How fresh-water biodiversity suffers from warming and runoff

The world's freshwater ecosystems are facing unprecedented threats due to climate change and human activities. Rising temperatures and altered precipitation patterns are disrupting the delicate balance of these ecosystems, leading to a decline in biodiversity. Freshwater species are particularly vulnerable to changes in water temperature and quality, which can have far-reaching consequences for the entire ecosystem. As global temperatures continue to rise, understanding the impacts of warming and runoff on freshwater biodiversity is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies to protect these vital ecosystems and the species that depend on them. The consequences are significant.
- The Impact of Warming and Runoff on Freshwater Biodiversity
-
Understanding the Impact of Climate Change and Agricultural Runoff on Freshwater Ecosystems
- 'What drives the decline of freshwater biodiversity?'
- Habitat Destruction and Alteration
- Pollution and Water Quality Degradation
- Overexploitation and Invasive Species
- What is the impact of rising temperatures on freshwater biodiversity?
- Changes in Species Distribution and Abundance
- Impacts on Freshwater Ecosystems Processes
- Conservation Implications
- What are the primary factors endangering freshwater ecosystems?
- Pollution and its Effects
- Habitat Destruction and its Consequences
- Climate Change Impacts
- What drives the most significant decline in global freshwater resources?
- Impact of Climate Change on Freshwater Resources
- Over-Extraction and Inefficient Use of Freshwater
- Pollution and Degradation of Freshwater Ecosystems
- Frequently Asked Questions
The Impact of Warming and Runoff on Freshwater Biodiversity
The world's freshwater ecosystems are facing unprecedented threats due to climate change and human activities. Rising temperatures and altered precipitation patterns are leading to increased runoff, which can have devastating effects on the delicate balance of freshwater biodiversity. As a result, many aquatic species are facing significant challenges to their survival, and the consequences of inaction could be severe.
Thermal Stress and its Consequences
Rising water temperatures are altering the habitats of many freshwater species, making it difficult for them to adapt and survive. Thermal stress can lead to changes in species distribution, behavior, and physiology, ultimately affecting the overall biodiversity of freshwater ecosystems. For example, many fish species are sensitive to temperature changes, and increased water temperature can lead to reduced growth rates, lower reproduction rates, and increased mortality.
Runoff and Water Quality
Runoff from agricultural fields, urban areas, and other human-dominated landscapes can carry a cocktail of pollutants into freshwater ecosystems, including nutrients, sediments, and pesticides. These pollutants can lead to eutrophication, algal blooms, and reduced water quality, making it difficult for aquatic species to survive. The impact of runoff can be particularly severe during heavy rainfall events, when large amounts of pollutants are washed into freshwater ecosystems.
Conservation Efforts and Management Strategies
To mitigate the impacts of warming and runoff on freshwater biodiversity, conservation efforts and management strategies are essential. This can include restoring habitats, implementing sustainable agricultural practices, and improving wastewater treatment. By taking a proactive and coordinated approach, it is possible to reduce the impacts of warming and runoff on freshwater ecosystems and protect the rich biodiversity they support.
| Impact | Causes | Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Stress | Rising water temperatures | Changes in species distribution, behavior, and physiology |
| Runoff and Water Quality | Agricultural runoff, urban runoff, and other human activities | Eutrophication, algal blooms, and reduced water quality |
| Conservation Efforts | Restoring habitats, sustainable agriculture, and improved wastewater treatment | Reduced impacts on freshwater biodiversity |
Understanding the Impact of Climate Change and Agricultural Runoff on Freshwater Ecosystems
'What drives the decline of freshwater biodiversity?'

The decline of freshwater biodiversity is a complex issue driven by multiple factors. Freshwater ecosystems, including rivers, lakes, and wetlands, are facing numerous threats that are resulting in the loss of species and ecosystem degradation.
Habitat Destruction and Alteration
Habitat destruction and alteration are significant drivers of freshwater biodiversity decline. Human activities such as damming, channelization, and land conversion for agriculture and urbanization have modified or destroyed habitats, disrupting the delicate balance of freshwater ecosystems.
