How wildlife migration shifts indicate changing climate zones

The migration patterns of various wildlife species have long fascinated scientists and naturalists alike, offering a glimpse into the intricate relationships between animals and their environments. As the planet continues to warm due to climate change, these migration patterns are shifting in response, providing a crucial indicator of the far-reaching impacts of global warming. Changes in the timing, route, or destination of wildlife migrations signal broader alterations to ecosystems and climate zones, highlighting the need for a deeper understanding of these changes to inform conservation efforts and predict future environmental shifts.
- Understanding the Impact of Climate Change on Wildlife Migration Patterns
-
Tracking Climate Zone Shifts through Wildlife Migration Patterns
- What impact will climate change have on the patterns of animal migration worldwide?
- Changes in Migration Timing
- Shifts in Migration Routes
- Impacts on Migration Success
- What role does climate change play in altering animal migration patterns?
- Shifts in Migration Timing
- Changes in Migration Routes
- Impacts on Migration Success
- How do shifts in wildlife migration patterns reflect changes in climate zones?
- Changes in Temperature and Precipitation Patterns
- Impact on Migratory Species
- Consequences for Ecosystems
- What role do changes in wildlife migration patterns play in indicating climate zone shifts?
- Impacts on Migration Timing
- Shifts in Migration Routes
- Consequences for Ecosystems
- Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding the Impact of Climate Change on Wildlife Migration Patterns
The migration patterns of various wildlife species are significantly influenced by environmental factors, including temperature, precipitation, and the availability of food resources. As the global climate continues to change, many species are altering their migration routes, timing, and behaviors in response to these shifts. This phenomenon serves as a critical indicator of the broader impacts of climate change on ecosystems around the world.
Changes in Migration Timing
Many species are adjusting the timing of their migrations in response to changing environmental conditions. For example, some bird species are migrating earlier in the spring or later in the fall as temperatures rise and seasonal patterns shift. This can have cascading effects on ecosystems, as mismatches between the timing of migration and the availability of food resources can impact the survival and reproductive success of these species. Changes in phenology, or the study of the timing of biological events, can provide valuable insights into the impacts of climate change on wildlife populations.
| Species | Change in Migration Timing | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Red Knot | Earlier spring migration | Mismatch with food availability |
| Caribou | Later fall migration | Impact on breeding success |
Shifts in Migration Routes
As climate zones shift poleward and to higher elevations, some species are altering their migration routes in response. This can involve changes in the geographic distribution of species, as well as the creation of new migration corridors. For example, some species are shifting their ranges northward in response to warming temperatures, leading to changes in community composition and potentially altering ecosystem processes. Understanding these changes is essential for predicting the impacts of climate change on biodiversity.
| Species | Change in Migration Route | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Gray Whale | Shift in migration route due to sea ice loss | Changes in feeding patterns |
| Songbirds | Northward shift in migration route | Impact on community composition |
Consequences for Ecosystem Resilience
The changes in wildlife migration patterns have significant implications for ecosystem resilience and biodiversity. As species adjust their migration behaviors, they may be more vulnerable to predators, competitors, or other environmental stressors. Furthermore, changes in migration patterns can have cascading effects on ecosystem processes, such as nutrient cycling and primary production. Understanding these impacts is critical for developing effective conservation strategies and promoting ecosystem resilience in the face of climate change.
| Ecosystem Process | Impact of Changes in Migration Patterns | Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrient Cycling | Changes in nutrient deposition | Impact on primary production |
| Predator-Prey Dynamics | Changes in predator-prey interactions | Impact on ecosystem stability |
Tracking Climate Zone Shifts through Wildlife Migration Patterns
What impact will climate change have on the patterns of animal migration worldwide?

Climate change is anticipated to significantly alter the patterns of animal migration worldwide. Rising temperatures, changes in precipitation patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events will disrupt the delicate timing and routes of migratory species. Many animals migrate to take advantage of seasonal food sources, breed, or escape harsh weather conditions. As climate change alters these conditions, it is expected that many migratory species will need to adjust their migration patterns to adapt.
Changes in Migration Timing
Changes in temperature and daylight hours are prompting many migratory species to alter their migration timing. Some species are migrating earlier or later than they used to, which can disrupt their synchronization with the timing of seasonal food sources or breeding seasons.
- Warmer temperatures are causing some species to migrate earlier in the spring, which can lead to mismatches between the timing of their arrival and the availability of food resources.
- Changes in daylight hours are also affecting the migration timing of some species, as some animals rely on daylight cues to trigger their migration.
- This can have cascading effects on ecosystems, as changes in the timing of one species' migration can impact the populations of other species that rely on them as a food source.
