How air pollution exacerbates climate change and respiratory illnesses
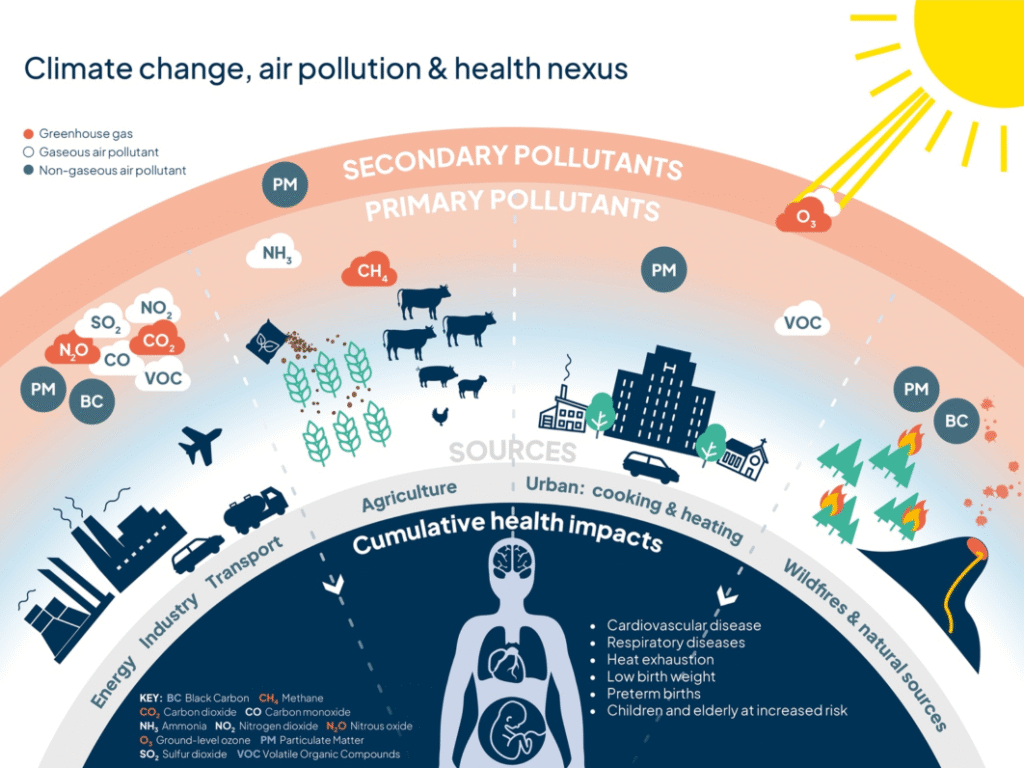
The increasing levels of air pollution have become a pressing concern globally, posing significant threats to both the environment and human health. As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change, the role of air pollution in exacerbating this phenomenon and its impact on respiratory illnesses cannot be overstated. The complex interplay between air pollution, climate change, and respiratory health is multifaceted, involving a range of pollutants and mechanisms that contribute to adverse health outcomes and environmental degradation. Understanding this relationship is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate these issues.
- The Devastating Consequences of Air Pollution on Climate Change and Respiratory Health
-
The Interconnected Threats of Air Pollution: Understanding its Impact on Climate Change and Respiratory Health
- What is the link between air pollution and the rise in respiratory diseases?
- Sources of Air Pollution
- Health Impacts of Air Pollution
- Mitigating the Effects of Air Pollution
- 'What is the impact of climate change on air quality?'
- Impact on Particulate Matter and Ozone Formation
- Effects on Atmospheric Circulation and Pollutant Dispersal
- Consequences for Human Health and Ecosystems
- 'How does air pollution impact respiratory health?'
- Short-term Effects on Respiratory Health
- Long-term Consequences for Respiratory Health
- Vulnerable Populations and Preventive Measures
- Frequently Asked Questions
The Devastating Consequences of Air Pollution on Climate Change and Respiratory Health
Air pollution is a pressing global issue that not only affects the environment but also has severe implications for human health. The release of pollutants into the atmosphere contributes to climate change and exacerbates respiratory illnesses, making it a critical concern that requires immediate attention. The intricate relationship between air pollution, climate change, and respiratory health is complex, involving various factors and pathways that ultimately lead to adverse outcomes.
