How declining biodiversity undermines resilience against climatic extremes
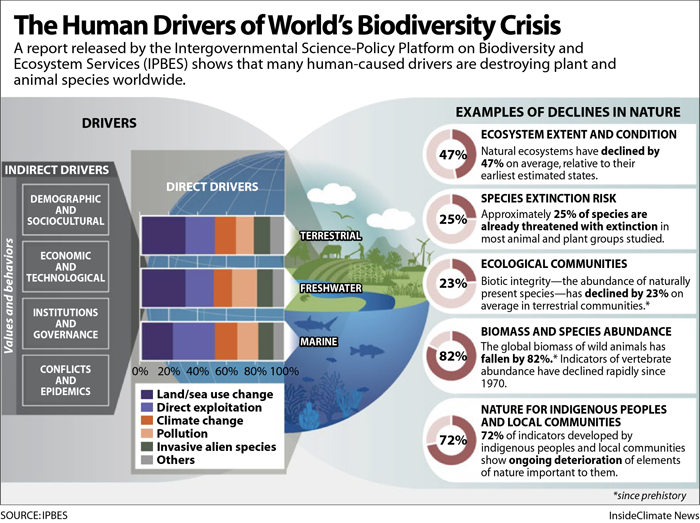
The increasing frequency and severity of climatic extremes, such as droughts, heatwaves and heavy rainfall events, pose significant threats to ecosystems and human societies. A crucial factor influencing the ability of ecosystems to withstand these extremes is biodiversity. As biodiversity declines due to various human activities, ecosystems become more vulnerable to the impacts of climatic extremes. Understanding the intricate relationship between biodiversity loss and resilience is essential for developing effective strategies to mitigate the effects of climate change. This article examines how declining biodiversity undermines the resilience of ecosystems against climatic extremes.
- Understanding the Impact of Biodiversity Loss on Climate Resilience
-
Understanding the Impact of Biodiversity Loss on Climate Resilience
- What role does biodiversity play in enhancing ecosystem resilience to climate change impacts?
- Ecosystem Services and Biodiversity
- Adaptation to Climate Change through Biodiversity
- Conservation and Restoration of Biodiversity
- What is the effect of reduced biodiversity on the ability of ecosystems to withstand climate extremes?
- Impact on Ecosystem Services
- Consequences for Ecosystem Resilience
- Implications for Climate Change Adaptation
- What is the impact of biodiversity loss on climate change resilience?
- Ecosystem Services and Biodiversity Loss
- Climate Change Resilience and Ecosystem Stability
- Consequences of Biodiversity Loss for Human Societies
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the relationship between biodiversity and resilience against climatic extremes?
- How does declining biodiversity affect ecosystem services during extreme weather events?
- Can the loss of specific species contribute to reduced resilience against climatic extremes?
- How can restoring biodiversity help improve resilience to climatic extremes?
Understanding the Impact of Biodiversity Loss on Climate Resilience
The relationship between biodiversity and climate change is complex and bidirectional. On one hand, climate change is a major driver of biodiversity loss, as changing environmental conditions make it difficult for many species to survive. On the other hand, the loss of biodiversity can undermine the resilience of ecosystems to climatic extremes, such as droughts, floods, and heatwaves. This creates a vicious cycle where climate change exacerbates biodiversity loss, and biodiversity loss in turn makes ecosystems more vulnerable to climate change.
The Role of Biodiversity in Ecosystem Services
Biodiversity is crucial for maintaining the health and functioning of ecosystems, which in turn provide essential services to humans, including air and water purification, soil formation and nutrient cycling, and climate regulation. Ecosystems with high levels of biodiversity are generally more resilient to disturbances and can recover more quickly from them. For example, diverse ecosystems can maintain their function even when some species are lost due to climate change or other disturbances. This is because different species often perform similar functions, providing a redundancy that allows ecosystems to continue functioning even in the face of species loss.