Shifts in Migration Routes
Climate change is also expected to cause shifts in the migration routes of many species. As temperatures rise, some areas that were previously too cold for certain species to inhabit during certain times of the year are becoming more hospitable.
- Some species are shifting their migration routes poleward, as warmer temperatures make it possible for them to survive in areas that were previously too cold.
- Changes in sea ice coverage are also altering the migration routes of some marine species, as they adapt to the changing availability of sea ice.
- This can lead to increased competition for resources in the new habitats, as well as potential conflicts with other species that already inhabit those areas.
Impacts on Migration Success
The impacts of climate change on animal migration patterns can have significant effects on the overall success of migrations. As species struggle to adapt to changing environmental conditions, many are facing increased mortality rates during migration.
- Changes in weather patterns are leading to increased frequency and severity of storms, which can be deadly for migratory species.
- Warmer temperatures are also altering the distribution of disease and parasites, which can have significant impacts on the health of migratory species.
- Human activities such as habitat destruction and fragmentation can further exacerbate the challenges faced by migratory species, making it more difficult for them to adapt to climate change.
What role does climate change play in altering animal migration patterns?

Climate change is significantly altering animal migration patterns worldwide. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events are disrupting the delicate timing and routes of many migratory species. As a result, many animals are adjusting their migration patterns to adapt to the new environmental conditions.
Shifts in Migration Timing
Changes in temperature and daylight patterns are causing many migratory species to alter their migration timing. Some species are migrating earlier or later than they used to, while others are changing the duration of their migration. This can have significant impacts on the species' ability to adapt to changing environmental conditions.
- Warmer temperatures are causing some species to migrate earlier in the spring, potentially disrupting their synchronization with food sources.
- Changes in daylight patterns are affecting the migratory cues for some species, leading to changes in their migration timing.
- Some species are adjusting their migration timing to avoid extreme weather events, such as heatwaves or droughts.
Changes in Migration Routes
Climate change is also causing many migratory species to alter their migration routes. As environmental conditions change, some species are finding their traditional migration routes less hospitable, and are instead migrating to new areas. This can lead to changes in the distribution of species and potentially alter the composition of ecosystems.
- Rising sea levels and changes in ocean circulation patterns are altering the migration routes of some marine species.
- Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns are causing some species to migrate to higher elevations or latitudes.
- Some species are shifting their migration routes to avoid areas with increased human activity or habitat destruction.
Impacts on Migration Success
The changes in animal migration patterns caused by climate change can have significant impacts on the success of migrations. Many species rely on specific environmental cues and conditions to successfully complete their migrations, and changes in these conditions can lead to reduced migration success.
- Changes in food availability and quality can impact the energy reserves of migratory species, making it more difficult for them to complete their migrations.
- Increased frequency of extreme weather events can directly impact migratory species, causing mortality or displacement.
- Changes in habitat quality and availability can affect the ability of migratory species to stopover and refuel during their migrations.
How do shifts in wildlife migration patterns reflect changes in climate zones?

Shifts in wildlife migration patterns are a significant indicator of changes in climate zones. As global temperatures rise and climate conditions alter, many species are being forced to adapt their migratory routes and schedules. This can be seen in various parts of the world where changes in temperature and precipitation patterns are affecting the availability of food, breeding grounds, and habitats for numerous species. The changes in migration patterns can be attributed to the alterations in the timing of seasonal events, such as the onset of spring or the duration of summer, which are critical for many migratory species.
Changes in Temperature and Precipitation Patterns
Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns are significantly influencing the migration patterns of wildlife. Warmer temperatures are causing plants to bloom earlier, and altering the distribution of insects and other invertebrates that are crucial food sources for many migratory species.
- The timing of seasonal events is being disrupted, affecting the synchronization between migratory species and their food sources.
- Rising temperatures are altering the distribution of habitats, forcing some species to migrate further or to different areas in search of suitable living conditions.
- Changes in precipitation patterns are affecting the quality and availability of habitats along migration routes.
Impact on Migratory Species
Migratory species are particularly vulnerable to changes in climate zones because their survival depends on the timely availability of food and suitable habitats along their migration routes. Changes in climate conditions can disrupt the delicate timing of their migrations, potentially leading to mismatches between the species' needs and the availability of resources.
- Many migratory species are shifting their migration timing to adapt to changing climate conditions.
- Some species are altering their migration routes in response to changes in habitat distribution and quality.
- The population sizes of some migratory species are declining due to their inability to adapt to the changing climate.
Consequences for Ecosystems
The shifts in wildlife migration patterns not only affect the species themselves but also have broader implications for the ecosystems they inhabit. Changes in the distribution and abundance of migratory species can alter the structure and function of ecosystems, potentially leading to cascading effects on other species and ecosystem processes.
