How hands-on environmental education enhances climate change understanding

As the world grapples with the escalating climate crisis, effective environmental education has become increasingly crucial. Hands-on environmental education is a dynamic approach that enables individuals, particularly students, to engage directly with their surroundings, fostering a deeper understanding of environmental issues. By participating in practical activities and real-world experiences, learners develop critical thinking skills, build environmental awareness and cultivate a sense of responsibility towards mitigating climate change. This experiential learning approach has been shown to enhance comprehension of complex climate concepts, ultimately empowering individuals to become proactive stewards of the planet. Hands-on education makes climate change more tangible.
- Enhancing Climate Change Understanding through Hands-on Environmental Education
-
Hands-on Learning: A Key to Unlocking Deeper Climate Change Understanding through Environmental Education
- 'How does experiential environmental education influence climate change awareness and understanding?'
- Experiential Learning and Climate Change Awareness
- Enhancing Understanding through Real-World Applications
- Fostering Engagement and Action through Experiential Education
- What role does experiential learning play in fostering a deeper understanding of climate change issues?
- Enhancing Awareness through Direct Experience
- Promoting Active Engagement and Problem-Solving
- Fostering Empathy and Community Involvement
- 'What hands-on educational approaches are most effective in fostering climate literacy across different age groups?'
- Experiential Learning for Younger Age Groups
- Project-Based Learning for Older Students
- Community Engagement for Adult Learners
- 'How crucial is environmental education in understanding the effects of climate change?'
- Understanding Climate Change Causes and Consequences
- Promoting Sustainable Practices and Behaviors
- Fostering Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation Efforts
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is hands-on environmental education?
- How does hands-on environmental education enhance climate change understanding?
- What are the benefits of hands-on environmental education for climate change understanding?
- Can hands-on environmental education be implemented in different educational settings?
Enhancing Climate Change Understanding through Hands-on Environmental Education
Hands-on environmental education is a powerful tool for enhancing understanding of climate change. By engaging individuals in direct experiences and practical activities, it fosters a deeper connection with the natural world and promotes a more nuanced comprehension of the complex issues surrounding climate change. This approach not only educates but also inspires action, as participants are more likely to be motivated to address climate change when they have a personal stake and understanding of the issue.
Experiential Learning and Climate Change Awareness
Experiential learning, a key component of hands-on environmental education, involves direct experience and hands-on activities that allow individuals to explore and understand climate change concepts in a tangible way. This can include activities such as conducting experiments to measure carbon footprint, participating in citizen science projects to monitor local climate indicators, or engaging in outdoor activities that illustrate the impacts of climate change on ecosystems. By making climate change more tangible and relatable, experiential learning can significantly enhance awareness and understanding.
Developing Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Skills
Hands-on environmental education also plays a crucial role in developing critical thinking and problem-solving skills, both of which are essential for addressing the complexities of climate change. Through activities that encourage inquiry, analysis, and creativity, individuals learn to evaluate information, identify patterns, and develop innovative solutions to climate-related challenges. This not only deepens their understanding of climate change but also empowers them to become active participants in mitigating its effects.
Promoting Stewardship and Community Engagement
Furthermore, hands-on environmental education promotes a sense of stewardship and community engagement, crucial elements in the fight against climate change. By involving individuals in local environmental projects and initiatives, it fosters a sense of responsibility towards the environment and encourages community-level action. This collective approach to addressing climate change can lead to more effective and sustainable solutions, as it leverages the power of community engagement and cooperation.
| Benefits of Hands-on Environmental Education | Description |
|---|---|
| Experiential Learning | Direct experience and hands-on activities that enhance climate change understanding |
| Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving | Development of skills necessary for addressing climate change complexities |
| Stewardship and Community Engagement | Fostering a sense of responsibility and encouraging community action against climate change |
Hands-on Learning: A Key to Unlocking Deeper Climate Change Understanding through Environmental Education
'How does experiential environmental education influence climate change awareness and understanding?'