Consequences of Biodiversity Loss for Ecosystem Functioning
When biodiversity is lost, ecosystems become less resilient and more vulnerable to climatic extremes. For instance, the loss of key pollinator species can impact plant reproduction, while the loss of decomposer species can disrupt nutrient cycling. This can have cascading effects throughout the ecosystem, leading to changes in ecosystem processes and potentially even ecosystem collapse. The table below illustrates some of the potential consequences of biodiversity loss for ecosystem functioning.
| Ecosystem Service | Impact of Biodiversity Loss |
|---|---|
| Pollination | Reduced crop yields and decreased plant diversity due to loss of pollinator species |
| Nutrient Cycling | Disrupted nutrient cycling due to loss of decomposer species, leading to changes in soil fertility |
| Climate Regulation | Reduced ability of ecosystems to regulate climate due to loss of carbon sequestration and other climate-related ecosystem services |
Implications for Climate Change Adaptation and Mitigation
The loss of biodiversity has significant implications for efforts to adapt to and mitigate the impacts of climate change. Ecosystems with high levels of biodiversity are better able to withstand climatic extremes and can provide important ecosystem-based adaptation opportunities. For example, restoring natural habitats such as wetlands and forests can help to reduce the risk of floods and droughts, while also providing carbon sequestration benefits. By conserving and restoring biodiversity, we can help to build resilience to climate change and reduce the risks associated with climatic extremes.
Understanding the Impact of Biodiversity Loss on Climate Resilience
What role does biodiversity play in enhancing ecosystem resilience to climate change impacts?

Biodiversity plays a crucial role in enhancing ecosystem resilience to climate change impacts. Ecosystems with high levels of biodiversity are better equipped to withstand and recover from disturbances, such as droughts, storms, and temperature fluctuations, associated with climate change. The variety of species, functional traits, and genetic diversity within ecosystems contribute to their overall resilience.
Ecosystem Services and Biodiversity
Biodiversity is essential for maintaining ecosystem services that are critical for human well-being, including air and water purification, soil formation, and climate regulation. As climate change alters ecosystems, the loss of biodiversity can disrupt these services, leading to cascading effects on ecosystems and human societies.
- Pollination services: Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can disrupt the delicate timing of plant-pollinator interactions, impacting crop yields and food security.
- Nutrient cycling: The loss of decomposer species can slow nutrient cycling, affecting soil fertility and plant growth.
- Water cycling: Changes in vegetation composition and structure can alter evapotranspiration rates, influencing local water cycles.
Adaptation to Climate Change through Biodiversity
Biodiversity provides the raw material for ecosystems to adapt to changing climate conditions. As species respond differently to climate change, the diversity of responses can help ecosystems to maintain their overall function and resilience.
- Species migration: Some species may shift their ranges in response to changing climate conditions, maintaining ecosystem processes.
- Evolutionary adaptation: Populations with high genetic diversity are more likely to adapt to changing environmental conditions through evolutionary processes.
- Functional redundancy: Ecosystems with multiple species performing similar functions can maintain ecosystem processes even if some species decline or disappear.
Conservation and Restoration of Biodiversity
Conserving and restoring biodiversity is critical for maintaining ecosystem resilience to climate change impacts. Effective conservation strategies can help to protect and promote biodiversity, enhancing ecosystem resilience.
- Protected areas: Establishing protected areas can safeguard biodiversity and ecosystem processes.
- Ecological restoration: Restoring degraded ecosystems can help to recover biodiversity and ecosystem function.
- Sustainable land-use planning: Integrating biodiversity conservation into land-use planning can minimize the impacts of human activities on ecosystems.
What is the effect of reduced biodiversity on the ability of ecosystems to withstand climate extremes?
The effect of reduced biodiversity on the ability of ecosystems to withstand climate extremes is a significant concern. Ecosystems with lower biodiversity are often less resilient to extreme climate events such as droughts, heatwaves, and floods. This is because diverse ecosystems have a wider range of species that can respond differently to changing environmental conditions, thereby providing a buffer against the impacts of climate extremes.
