading effects on ecosystems, including changes in species composition and ecosystem services.
Mitigation Strategies
To mitigate the impact of industrial emissions on the global atmospheric carbon balance, several strategies can be employed, including the transition to renewable energy sources, carbon capture and storage (CCS), and energy efficiency improvements. Additionally, sustainable land use practices and reforestation efforts can help to sequester CO2 from the atmosphere, restoring balance to the carbon cycle.
| Emission Source | CO2 Emissions (Gt) |
|---|---|
| Fossil Fuel Combustion | 32.3 |
| Industrial Processes | 4.3 |
| Land Use Change | 2.2 |
Understanding the Impact of Industrial Emissions on Global Atmospheric Carbon Balance
What is the impact of industrial carbon emissions on the global atmospheric carbon balance?

The impact of industrial carbon emissions on the global atmospheric carbon balance is a significant concern, as it plays a crucial role in shaping the Earth's climate. Industrial activities, such as the burning of fossil fuels, cement production, and land-use changes, release large amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere, contributing to the increase in atmospheric CO2 concentrations. This, in turn, enhances the natural greenhouse effect, leading to global warming and associated climate change impacts.
Effects on Atmospheric CO2 Concentrations
The increase in atmospheric CO2 concentrations due to industrial emissions has been a major driver of global climate change. As CO2 is a potent greenhouse gas, its rising concentrations trap more heat in the atmosphere, leading to a global average temperature increase. The effects of this increase are far-reaching and multifaceted. Some of the key consequences include:
- Rising global temperatures, leading to more frequent and severe heatwaves and droughts
- More intense and frequent extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and heavy rainfall
- Melting of polar ice caps and glaciers, resulting in sea-level rise and altered ecosystems
Consequences for Global Carbon Sinks
Industrial carbon emissions not only increase atmospheric CO2 concentrations but also affect the ability of natural carbon sinks to sequester carbon. For instance, the increased CO2 levels can lead to ocean acidification, reducing the capacity of oceans to absorb CO2. Similarly, changes in land use and climate can impact the ability of forests and soils to act as carbon sinks. The consequences of this include:
- Reduced ocean carbon sequestration due to acidification and changes in ocean circulation
- Degradation of forests and soils, leading to increased greenhouse gas emissions
- Loss of biodiversity and ecosystem disruption due to climate change and land-use changes
Mitigation Strategies and Challenges
To mitigate the impact of industrial carbon emissions on the global atmospheric carbon balance, various strategies can be employed. These include transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and implementing carbon capture and storage technologies. However, there are significant challenges associated with implementing these strategies, including:
- High upfront costs and infrastructure requirements for renewable energy and carbon capture technologies
- Policy and regulatory frameworks needed to support the transition to a low-carbon economy
- Public acceptance and awareness of the need for climate action and the benefits of mitigation strategies
What is the impact of industrial emissions on the global atmospheric carbon balance?