Experiential environmental education plays a significant role in shaping individuals' awareness and understanding of climate change. By engaging participants in hands-on experiences and real-world applications, experiential environmental education fosters a deeper connection to the natural world and promotes a more nuanced comprehension of the complex issues surrounding climate change. This approach to learning encourages individuals to explore the intricate relationships between human activities and environmental consequences, ultimately cultivating a more informed and empathetic response to the challenges posed by climate change.
Experiential Learning and Climate Change Awareness
Experiential environmental education raises climate change awareness by providing individuals with direct experiences that illustrate the impacts of climate change. These experiences can range from observing changes in local ecosystems to participating in citizen science projects that monitor climate-related phenomena. Through these experiences, individuals develop a more personal connection to the issue, which can motivate them to learn more and become involved in addressing climate change. Some key aspects of experiential learning that contribute to climate change awareness include:
- Direct observation of climate-related changes in local environments
- Participation in hands-on activities that demonstrate climate change impacts
- Engagement with community members who share personal experiences related to climate change
Enhancing Understanding through Real-World Applications
Experiential environmental education enhances understanding of climate change by providing real-world contexts for learning. By applying theoretical knowledge to practical problems, individuals develop a more comprehensive grasp of climate change causes, consequences, and potential solutions. This approach helps bridge the gap between abstract concepts and tangible realities, making climate change more accessible and understandable. Key elements of real-world applications that enhance understanding include:
- Analyzing case studies of climate change impacts on local ecosystems and communities
- Developing and implementing projects that address climate-related issues
- Collaborating with experts from various fields to gain insights into climate change mitigation and adaptation strategies
Fostering Engagement and Action through Experiential Education
Experiential environmental education not only informs individuals about climate change but also empowers them to take action. By engaging participants in meaningful experiences and providing opportunities for reflection and discussion, experiential education can inspire a sense of personal responsibility and motivate individuals to adopt climate-friendly behaviors. Key factors that contribute to fostering engagement and action include:
- Opportunities for participants to reflect on their experiences and connect them to broader climate change issues
- Guided discussions that explore the implications of climate change and potential responses
- Support for developing and implementing personal or community-based climate action projects
What role does experiential learning play in fostering a deeper understanding of climate change issues?

Experiential learning plays a vital role in fostering a deeper understanding of climate change issues by providing individuals with hands-on experiences and real-world applications that enhance their knowledge and engagement. Through experiential learning, participants can directly observe the impacts of climate change, such as rising sea levels, melting glaciers, or extreme weather events, which can evoke emotional responses and motivate action. This approach complements traditional teaching methods by making complex concepts more tangible and accessible.
Enhancing Awareness through Direct Experience
Experiential learning enhances awareness by immersing individuals in environments where they can directly witness the effects of climate change. This direct exposure can stimulate curiosity and encourage a deeper exploration of the subject. For instance, participating in field trips to areas affected by climate change can provide a firsthand understanding of its consequences.
- Visiting ecosystems threatened by climate change, such as coral reefs or arctic regions, to observe the impacts.
- Engaging in citizen science projects that involve monitoring climate-related phenomena.
- Participating in community-based initiatives that focus on climate change adaptation and resilience.
Promoting Active Engagement and Problem-Solving
Experiential learning encourages active engagement and problem-solving by challenging individuals to address climate change-related issues through practical projects. By working on real-world problems, participants develop critical thinking skills and creativity as they seek innovative solutions. This hands-on approach helps bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application.
- Designing and implementing projects that reduce carbon footprint or promote sustainable practices.
- Collaborating with local communities to develop climate change mitigation strategies.
- Developing and presenting proposals for climate-resilient infrastructure or policies.
Fostering Empathy and Community Involvement
Experiential learning fosters empathy and community involvement by connecting individuals with the people and places affected by climate change. Through interactions with local communities and stakeholders, participants gain a deeper understanding of the social and cultural dimensions of climate change. This empathetic understanding can inspire a sense of responsibility and motivate individuals to take action.
- Engaging with local narratives and stories about climate change experiences.
- Participating in workshops or forums that discuss climate change impacts on different communities.
- Collaborating with community leaders to develop and implement climate change adaptation plans.
'What hands-on educational approaches are most effective in fostering climate literacy across different age groups?'