Impact on Climate Change
The impact of air pollution on climate change is multifaceted. Certain pollutants, such as black carbon and methane, are potent greenhouse gases that contribute significantly to global warming. These pollutants not only accelerate climate change but also have a profound impact on atmospheric conditions, influencing weather patterns and leading to more extreme climate events. Understanding the role of air pollution in climate change is essential for developing effective mitigation strategies.
Exacerbating Respiratory Illnesses
Air pollution is a major risk factor for respiratory illnesses, including asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The inhalation of pollutants such as particulate matter (PM), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and ozone (O3) can cause inflammation and damage to the lungs, leading to respiratory problems. The most vulnerable populations, including children, the elderly, and those with pre-existing health conditions, are disproportionately affected by poor air quality.
Key Pollutants and Their Effects
Several key pollutants are associated with adverse health and environmental outcomes. Particulate matter (PM) is particularly harmful, as it can penetrate deep into the lungs, causing inflammation and damage. Other pollutants, such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and sulfur dioxide (SO2), also have significant impacts on air quality and health. Understanding the sources and effects of these pollutants is crucial for developing effective air quality management strategies.
| Pollutant | Health Effects | Environmental Impacts |
|---|---|---|
| Particulate Matter (PM) | Respiratory problems, cardiovascular disease | Reduced visibility, climate change |
| Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) | Respiratory problems, asthma | Contributes to ground-level ozone formation |
| Ozone (O3) | Respiratory problems, lung damage | Damages crops, vegetation |
The Interconnected Threats of Air Pollution: Understanding its Impact on Climate Change and Respiratory Health
What is the link between air pollution and the rise in respiratory diseases?
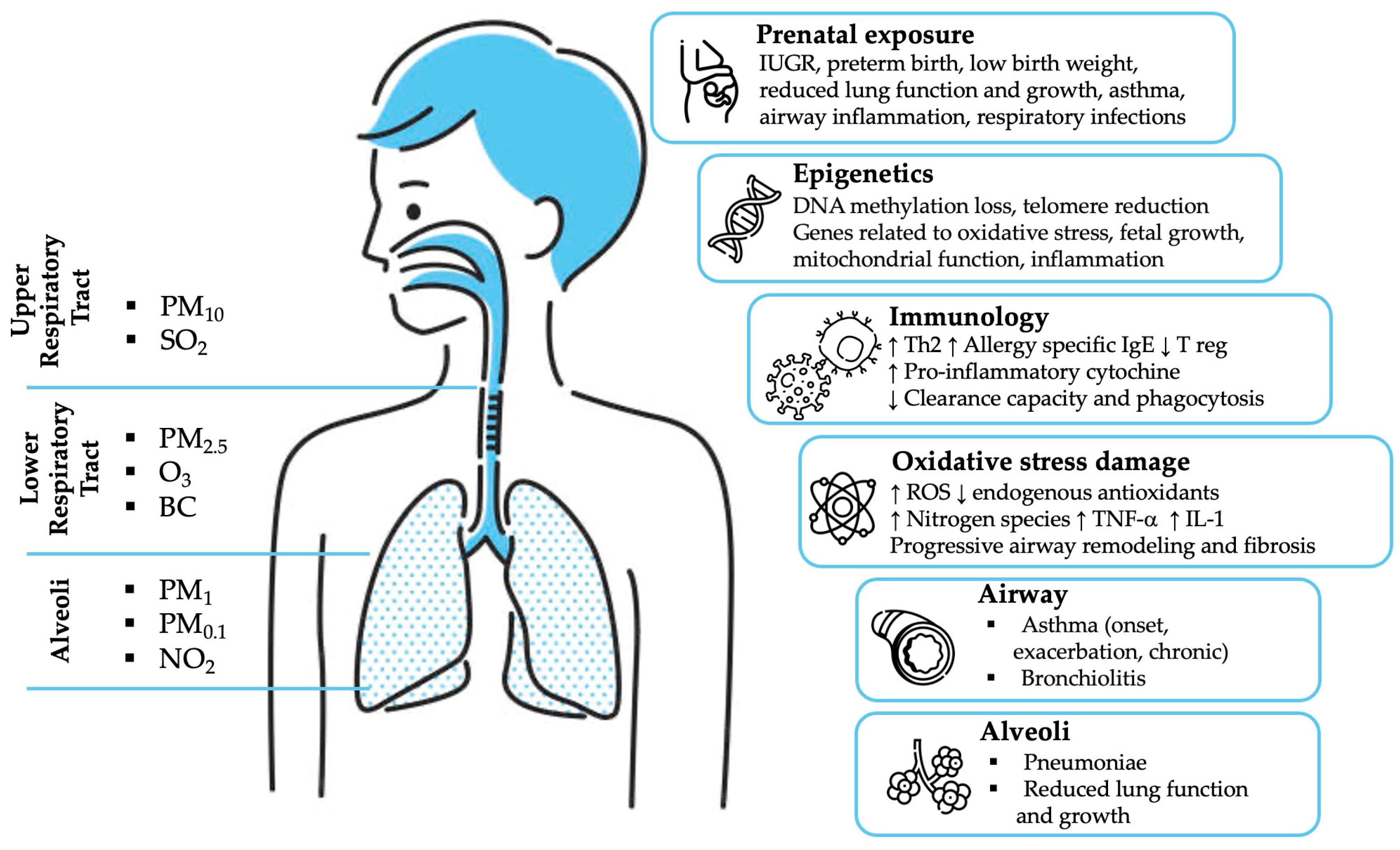
The link between air pollution and the rise in respiratory diseases is a significant concern globally. Air pollution is known to have severe impacts on human health, particularly on the respiratory system. The pollutants present in the air can cause a range of health problems, from mild irritation to serious diseases.
Sources of Air Pollution
The primary sources of air pollution are emissions from vehicles, industrial activities, and the burning of fossil fuels. These sources release a variety of pollutants into the atmosphere, including particulate matter (PM), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), ozone (O3), and sulfur dioxide (SO2). The effects of these pollutants on respiratory health can be significant, contributing to conditions such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Some of the key factors include:
- Emissions from vehicles, which release NO2 and PM into the atmosphere.
- Industrial activities, which can release a range of pollutants, including SO2 and PM.
- The burning of fossil fuels for energy, which releases pollutants such as NO2 and SO2.
Health Impacts of Air Pollution
The health impacts of air pollution are far-reaching, with significant effects on the respiratory system. Exposure to poor air quality can exacerbate existing respiratory conditions and contribute to the development of new ones. The pollutants in the air can irritate the lungs, throat, and airways, making it difficult to breathe. Some of the specific health impacts include:
