How forest biodiversity loss increases carbon release rates
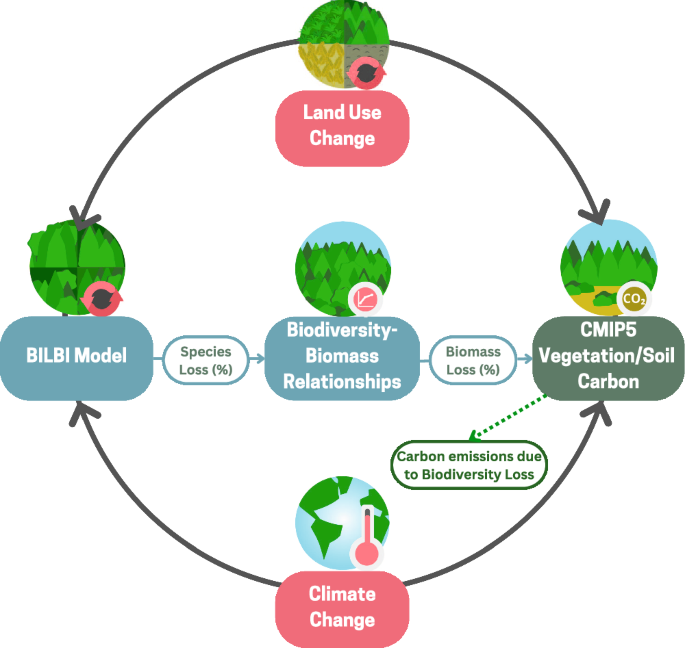
Forests play a crucial role in regulating the global carbon cycle, with their ecosystems storing significant amounts of carbon in trees, soil, and other organic matter. However, the loss of forest biodiversity due to human activities such as deforestation and fragmentation is having a profound impact on the ability of forests to sequester carbon. As forest ecosystems become less diverse, their capacity to store carbon is compromised, leading to increased rates of carbon release into the atmosphere, and this has significant implications for global climate change mitigation efforts. The relationship between forest biodiversity and carbon release is complex.
- Understanding the Impact of Forest Biodiversity Loss on Carbon Release
-
Understanding the Impact of Forest Biodiversity Loss on Carbon Emissions
- 'How does deforestation impact carbon sequestration in forests?'
- Impact on Carbon Storage
- Consequences for Forest Ecosystems
- Effects on Climate Change Mitigation
- 'How is forest carbon absorption impacted by biodiversity loss?'
- Impact of Tree Species Diversity on Carbon Sequestration
- Effects of Biodiversity Loss on Forest Ecosystem Processes
- Consequences of Reduced Forest Biodiversity on Climate Change Mitigation
- What role does biodiversity play in regulating the carbon cycle in forest ecosystems?
- Carbon Sequestration through Diverse Tree Species
- Soil Carbon Storage and Microbial Diversity
- Functional Diversity and Ecosystem Processes
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the relationship between forest biodiversity and carbon release?
- How does forest fragmentation contribute to biodiversity loss and carbon release?
- Can reforestation efforts mitigate the effects of biodiversity loss on carbon release?
- What role do forest management practices play in maintaining biodiversity and reducing carbon release?
Understanding the Impact of Forest Biodiversity Loss on Carbon Release
The loss of biodiversity in forests is a critical issue that not only affects ecosystems but also has significant implications for the global carbon cycle. When forests lose biodiversity, the rate at which carbon is released into the atmosphere can increase. This is because diverse forests have a more complex structure and a variety of tree species, which can lead to more efficient carbon sequestration. Conversely, when biodiversity is lost, the remaining trees may not be as effective at storing carbon, leading to increased carbon emissions.
The Role of Tree Species Diversity in Carbon Sequestration
Tree species diversity plays a crucial role in carbon sequestration. Different tree species have varying capacities to absorb and store carbon dioxide. Forests with a higher diversity of tree species tend to be more resilient and better at sequestering carbon. For example, some tree species are more efficient at photosynthesis, while others may have deeper roots that allow them to store carbon in the soil. When these diverse species are lost, the forest's overall ability to sequester carbon is diminished. The table below illustrates the carbon sequestration potential of different tree species.
| Tree Species | Carbon Sequestration Potential (tons/ha/year) |
|---|---|
| Eucalyptus | 10-20 |
| Oak | 5-15 |
| Pine | 8-18 |
Impact of Forest Fragmentation on Carbon Release
Forest fragmentation, which is often a result of biodiversity loss, can lead to increased carbon release. When forests are fragmented, the remaining patches of forest are more susceptible to edge effects, such as increased temperatures and reduced humidity. This can lead to increased tree mortality and a shift in species composition, favoring species that are less effective at storing carbon. As a result, the carbon stored in these forests is released into the atmosphere at a faster rate.