Hands-on educational approaches are essential in fostering climate literacy across different age groups as they enable learners to engage directly with the subject matter, promoting a deeper understanding of climate change causes, effects, and mitigation strategies. Effective approaches often incorporate real-world examples, experiments, and projects that cater to diverse learning styles and age-specific needs.
Experiential Learning for Younger Age Groups
For younger learners, hands-on activities such as gardening, outdoor experiments, and simple climate-related crafts can be highly effective. These activities not only introduce basic climate concepts but also foster curiosity and a connection with nature.
- Planting trees or starting a school garden to learn about carbon sequestration and sustainable practices.
- Conducting simple weather-related experiments, such as making rain gauges or cloud in a jar.
- Creating art projects using recycled materials to understand waste management and reduction.
Project-Based Learning for Older Students
Older students benefit from more complex, project-based learning that integrates climate literacy with other subjects like science, mathematics, and language arts. This approach encourages critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaboration.
- Designing and implementing a school or community energy audit to identify areas for energy efficiency improvements.
- Developing a local climate action plan that incorporates data analysis, research, and stakeholder engagement.
- Creating public awareness campaigns about climate change impacts and mitigation strategies.
Community Engagement for Adult Learners
Adult learners can benefit from hands-on educational approaches that involve community engagement and practical application. This can include workshops, citizen science projects, and community-based initiatives that address local climate challenges.
- Participating in citizen science projects that monitor local climate indicators, such as temperature or water quality.
- Attending workshops on climate-resilient practices for gardening, agriculture, or home improvement.
- Joining community groups focused on climate action, such as advocacy campaigns or local sustainability initiatives.
'How crucial is environmental education in understanding the effects of climate change?'
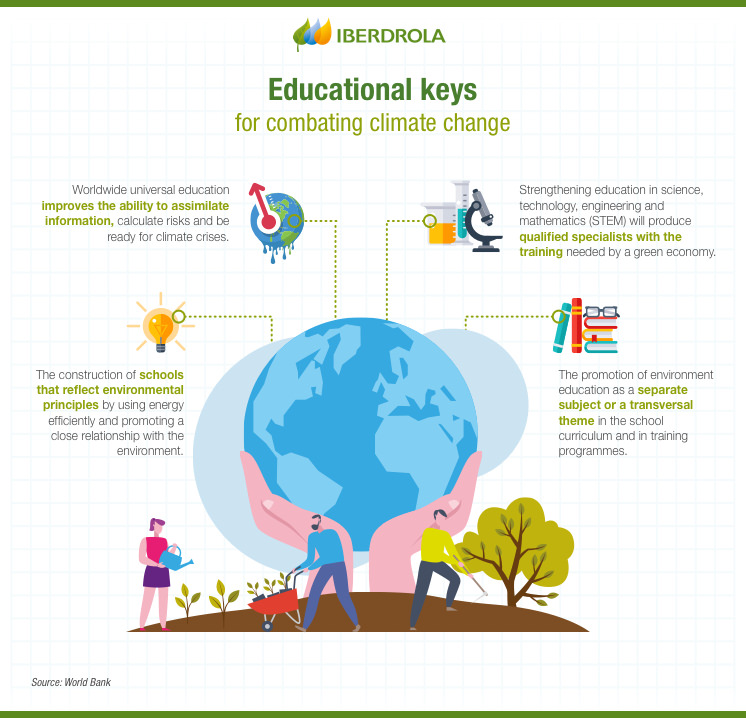
Environmental education plays a vital role in understanding the effects of climate change as it empowers individuals with the knowledge, skills, and awareness necessary to comprehend the complexities of this global issue. By integrating environmental education into school curricula and community programs, people can gain a deeper understanding of the causes and consequences of climate change, as well as the potential solutions and actions that can be taken to mitigate its impacts.
Understanding Climate Change Causes and Consequences
Environmental education helps individuals understand the science behind climate change, including the role of greenhouse gases, deforestation, and other human activities that contribute to global warming. This knowledge enables people to appreciate the far-reaching consequences of climate change, such as rising sea levels, more frequent natural disasters, and changes in weather patterns.
- It allows individuals to grasp the interconnectedness of human and natural systems.
- It fosters an understanding of the disproportionate impacts of climate change on vulnerable populations.
- It highlights the importance of addressing climate change through collective action.
Promoting Sustainable Practices and Behaviors
Environmental education encourages individuals to adopt sustainable practices and behaviors that reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a more climate-resilient future. By learning about climate-friendly technologies, sustainable land use practices, and eco-friendly consumption patterns, people can make informed choices that support a low-carbon economy.
- It inspires individuals to reduce their energy consumption and reliance on fossil fuels.
- It promotes the adoption of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power.
- It encourages sustainable agriculture practices and reduced food waste.
Fostering Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation Efforts
Environmental education is crucial for fostering climate change mitigation and adaptation efforts at the local, national, and international levels. By educating individuals about climate change, we can build a global community that is equipped to address this pressing issue.
- It enables communities to develop and implement effective climate change mitigation strategies.
- It supports the development of climate-resilient infrastructure and agriculture.
- It promotes international cooperation and knowledge sharing on climate change issues.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is hands-on environmental education?
Hands-on environmental education involves interactive and experiential learning activities that allow students to engage directly with the natural environment. This approach enables students to develop a deeper understanding of environmental concepts and issues, including climate change, through practical experiences and real-world observations. By participating in hands-on activities, students can gain a more nuanced understanding of the complex relationships within ecosystems.
How does hands-on environmental education enhance climate change understanding?
Hands-on environmental education enhances climate change understanding by allowing students to explore and investigate the impacts of climate change in a tangible and meaningful way. Through activities such as field observations, experiments, and projects, students can develop a deeper understanding of the causes and effects of climate change, as well as potential solutions and mitigation strategies.
What are the benefits of hands-on environmental education for climate change understanding?
The benefits of hands-on environmental education for climate change understanding include increased student engagement, improved knowledge retention, and the development of critical thinking and problem-solving skills. By providing students with direct experiences and opportunities for inquiry, hands-on environmental education can help to foster a deeper understanding of climate change and promote environmental literacy.
Can hands-on environmental education be implemented in different educational settings?
Yes, hands-on environmental education can be implemented in various educational settings, including traditional classrooms, outdoor classrooms, and community-based programs. Educators can adapt hands-on activities to suit different age groups, subjects, and learning environments, making it a versatile and effective approach to teaching climate change and environmental education.

Leave a Reply