How citizen science programs contribute climate-research data accuracy
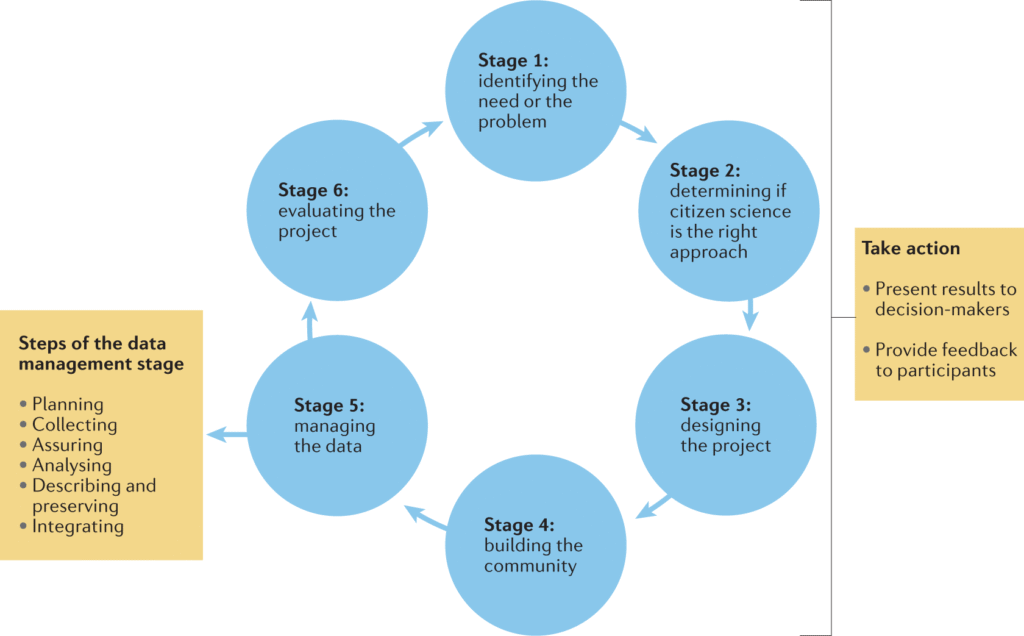
Climate change is one of the most pressing issues of our time, and accurate data is crucial for understanding its impacts and developing effective mitigation strategies. Citizen science programs have emerged as a valuable tool in the fight against climate change, providing a vast amount of data that can be used to inform climate research. By engaging the public in data collection, these programs not only increase the quantity of available data but also contribute to its accuracy, helping to build a more comprehensive picture of our changing climate and its effects on various ecosystems.
- Enhancing Climate Research Data Accuracy through Citizen Science Initiatives
-
Enhancing Climate Research Data Accuracy through Citizen Science Initiatives
- Can citizen science initiatives provide reliable data for climate research?
- Data Collection and Quality Control
- Benefits and Limitations
- Examples and Applications
- What role does citizen science play in enhancing the accuracy of climate research data?
- Citizen Science Data Collection
- Improving Climate Model Accuracy
- Enhancing Community Engagement
- Can crowdsourced environmental data improve the reliability of climate research findings?
- Benefits of Crowdsourced Environmental Data
- Challenges and Limitations of Crowdsourced Environmental Data
- Applications of Crowdsourced Environmental Data in Climate Research
- What metrics assess the effectiveness of citizen science in climate research?
- Data Quality and Accuracy
- Project Reach and Engagement
- Impact on Climate Research and Policy
- Frequently Asked Questions
Enhancing Climate Research Data Accuracy through Citizen Science Initiatives
Citizen science programs have emerged as a vital component in the quest to improve the accuracy of climate-research data. By engaging the public in the collection of environmental data, these initiatives not only expand the scope of data collection but also provide valuable insights that can be used to inform climate models and policy decisions. The integration of citizen science into climate research represents a significant shift towards a more inclusive and comprehensive approach to understanding and addressing climate change.
The Role of Citizen Science in Data Collection
Citizen science initiatives empower individuals and communities to participate in the collection of climate-related data, such as temperature, precipitation, and phenological observations. This not only increases the spatial and temporal resolution of data but also fosters a deeper understanding of local climate conditions. By leveraging the contributions of a diverse group of participants, researchers can gather a more extensive and nuanced dataset that better captures the complexities of climate variability.
| Data Type | Description | Collection Method |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Air temperature readings | Personal weather stations, mobile apps |
| Precipitation | Rainfall and snowfall measurements | Rain gauges, citizen weather stations |
| Phenological observations | Records of plant flowering, animal migrations | Visual observations, camera traps |
Improving Data Accuracy through Validation and Calibration
To ensure the reliability of data collected through citizen science programs, it is crucial to implement robust validation and calibration procedures. This involves comparing citizen-collected data with data from trusted sources, such as official weather stations, to assess accuracy and identify potential biases. By doing so, researchers can develop correction factors and improve the overall quality of the dataset, thereby enhancing its utility for climate research applications.