Impact on Ecosystem Services
Reduced biodiversity can impair the functioning of ecosystems, leading to a decline in essential services such as air and water purification, soil formation, and nutrient cycling. When ecosystems are subjected to climate extremes, the loss of these services can have far-reaching consequences for human well-being and the environment. Some of the key ecosystem services that are affected by reduced biodiversity include:
- Disruption of nutrient cycles, leading to decreased fertility and increased pollution
- Loss of pollination services, impacting agricultural productivity and food security
- Decreased water quality, affecting human consumption and aquatic ecosystems
Consequences for Ecosystem Resilience
Ecosystem resilience is the ability of an ecosystem to resist and recover from disturbances, including climate extremes. Reduced biodiversity can erode this resilience, making ecosystems more vulnerable to collapse. The loss of key species can trigger cascading effects throughout the ecosystem, leading to a decline in its overall resilience. Some of the factors that contribute to the decline in ecosystem resilience include:
- The loss of functional redundancy, where the loss of one species cannot be compensated by another
- The disruption of species interactions, such as predator-prey relationships
- The degradation of ecosystem processes, such as primary production and decomposition
Implications for Climate Change Adaptation
The impact of reduced biodiversity on ecosystem resilience has significant implications for climate change adaptation. As climate extremes become more frequent and intense, ecosystems with low biodiversity may be less able to adapt, leading to a decline in their ability to provide essential services. Some of the strategies that can help maintain ecosystem resilience in the face of climate change include:
- Conservation and restoration of habitats to maintain biodiversity
- Assisted migration of species to help them adapt to changing environmental conditions
- Ecosystem-based adaptation approaches that prioritize natural ecosystem processes
What is the impact of biodiversity loss on climate change resilience?
The impact of biodiversity loss on climate change resilience is a complex and multifaceted issue. Biodiversity loss can exacerbate the effects of climate change by reducing the ability of ecosystems to withstand and recover from disturbances, such as droughts, heatwaves, and storms. This is because diverse ecosystems tend to have a wider range of responses to environmental changes, making them more resilient to climate-related stressors.
Ecosystem Services and Biodiversity Loss
Biodiversity loss can disrupt essential ecosystem services that help mitigate the effects of climate change, including carbon sequestration, air and water filtration, and soil formation. For example, the loss of pollinator species can impact agricultural productivity, while the degradation of forests can reduce their ability to act as carbon sinks. Some of the ecosystem services that are affected by biodiversity loss include:
- Carbon sequestration and storage
- Soil formation and nutrient cycling
- Water filtration and regulation
Climate Change Resilience and Ecosystem Stability
The loss of biodiversity can also reduce the stability of ecosystems, making them more vulnerable to climate-related disturbances. This is because diverse ecosystems tend to have a more complex web of interactions between species, which can help to maintain ecosystem function even in the face of environmental changes. For instance, ecosystems with a diverse range of plant species are more likely to be able to recover from droughts and heatwaves. Some of the factors that contribute to ecosystem stability include:
- Species diversity and richness
- Functional diversity and redundancy
- Ecosystem connectivity and fragmentation
Consequences of Biodiversity Loss for Human Societies
The impact of biodiversity loss on climate change resilience also has significant consequences for human societies. For example, the degradation of ecosystems can reduce the availability of natural resources, such as clean water and food, while also increasing the risk of natural disasters and climate-related health impacts. Furthermore, the loss of ecosystem services can also have economic and social impacts, particularly for communities that depend heavily on natural resources for their livelihoods. Some of the consequences of biodiversity loss for human societies include:
- Reduced access to clean water and food
- Increased risk of natural disasters and climate-related health impacts
- Economic and social impacts on communities that depend on natural resources
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the relationship between biodiversity and resilience against climatic extremes?
Biodiversity plays a crucial role in maintaining ecosystem resilience against climatic extremes. Ecosystems with higher biodiversity are better able to withstand and recover from disturbances such as droughts, floods, and heatwaves. The loss of biodiversity can erode this resilience, making ecosystems more vulnerable to the impacts of climate change.
How does declining biodiversity affect ecosystem services during extreme weather events?
Declining biodiversity can significantly impact ecosystem services during extreme weather events. With fewer species, ecosystems are less able to maintain essential services like nutrient cycling, soil formation, and water regulation. This can exacerbate the impacts of extreme weather, leading to increased damage to infrastructure, agriculture, and human settlements. Ecosystem services are also less able to recover after the event.
Can the loss of specific species contribute to reduced resilience against climatic extremes?
Yes, the loss of specific species can significantly contribute to reduced resilience against climatic extremes. Key species, such as pollinators, seed dispersers, or ecosystem engineers, play critical roles in maintaining ecosystem function. Losing these species can create cascading effects, leading to reduced ecosystem resilience and increased vulnerability to climatic extremes.
How can restoring biodiversity help improve resilience to climatic extremes?
Restoring biodiversity can help improve resilience to climatic extremes by reinstating ecosystem processes and services. By reintroducing native species, restoring habitats, and promoting ecological connectivity, ecosystems can regain their ability to withstand and recover from disturbances. This can also enhance ecosystem services, reducing the impacts of extreme weather on human communities and infrastructure.

Leave a Reply