Consequences of Biodiversity Loss on Forest Ecosystem Processes
The loss of biodiversity in forests can have cascading effects on ecosystem processes, including nutrient cycling and decomposition. For example, the loss of certain species can disrupt nutrient cycling, leading to changes in soil fertility and affecting the overall health of the forest. This, in turn, can impact the forest's ability to sequester carbon, as healthy forests with diverse species are generally more effective at storing carbon. The impact of biodiversity loss on ecosystem processes can be seen in the changes to forest composition and structure.
| Ecosystem Process | Impact of Biodiversity Loss |
|---|---|
| Nutrient Cycling | Disrupted nutrient cycles leading to reduced soil fertility |
| Decomposition | Changes in decomposition rates affecting carbon storage |
| Primary Production | Reduced primary production due to loss of functional diversity |
Understanding the Impact of Forest Biodiversity Loss on Carbon Emissions
'How does deforestation impact carbon sequestration in forests?'

Deforestation significantly impacts carbon sequestration in forests as it disrupts the delicate balance between the carbon cycle and forest ecosystems. Forests act as massive carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through the process of photosynthesis and storing it in trees, soil, and other organic matter. When forests are cleared or degraded, the stored carbon is released back into the atmosphere, contributing to the increase in greenhouse gases and exacerbating climate change.
Impact on Carbon Storage
The removal of trees through deforestation directly affects the ability of forests to store carbon. Trees are significant carbon reservoirs, and when they are cut down or burned, the carbon they store is released.
- The immediate release of stored carbon into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide.
- Loss of the tree's future carbon sequestration potential.
- Soil degradation, as tree roots and leaf litter contribute to soil carbon.
Consequences for Forest Ecosystems
Deforestation not only impacts carbon sequestration but also has broader implications for forest ecosystems. The loss of trees can disrupt the habitat of countless species, leading to biodiversity loss and ecosystem degradation.
- Disruption of nutrient cycles and water regulation within the forest.
- Loss of habitat for a wide range of flora and fauna.
- Soil erosion and decreased fertility due to the loss of tree cover.
Effects on Climate Change Mitigation
Forests play a crucial role in mitigating climate change by absorbing carbon dioxide, a key greenhouse gas. Deforestation undermines this role, making it more challenging to combat climate change.
- Increased greenhouse gas emissions due to the release of stored carbon.
- Reduced capacity for future carbon sequestration.
- Exacerbation of climate change impacts, including more extreme weather events.
'How is forest carbon absorption impacted by biodiversity loss?'

Forests play a crucial role in the global carbon cycle by absorbing and storing carbon dioxide, a key greenhouse gas. The capacity of forests to absorb carbon is influenced by various factors, including biodiversity. Biodiversity loss can significantly impact forest carbon absorption. When biodiversity is high, forests tend to have a more complex structure with a variety of tree species, which can lead to more efficient carbon sequestration. This is because different species have different growth rates, wood densities, and litter qualities, contributing to a more diverse and resilient carbon storage.
Impact of Tree Species Diversity on Carbon Sequestration
The diversity of tree species in a forest is directly related to its carbon sequestration potential. Forests with a higher diversity of tree species tend to have a greater capacity for carbon storage. This is attributed to the complementary effects of different species on ecosystem processes.
- Diverse tree species can occupy different niches, maximizing the use of resources such as light, water, and nutrients.
- Different species contribute to varying litter qualities and decomposition rates, influencing soil carbon storage.
- A mix of fast-growing and slow-growing species can lead to a more stable carbon storage over time.
Effects of Biodiversity Loss on Forest Ecosystem Processes
Biodiversity loss can disrupt forest ecosystem processes that are crucial for carbon absorption. The reduction in species diversity can lead to changes in forest structure and function, impacting carbon sequestration.
- Loss of key species can disrupt nutrient cycling, affecting the overall health and productivity of the forest.
- Reduced diversity can make forests more vulnerable to disturbances such as pests and diseases, potentially leading to carbon losses.
- Changes in forest composition can alter the microclimate, affecting carbon sequestration rates.
Consequences of Reduced Forest Biodiversity on Climate Change Mitigation
The impact of biodiversity loss on forest carbon absorption has significant implications for climate change mitigation strategies. Forests are considered a critical component in efforts to reduce atmospheric carbon dioxide levels.
- Preserving biodiversity is essential for maintaining the carbon sequestration potential of forests.
- Restoration efforts should focus on re-establishing diverse forest ecosystems to enhance carbon storage.