| Validation Method | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Comparison with official weather stations | Direct comparison of citizen-collected data with official records | Improved accuracy, identification of biases |
| Calibration of equipment | Adjustment of citizen science equipment to match official standards | Enhanced data quality, reduced errors |
| Data cleaning and filtering | Removal of erroneous or inconsistent data points | Increased data reliability, improved model performance |
Empowering Communities through Climate Literacy
Citizen science programs not only contribute to the advancement of climate research but also play a vital role in promoting climate literacy among participants. By engaging with the data collection process, individuals gain a deeper understanding of climate dynamics and the impacts of climate change on their local environment. This, in turn, fosters a sense of ownership and empowerment, encouraging communities to develop and implement effective climate adaptation and mitigation strategies.
| Climate Literacy Outcome | Description | Community Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Understanding of climate change impacts | Awareness of local climate-related issues | Informed decision-making, climate resilience |
| Knowledge of climate mitigation strategies | Familiarity with practices to reduce greenhouse gas emissions | Reduced carbon footprint, sustainable practices |
| Community engagement and action | Participation in climate-related projects and initiatives | Community cohesion, collective action on climate change |
Enhancing Climate Research Data Accuracy through Citizen Science Initiatives
Can citizen science initiatives provide reliable data for climate research?
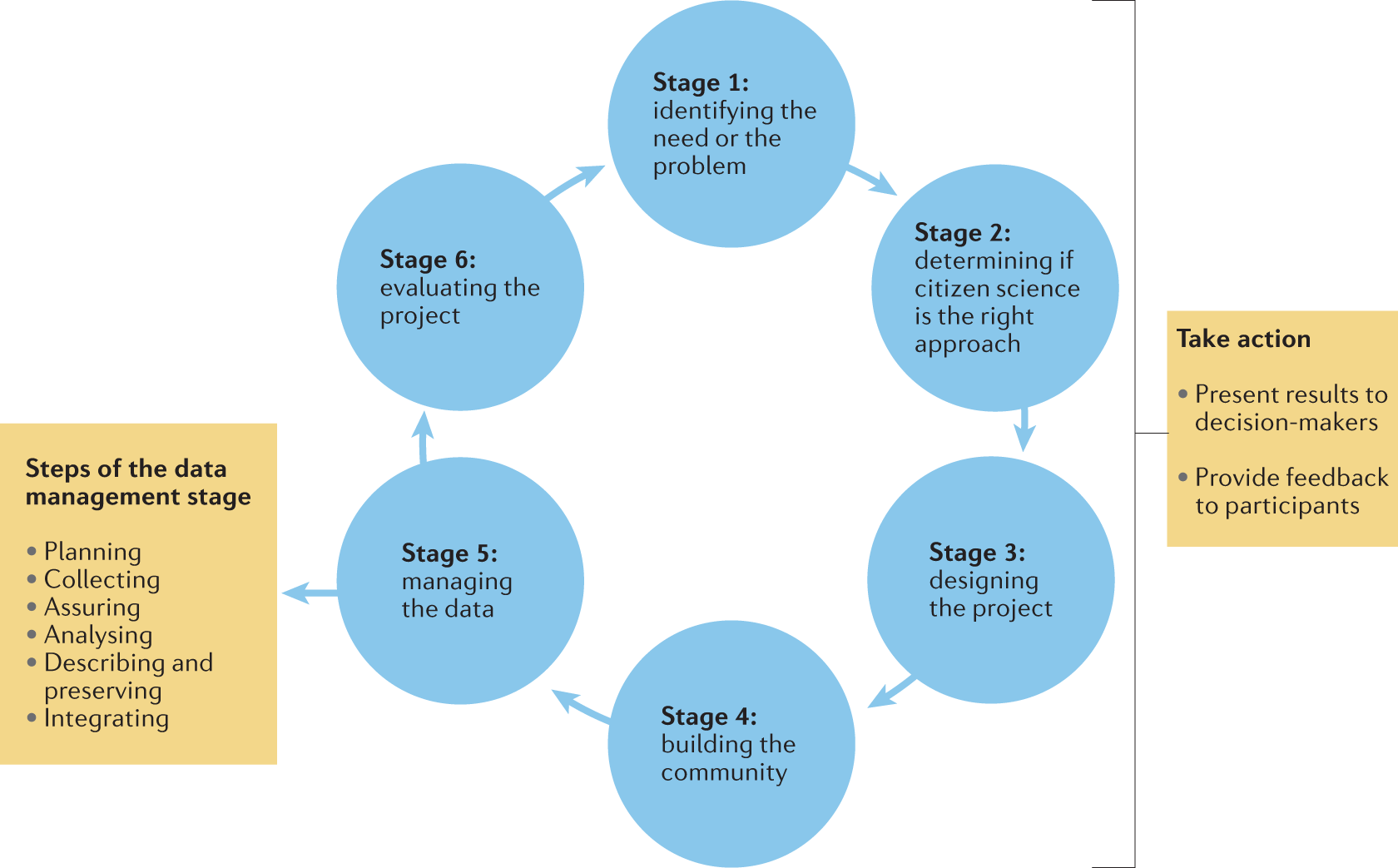
Citizen science initiatives have gained significant attention in recent years for their potential to contribute to climate research. These initiatives involve the participation of non-expert individuals in scientific research, often through the collection and analysis of data. The reliability of data collected through citizen science initiatives is a crucial aspect to consider when evaluating their potential to inform climate research.