- Construction of dams and reservoirs alters the natural flow of rivers, affecting the migration and breeding patterns of aquatic species.
- Channelization and dredging of rivers can lead to the loss of habitats and the degradation of water quality.
- Land conversion for agriculture and urbanization results in the destruction of wetlands and riparian zones, which are critical habitats for many freshwater species.
Pollution and Water Quality Degradation
Pollution and water quality degradation are also major contributors to the decline of freshwater biodiversity. The release of pollutants, such as industrial effluents, agricultural runoff, and sewage, can alter the chemical composition of freshwater ecosystems, making them inhospitable to many species.
- Agricultural runoff containing fertilizers and pesticides can lead to eutrophication and the degradation of water quality.
- Industrial effluents can release toxic substances that are harmful to aquatic life.
- Sewage and wastewater can introduce pathogens and excess nutrients into freshwater ecosystems, promoting the growth of algae and degrading water quality.
Overexploitation and Invasive Species
Overexploitation and the introduction of invasive species are additional factors driving the decline of freshwater biodiversity. Overfishing and the harvesting of other aquatic resources can deplete populations, while the introduction of non-native species can lead to competition for resources and habitat disruption.
- Overfishing can deplete fish populations, affecting the food chain and ecosystem balance.
- The introduction of invasive species can lead to the displacement of native species and alter ecosystem processes.
- The aquarium trade and other forms of species introduction can facilitate the spread of invasive species.
What is the impact of rising temperatures on freshwater biodiversity?

Rising temperatures are having a profound impact on freshwater biodiversity, affecting the delicate balance of ecosystems and the distribution of species that inhabit them. Freshwater ecosystems, including rivers, lakes, and wetlands, are particularly vulnerable to changes in temperature, as many of the species that live in these environments are adapted to specific thermal regimes.
Changes in Species Distribution and Abundance
As temperatures rise, many freshwater species are shifting their ranges poleward or to higher elevations in search of cooler waters. This can lead to changes in community composition, as some species are able to adapt to the new temperature conditions while others are not.
- Changes in species distribution can lead to the loss of unique genetic diversity as populations become isolated.
- Some species may be able to migrate to new habitats, while others may be unable to do so due to geographical or other barriers.
- The resulting changes in community composition can have cascading effects on ecosystem functioning.
Impacts on Freshwater Ecosystems Processes
Rising temperatures can also affect the functioning of freshwater ecosystems, altering the rates of important processes such as primary production, decomposition, and nutrient cycling.
- Warmer waters can stimulate the growth of algae, potentially leading to eutrophication and decreased water quality.
- Changes in temperature can also alter the timing of seasonal events, such as the timing of fish migrations or the breeding of aquatic insects.
- This can have implications for the overall health and resilience of freshwater ecosystems.
Conservation Implications
The impact of rising temperatures on freshwater biodiversity highlights the need for effective conservation and management strategies.
- Protecting and restoring habitats can help to maintain connectivity and allow species to migrate to new areas.
- Reducing other stressors, such as pollution and overfishing, can help to increase the resilience of freshwater ecosystems to climate change.
- Developing and implementing conservation plans that take into account the projected impacts of climate change is crucial for maintaining freshwater biodiversity.
What are the primary factors endangering freshwater ecosystems?