The impact of industrial emissions on the global atmospheric carbon balance is significant, as these emissions release large amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere, contributing to the greenhouse effect and climate change. Industrial activities, such as the burning of fossil fuels for energy and the production of cement, are among the largest sources of CO2 emissions.
Effects on Atmospheric CO2 Concentration
The increased CO2 emissions from industrial activities have led to a significant rise in atmospheric CO2 concentration. This increase enhances the natural greenhouse effect, trapping more heat in the atmosphere and contributing to global warming. The effects of this can be observed in various aspects of the environment.
- The rise in CO2 concentration accelerates the rate of global warming.
- It contributes to more extreme weather events, such as heatwaves and droughts.
- It affects ecosystems and biodiversity, potentially leading to the loss of habitats and extinction of species.
Influence on Climate Change Mitigation Efforts
Industrial emissions not only affect the atmospheric carbon balance but also pose a challenge to climate change mitigation efforts. Reducing these emissions requires significant changes in industrial practices and energy sources. Strategies to mitigate the impact include transitioning to renewable energy sources and improving energy efficiency.
- Transitioning to renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, can significantly reduce CO2 emissions.
- Improving energy efficiency in industrial processes can decrease the amount of energy required.
- Implementing carbon capture and storage technologies can reduce emissions from industrial sources.
Global Response and Cooperation
Addressing the issue of industrial emissions requires a global response and cooperation among countries. International agreements and cooperation are crucial for developing and implementing effective strategies to reduce industrial emissions. This includes sharing technologies and best practices.
- International agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, aim to reduce global greenhouse gas emissions.
- Countries can share technologies and best practices to help others reduce their emissions.
- Global cooperation can facilitate the development of new technologies and strategies for emission reduction.
What impact has the Industrial Revolution had on atmospheric carbon levels?
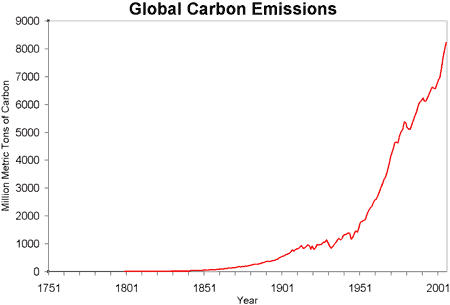
The Industrial Revolution, which began in the late 18th century, has had a profound impact on the environment, particularly on atmospheric carbon levels. The widespread adoption of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and gas has led to a significant increase in carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, contributing to the enhancement of the greenhouse effect and global warming.
Increase in CO2 Emissions
The Industrial Revolution marked a significant shift from manual labor to machine-based manufacturing, resulting in a substantial increase in energy consumption. The primary source of this energy was fossil fuels, which released large amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere when burned. This led to a steady rise in atmospheric CO2 concentrations.
- Pre-industrial CO2 levels were around 280 parts per million (ppm).
- The widespread use of fossil fuels during the Industrial Revolution led to a significant increase in CO2 emissions.
- By the mid-20th century, CO2 levels had risen to over 310 ppm.
Impact on Global Carbon Cycle
The increased CO2 emissions from industrial activities have disrupted the global carbon cycle, leading to an imbalance between the amount of CO2 emitted and the amount absorbed by natural sinks such as oceans and forests. This has resulted in a steady accumulation of CO2 in the atmosphere.
- The burning of fossil fuels releases CO2 into the atmosphere at a rate faster than natural processes can absorb it.
- Deforestation and land-use changes have reduced the ability of forests to act as carbon sinks.
- The increased CO2 levels have also led to ocean acidification, affecting marine ecosystems.
Consequences for Climate Change
The rise in atmospheric CO2 levels due to the Industrial Revolution has contributed significantly to climate change. The enhanced greenhouse effect has led to global warming, with associated impacts on weather patterns, sea levels, and ecosystems.
- Rising global temperatures are causing more frequent and severe heatwaves and droughts.
- Melting glaciers and ice sheets are contributing to sea-level rise.
- Changes in precipitation patterns are affecting ecosystems and human settlements.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the impact of industrial emissions on global atmospheric carbon balance?
Industrial emissions release large amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, significantly altering the global carbon balance. This increase in CO2 contributes to the greenhouse effect, leading to global warming and climate change. The carbon balance is disrupted as the amount of CO2 emitted exceeds the amount that can be absorbed by natural sinks like oceans and forests.
How do industrial activities contribute to carbon emissions?
Industrial activities such as manufacturing, mining, and construction contribute to carbon emissions through the burning of fossil fuels for energy and the release of CO2 as a byproduct of industrial processes. The production of cement, steel, and chemicals are particularly carbon-intensive. These activities result in significant emissions of CO2, a potent greenhouse gas that contributes to global warming.
Can industrial emissions be reduced without impacting economic growth?
Yes, industrial emissions can be reduced without negatively impacting economic growth. Implementing cleaner production technologies, increasing energy efficiency, and transitioning to renewable energy sources can significantly reduce emissions. Additionally, adopting circular economy practices and reducing waste can also lower emissions while maintaining or even boosting economic activity through cost savings and new job creation.
What role do governments and policies play in mitigating industrial emissions?
Governments and policies play a crucial role in mitigating industrial emissions by setting emission standards, implementing carbon pricing, and offering incentives for cleaner production. Regulations and international agreements can drive the adoption of low-carbon technologies and practices. Policies can also support research and development in clean technologies, helping industries transition to a low-carbon future.

Leave a Reply