Data Collection and Quality Control
Citizen science initiatives can provide reliable data for climate research if proper protocols are put in place to ensure data quality. This includes developing clear guidelines for data collection, providing training to participants, and implementing quality control measures to verify the accuracy of the data.
- Standardized data collection protocols help minimize errors and ensure consistency across different locations and participants.
- Training programs for participants can improve data quality by educating them on the correct methods and procedures.
- Data validation and verification processes can be implemented to detect and correct errors or inconsistencies in the data.
Benefits and Limitations
Citizen science initiatives have several benefits, including the ability to collect large amounts of data over a wide geographic area, increased public engagement and awareness of climate issues, and the potential to provide new insights and perspectives. However, there are also limitations to consider, such as the potential for biases or errors in the data, and the need for careful design and implementation to ensure data quality.
- The large number of participants in citizen science initiatives can provide a high volume of data, which can be particularly useful for climate research that requires large datasets.
- Citizen science initiatives can provide insights into local conditions and phenomena that may not be captured by traditional research methods.
- The involvement of non-expert individuals can introduce biases or errors into the data if not properly addressed through training and quality control measures.
Examples and Applications
There are numerous examples of citizen science initiatives that have contributed to climate research, including projects focused on monitoring weather patterns, tracking changes in ecosystems, and studying the impacts of climate change on human communities. These initiatives demonstrate the potential for citizen science to inform climate research and support decision-making.
- Projects such as the National Weather Service's CoCoRaHS program engage citizens in monitoring precipitation and other weather phenomena.
- Initiatives like the Zooniverse platform provide opportunities for citizens to contribute to a wide range of climate-related research projects.
- Locally-focused citizen science initiatives can provide valuable insights into the impacts of climate change on specific communities or ecosystems.
What role does citizen science play in enhancing the accuracy of climate research data?
Citizen science plays a significant role in enhancing the accuracy of climate research data by providing a vast amount of observational data that can be used to validate and improve climate models. The involvement of citizens in data collection helps to increase the spatial and temporal resolution of climate data, which is essential for understanding local and regional climate phenomena.
Citizen Science Data Collection
Citizen science initiatives enable individuals to participate in data collection, often using simple and low-cost methods, such as reporting weather conditions or observing changes in their local environment. This approach not only increases the quantity of data available but also provides insights into local conditions that may not be captured by traditional monitoring networks.
- Data is collected through various means, including mobile apps and online platforms.
- Participants can report observations on various climate-related phenomena, such as temperature, precipitation, and extreme weather events.
- The collected data is then shared and aggregated, providing a comprehensive picture of climate conditions.
Improving Climate Model Accuracy
The data collected through citizen science initiatives can be used to improve the accuracy of climate models by providing additional information that can be used to validate model outputs. By comparing model predictions with real-world observations, researchers can identify areas where models need improvement and refine their predictions.
- Citizen science data can be used to validate climate model outputs at local and regional scales.
- The integration of citizen science data into climate models can improve their accuracy and reduce uncertainty.
- This, in turn, enables policymakers and stakeholders to make more informed decisions based on more accurate climate information.
Enhancing Community Engagement
Citizen science initiatives not only contribute to the accuracy of climate research data but also enhance community engagement and awareness about climate change. By involving citizens in the data collection process, these initiatives promote a sense of ownership and responsibility among community members, encouraging them to take action to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
- Citizen science initiatives raise awareness about climate change and its local impacts.
- Community members become more engaged in climate-related issues and are more likely to participate in climate mitigation efforts.
- This increased engagement can lead to the development of more effective climate adaptation and mitigation strategies.
Can crowdsourced environmental data improve the reliability of climate research findings?