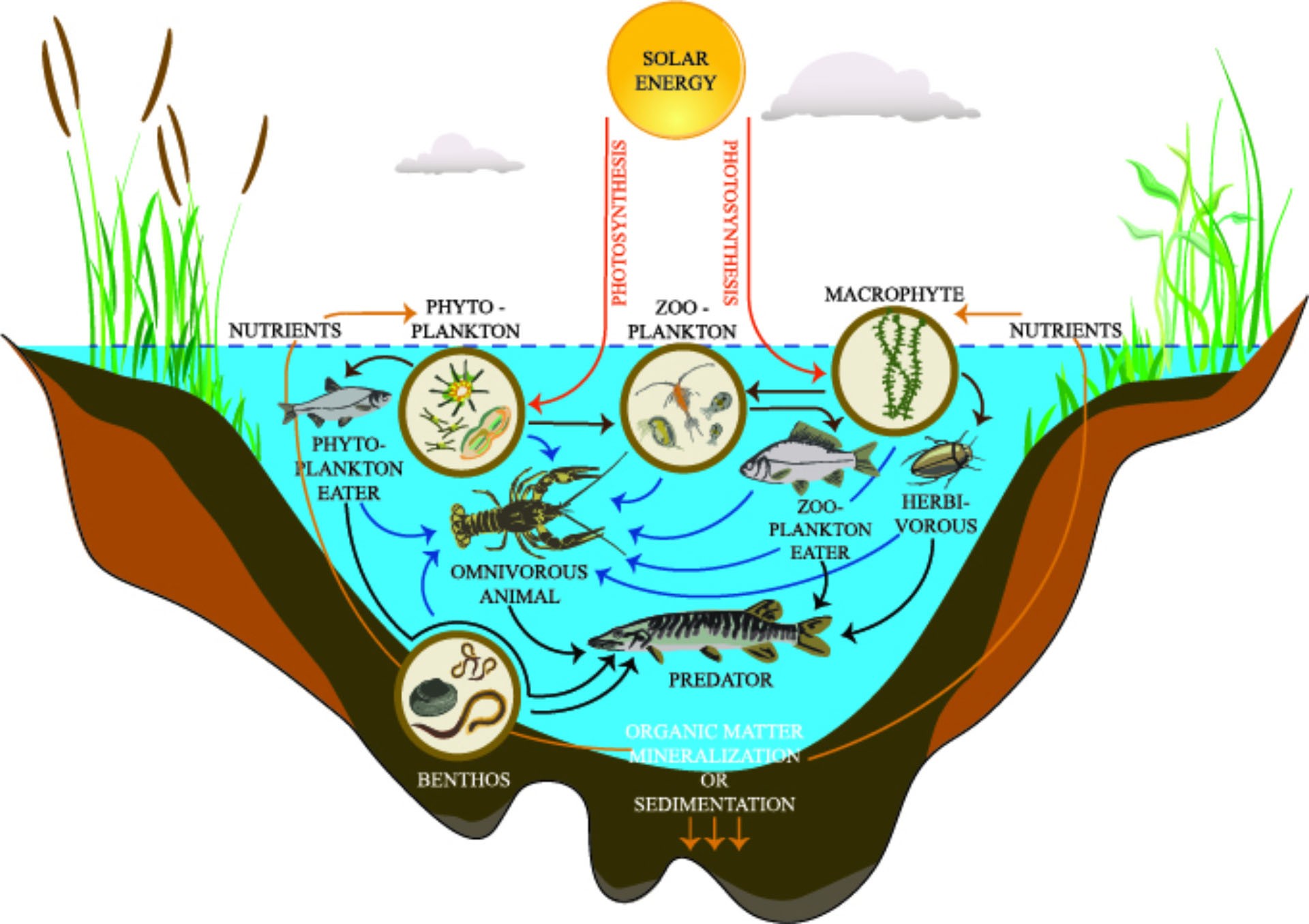
Freshwater ecosystems are being threatened by various human activities and natural factors. The primary factors endangering these ecosystems include pollution, habitat destruction, and climate change, among others.