- Increased risk of respiratory diseases, such as asthma and COPD.
- Irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat due to pollutants in the air.
- Reduced lung function, making it harder for the body to take in oxygen.
Mitigating the Effects of Air Pollution
To mitigate the effects of air pollution on respiratory health, a range of strategies can be implemented. These include reducing emissions from vehicles and industrial activities, increasing energy efficiency, and promoting the use of cleaner energy sources. Individuals can also take steps to protect themselves, such as avoiding heavily polluted areas and using air purifiers in their homes. Some of the key measures include:
- Implementing policies to reduce emissions from vehicles and industrial activities.
- Promoting the use of cleaner energy sources, such as solar and wind power.
- Encouraging individuals to take steps to protect themselves from air pollution.
'What is the impact of climate change on air quality?'

Climate change has a significant impact on air quality, as it can lead to increased levels of air pollutants and altered atmospheric conditions that affect the formation and dispersal of pollutants. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events all play a role in shaping air quality.
Impact on Particulate Matter and Ozone Formation
Climate change can lead to increased levels of particulate matter (PM) in the air, which is a major concern for human health. Warmer temperatures can increase the formation of ground-level ozone, a key component of smog, by accelerating the chemical reactions that form ozone. This can be particularly problematic in urban areas, where high population densities and emissions from vehicles and industrial activities already contribute to poor air quality. Some of the key factors that contribute to increased PM and ozone formation include:
- Increased temperatures, which can accelerate chemical reactions that form ozone and PM
- Changes in precipitation patterns, which can lead to droughts and increased wildfires that produce PM
- Increased frequency of heatwaves, which can exacerbate ozone formation and increase mortality
Effects on Atmospheric Circulation and Pollutant Dispersal
Climate change can also affect atmospheric circulation patterns, which can influence the dispersal of air pollutants. Changes in wind patterns, temperature gradients, and other atmospheric conditions can alter the transport and deposition of pollutants, potentially leading to increased concentrations in some areas. For example, changes in wind patterns can cause pollutants to become trapped in valleys or basins, leading to poor air quality. Some of the key factors that contribute to changes in atmospheric circulation and pollutant dispersal include:
- Changes in wind patterns, which can alter the transport of pollutants
- Shifts in temperature gradients, which can influence the formation of temperature inversions that trap pollutants
- Changes in atmospheric stability, which can affect the vertical mixing of pollutants
Consequences for Human Health and Ecosystems
The impact of climate change on air quality has significant consequences for human health and ecosystems. Poor air quality can exacerbate respiratory diseases, such as asthma, and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. Climate change can also affect ecosystems by altering the distribution and abundance of plants and animals, and by changing the chemistry of soils and waters. Some of the key consequences of climate change on air quality include:
- Increased mortality and morbidity due to poor air quality
- Impacts on agricultural productivity and food security
- Changes in ecosystem function and biodiversity
'How does air pollution impact respiratory health?'