Crowdsourced environmental data can potentially improve the reliability of climate research findings by providing a large volume of data from diverse sources and locations. The use of crowdsourced data can help to fill gaps in traditional data collection methods, such as satellite or weather station data, which may be limited by their spatial or temporal resolution. By leveraging the collective efforts of a large number of individuals, crowdsourced data can provide a more comprehensive understanding of environmental phenomena.
Benefits of Crowdsourced Environmental Data
Crowdsourced environmental data offers several benefits for climate research, including increased spatial and temporal resolution, improved data accuracy, and enhanced community engagement. The use of crowdsourced data can also facilitate the collection of data in areas that are difficult or impossible to access using traditional methods. Some of the key advantages of crowdsourced environmental data include:
- the ability to collect data in real-time, allowing for more timely and responsive research
- the potential for increased data accuracy through the use of multiple data sources and validation techniques
- the opportunity for community members to participate in the research process, promoting education and awareness about climate-related issues
Challenges and Limitations of Crowdsourced Environmental Data
While crowdsourced environmental data has the potential to improve the reliability of climate research findings, there are also several challenges and limitations to be considered. Some of the key challenges include ensuring the accuracy and quality of the data, addressing issues related to data standardization and interoperability, and managing the large volumes of data generated through crowdsourcing. Some of the key challenges and limitations of crowdsourced environmental data include:
- the potential for data quality issues due to variations in measurement techniques or equipment
- the need for robust data validation and quality control processes to ensure data accuracy
- the importance of developing effective data management strategies to handle large volumes of data
Applications of Crowdsourced Environmental Data in Climate Research
Crowdsourced environmental data has a range of potential applications in climate research, including the study of climate-related phenomena such as temperature, precipitation, and extreme weather events. The use of crowdsourced data can also facilitate the development of more accurate climate models and improve our understanding of climate-related impacts on ecosystems and human societies. Some of the key applications of crowdsourced environmental data in climate research include:
- the use of crowdsourced data to validate climate models and improve their accuracy
- the application of crowdsourced data to study climate-related impacts on ecosystems and human societies
- the potential for crowdsourced data to inform climate change mitigation and adaptation strategies
What metrics assess the effectiveness of citizen science in climate research?
The effectiveness of citizen science in climate research can be assessed through various metrics that evaluate its impact, quality, and reach. These metrics help in understanding how citizen science projects contribute to climate research and identify areas for improvement.
Data Quality and Accuracy
The quality and accuracy of data collected through citizen science projects are crucial in determining their effectiveness in climate research. High-quality data is essential for making reliable conclusions and informing policy decisions. The accuracy of citizen science data can be assessed by comparing it with data collected through traditional methods.
- Validation of citizen science data against professional datasets
- Use of standardized protocols and training for citizen scientists
- Implementation of quality control measures
Project Reach and Engagement
The reach and engagement of citizen science projects are important metrics for assessing their effectiveness. A project's ability to engage a large and diverse group of participants can increase its impact and contribute to a broader understanding of climate issues. Metrics such as the number of participants, geographic coverage, and level of participation can be used to evaluate a project's reach and engagement.
- Number of participants and their demographic characteristics
- Geographic distribution of participants and data collection points
- Level of participation and retention rate among participants
Impact on Climate Research and Policy
The ultimate measure of the effectiveness of citizen science in climate research is its impact on our understanding of climate issues and the development of climate policies. Citizen science projects can contribute to climate research by providing new insights, validating models, and informing policy decisions.
- Publication of citizen science data in peer-reviewed journals
- Influence on climate policy and decision-making processes
- Contribution to the development of new research questions and hypotheses
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of citizen science in climate research?
Citizen science programs play a significant role in climate research by providing valuable data that enhances the understanding of climate change. Volunteers collect and analyze data on various climate-related parameters, such as temperature, precipitation, and weather patterns, which helps researchers to identify trends and patterns. This data is often used to validate and improve climate models.
How do citizen science programs contribute to climate-research data accuracy?
Citizen science programs contribute to climate-research data accuracy by providing large datasets that are often difficult or expensive to collect through traditional research methods. The data collected by citizens is typically validated and quality-controlled, ensuring its accuracy and reliability. This data is then used to improve climate models, validate satellite data, and monitor climate-related phenomena.
What are the benefits of involving citizens in climate research?
Involving citizens in climate research has several benefits, including increased data collection, improved data accuracy, and enhanced community engagement. Citizen science programs also provide opportunities for education and outreach, raising awareness about climate change and its impacts. By engaging citizens in the research process, scientists can gain a better understanding of local climate-related issues and develop more effective solutions.
Can citizen science data be trusted for climate research?
Yes, citizen science data can be trusted for climate research if it is properly collected, validated, and quality-controlled. Many citizen science programs implement robust data collection protocols and quality control measures to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data. Researchers also often validate citizen science data against other data sources to ensure its consistency and accuracy, making it a valuable resource for climate research.

Leave a Reply