- Conservation strategies need to consider the complex interactions between biodiversity and carbon cycling in forests.
What role does biodiversity play in regulating the carbon cycle in forest ecosystems?
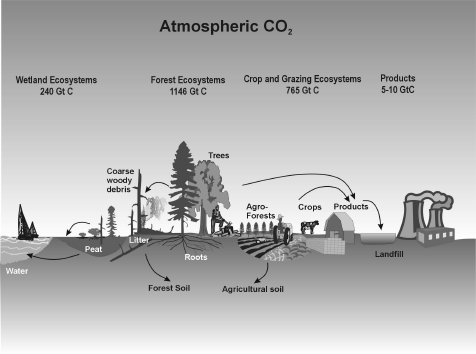
Biodiversity plays a crucial role in regulating the carbon cycle in forest ecosystems. Forests are significant carbon sinks, and their ability to sequester carbon is influenced by the variety of plant and animal species they harbor. The diversity of tree species, for example, can affect the overall carbon storage capacity of a forest, as different species have varying rates of carbon sequestration and storage.
Carbon Sequestration through Diverse Tree Species
The presence of diverse tree species in a forest ecosystem contributes to its overall carbon sequestration potential. Different tree species have unique characteristics that influence their carbon sequestration rates, such as growth rates, wood density, and leaf area index. A forest with a diverse array of tree species is likely to have a more stable and resilient carbon sequestration capacity.
- Some tree species, like fast-growing pioneers, can rapidly colonize disturbed areas and sequester carbon quickly.
- Other species, like slow-growing, long-lived trees, can store carbon for extended periods.
- A mix of tree species with different growth strategies can create a more stable carbon sink.
Soil Carbon Storage and Microbial Diversity
Soil is a critical component of the forest carbon cycle, and its carbon storage capacity is influenced by the diversity of microorganisms present. A diverse soil microbial community can break down organic matter more efficiently, influencing the amount of carbon stored in soils. The presence of diverse microorganisms also affects the formation of soil aggregates, which can protect carbon-rich soil particles from erosion and decomposition.
- Diverse microbial communities can decompose organic matter more thoroughly, reducing the amount of labile carbon.
- The presence of mycorrhizal fungi can enhance soil carbon storage by improving soil aggregation.
- A diverse array of microorganisms can also influence nutrient cycling, affecting the overall carbon balance of the ecosystem.
Functional Diversity and Ecosystem Processes
Functional diversity, which refers to the variety of ecological roles played by different species within an ecosystem, is crucial for maintaining ecosystem processes that regulate the carbon cycle. In forest ecosystems, functional diversity can influence processes like litter decomposition, nutrient cycling, and primary production, all of which impact carbon sequestration and storage.
- A diverse array of functional traits among plant species can influence litter quality and decomposition rates.
- The presence of species with different nutrient acquisition strategies can affect nutrient cycling patterns.
- Functional diversity can also influence the resilience of ecosystem processes to disturbances and climate change.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the relationship between forest biodiversity and carbon release?
Forest biodiversity loss is linked to increased carbon release rates. When forests become less diverse, they are more vulnerable to disturbances and less able to sequester carbon. This is because diverse forests have a wider range of tree species, ages, and structures, allowing them to store more carbon. As biodiversity declines, forests become more susceptible to droughts, fires, and other disturbances that release stored carbon.
How does forest fragmentation contribute to biodiversity loss and carbon release?
Forest fragmentation breaks up large areas of forest into smaller, isolated patches, leading to biodiversity loss and increased carbon release. Fragmented forests have more edges, making them more vulnerable to invasive species, fires, and other disturbances. This can lead to the loss of tree species and a decline in forest carbon storage, ultimately resulting in increased carbon release rates. Fragmentation also disrupts nutrient cycles and alters ecosystem processes.
Can reforestation efforts mitigate the effects of biodiversity loss on carbon release?
Reforestation efforts can help mitigate the effects of biodiversity loss on carbon release. By restoring diverse forests, reforestation can reestablish ecosystem processes and promote carbon sequestration. However, the effectiveness of reforestation depends on factors like tree species selection, forest management, and the surrounding landscape. Reforestation with diverse, native species can help restore ecosystem function and reduce carbon release rates.
What role do forest management practices play in maintaining biodiversity and reducing carbon release?
Forest management practices play a crucial role in maintaining biodiversity and reducing carbon release. Sustainable practices like selective logging, agroforestry, and conservation forestry can help maintain ecosystem function and promote carbon sequestration. By adopting practices that prioritize biodiversity and ecosystem services, forest managers can reduce the risk of carbon release and maintain the health and resilience of forest ecosystems.

Leave a Reply