Air pollution is a significant environmental risk factor that affects respiratory health in various ways. The impact of air pollution on respiratory health is multifaceted and can be detrimental, as it can exacerbate existing respiratory conditions, trigger new ones, and even affect lung development in children. The primary pollutants that affect respiratory health include particulate matter (PM), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), ozone (O3), and sulfur dioxide (SO2), which can come from various sources such as industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, and natural events like wildfires.
Short-term Effects on Respiratory Health
Exposure to poor air quality over a short period can have immediate and noticeable effects on respiratory health. For individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions like asthma, short-term exposure to air pollutants can trigger symptoms such as wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath. The mechanisms behind these effects involve inflammation and irritation of the airways.
- Increased respiratory rate and depth due to irritation of the lungs.
- Triggering of asthma attacks and exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) symptoms.
- Inflammation of the airways, which can lead to increased mucus production and airway constriction.
Long-term Consequences for Respiratory Health
Prolonged exposure to air pollution is associated with more severe and chronic impacts on respiratory health. Long-term exposure can lead to the development of chronic respiratory diseases and can reduce lung function. The chronic inflammation and oxidative stress caused by continuous exposure to pollutants contribute to the pathogenesis of diseases like COPD and lung cancer.
- Development of chronic respiratory diseases such as COPD and chronic bronchitis.
- Reduced lung function and lung growth in children and adolescents.
- Increased risk of developing lung cancer due to long-term exposure to carcinogenic pollutants.
Vulnerable Populations and Preventive Measures
Certain populations are more vulnerable to the adverse effects of air pollution on respiratory health. These include children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing heart or lung conditions. Understanding the risks and taking preventive measures can mitigate some of the negative impacts.
- Avoiding heavily polluted areas and reducing outdoor activities during peak pollution times.
- Using air purifiers indoors to reduce exposure to indoor pollutants.
- Supporting policies and practices that reduce emissions and improve air quality.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the relationship between air pollution and climate change?
Air pollution and climate change are closely linked. Pollutants like carbon dioxide, methane, and black carbon contribute to global warming, while climate change in turn exacerbates air pollution by increasing the formation of ground-level ozone and particulate matter. This vicious cycle accelerates climate change and worsens air quality, posing significant threats to human health and the environment.
How does air pollution affect respiratory health?
Air pollution significantly impacts respiratory health by irritating the lungs, exacerbating conditions like asthma, and increasing the risk of respiratory infections. Pollutants like particulate matter, nitrogen dioxide, and ozone can penetrate deep into the lungs, causing inflammation and damage. Long-term exposure can lead to chronic respiratory diseases, reduced lung function, and increased mortality rates, particularly among vulnerable populations like children and the elderly.
What are the primary air pollutants that contribute to climate change?
The primary air pollutants that contribute to climate change include carbon dioxide, methane, black carbon, and nitrous oxide. These pollutants trap heat in the atmosphere, driving global warming. Carbon dioxide is the most prevalent, resulting from fossil fuel combustion and deforestation. Methane and black carbon have significant warming potentials, while nitrous oxide is a potent greenhouse gas emitted by industrial processes and agriculture.
Can reducing air pollution mitigate climate change?
Reducing air pollution can significantly mitigate climate change. By decreasing emissions of pollutants like carbon dioxide, methane, and black carbon, we can slow global warming. Strategies like transitioning to cleaner energy sources, increasing energy efficiency, and implementing emission controls can simultaneously improve air quality and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, yielding co-benefits for both climate change and public health.

Leave a Reply