Pollution and its Effects
Pollution is a significant threat to freshwater ecosystems. The release of industrial, agricultural, and domestic waste into water bodies has devastating effects on the environment. This can lead to the degradation of water quality, harming aquatic life and potentially affecting human health. Some of the key pollutants include:
- Chemical pollutants from industrial and agricultural runoff
- Domestic sewage and waste disposal
- Microplastics and other non-biodegradable materials
Habitat Destruction and its Consequences
Habitat destruction is another major factor endangering freshwater ecosystems. Human activities such as deforestation, dam construction, and wetland drainage have led to the loss of natural habitats for many aquatic species. This can disrupt the delicate balance of the ecosystem and lead to the loss of biodiversity. The effects of habitat destruction include:
- Loss of spawning grounds for fish and other aquatic species
- Disruption of nutrient cycles and water quality
- Reduced habitat for plants and animals that depend on freshwater ecosystems
Climate Change Impacts
Climate change is also having a profound impact on freshwater ecosystems. Rising temperatures and altered precipitation patterns are changing the dynamics of these ecosystems. This can lead to changes in water levels, flow rates, and water quality, making it difficult for plants and animals to adapt. Some of the key impacts of climate change include:
- Changes in water temperature and chemistry
- Altered flow regimes and water levels
- Increased frequency and severity of extreme weather events
What drives the most significant decline in global freshwater resources?

The most significant decline in global freshwater resources is driven by a combination of factors, primarily influenced by human activities and climate change. The increasing global population and the subsequent rise in water demand for domestic, industrial, and agricultural purposes have put immense pressure on available freshwater resources.
Impact of Climate Change on Freshwater Resources
Climate change plays a crucial role in the decline of global freshwater resources. Rising temperatures alter precipitation patterns, leading to more frequent and severe droughts and floods. This variability affects the availability of freshwater, making it challenging to manage water resources sustainably.
- Changes in precipitation patterns due to climate change.
- Increased evaporation from water bodies and soil due to warmer temperatures.
- Melting of glaciers and ice caps, affecting seasonal water availability.
Over-Extraction and Inefficient Use of Freshwater
The over-extraction of groundwater is another significant factor contributing to the decline in freshwater resources. As the global demand for water increases, aquifers are being depleted at a rate that exceeds their natural recharge, leading to water scarcity and land subsidence in many regions.
- Over-extraction of groundwater for irrigation and drinking water.
- Inefficient irrigation practices leading to water waste.
- Lack of effective water management policies and regulations.
Pollution and Degradation of Freshwater Ecosystems
Pollution from industrial, agricultural, and domestic activities degrades freshwater ecosystems, reducing the availability of clean water. The release of untreated wastewater and agricultural runoff containing fertilizers and pesticides contaminates rivers, lakes, and groundwater.
- Discharge of untreated industrial and domestic wastewater.
- Agricultural runoff and the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
- Destruction of natural habitats and wetlands that help purify water.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the impact of warming on fresh-water biodiversity?
Warming affects fresh-water biodiversity by altering ecosystems, changing species distribution, and disrupting delicate balances. Rising temperatures can lead to the loss of habitats and extinction of temperature-sensitive species. Freshwater ecosystems, already under stress from human activities, are further threatened by warming, which can exacerbate issues like eutrophication and algal blooms.
How does runoff affect fresh-water ecosystems?
Runoff significantly impacts fresh-water ecosystems by carrying pollutants, sediments, and excess nutrients into water bodies. This can lead to eutrophication, decreased water quality, and altered habitats. Runoff also introduces invasive species and pathogens, further threatening native biodiversity. The cumulative effect is a degradation of ecosystem services and resilience, making them more vulnerable to other disturbances like warming.
Can fresh-water biodiversity adapt to warming and runoff?
Fresh-water biodiversity has some capacity to adapt to changing conditions, but this is limited. Some species may migrate or evolve in response to warming and altered water chemistry. However, the rapid pace of change and cumulative impacts often outstrip the ability of ecosystems to adapt, leading to losses in biodiversity. Conservation efforts are essential to enhance resilience and protect vulnerable species.
What conservation actions can mitigate the impact of warming and runoff?
Conservation actions such as restoring habitats, improving water quality, and protecting riparian zones can help mitigate the impacts of warming and runoff. Implementing sustainable land-use practices reduces runoff and pollutant entry into water bodies. Enhancing ecosystem connectivity and promoting ecological restoration can also support biodiversity resilience. These actions require coordinated efforts among stakeholders to effectively safeguard fresh-water ecosystems.

Leave a Reply