- Changes in the populations of migratory species can impact predator-prey dynamics and nutrient cycling in ecosystems.
- The loss of migratory species can lead to reduced ecosystem resilience and biodiversity.
- Ecosystems that rely on migratory species for seed dispersal, pollination, or other ecological functions may be particularly vulnerable to changes in migration patterns.
What role do changes in wildlife migration patterns play in indicating climate zone shifts?
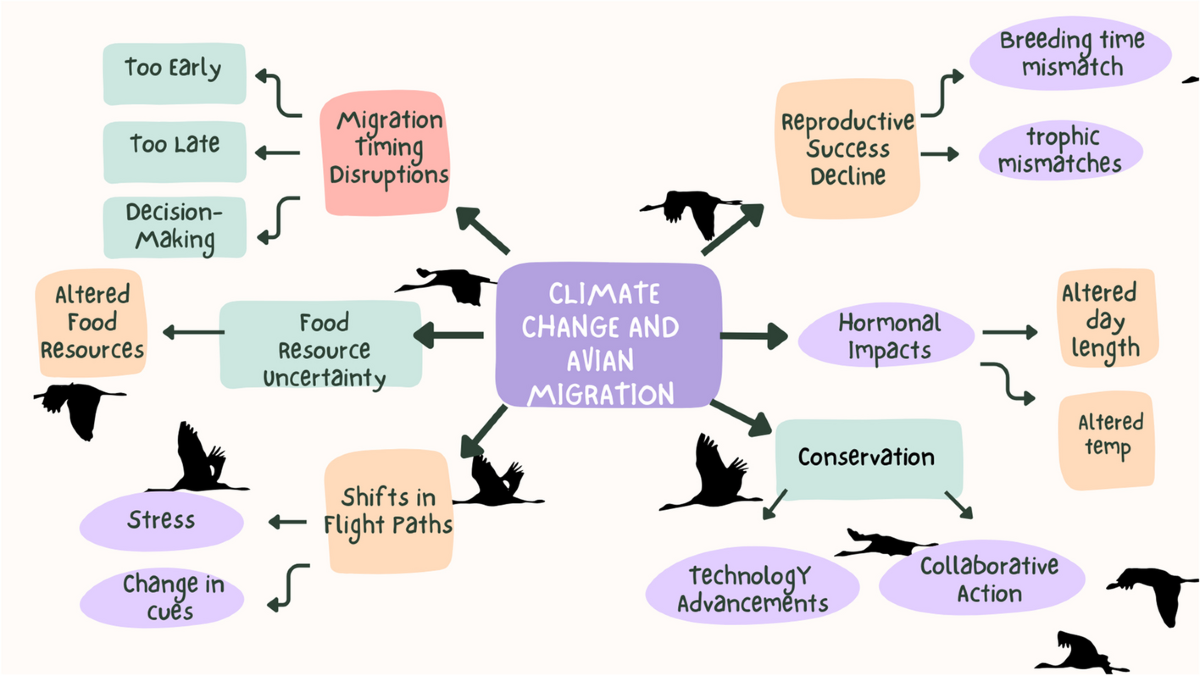
Changes in wildlife migration patterns play a significant role in indicating climate zone shifts. As the climate continues to change, many species are being forced to adapt their migration routes and schedules in response to shifting temperature and precipitation patterns. This can be seen in various parts of the world, where changes in the timing and duration of migrations are being observed.
Impacts on Migration Timing
Changes in migration timing are one of the most noticeable effects of climate change on wildlife migration patterns. Many species are shifting their migration schedules in response to changes in temperature and daylight hours. For example, some bird species are arriving at their breeding grounds earlier in the spring, while others are delaying their departure from their wintering grounds. Some key aspects of migration timing that are being affected by climate change include:
- Changes in the timing of seasonal events, such as flowering and leafing, which can disrupt the synchronization between migratory species and their food sources.
- Shifts in the duration of stopover sites, where migratory species rest and refuel during their journeys.
- Alterations in the phenology of migratory species, such as changes in breeding and molting schedules.
Shifts in Migration Routes
Climate change is also driving changes in the migration routes used by various species. As temperatures and precipitation patterns shift, some areas that were previously suitable for migration are becoming less hospitable, while others are becoming more attractive. This is leading to changes in the distribution and abundance of migratory species, as they adapt to the new climate conditions. Some key factors influencing changes in migration routes include:
- Changes in the availability of food and water resources along migration routes.
- Shifts in the distribution of predators and competitors, which can affect the safety and success of migratory species.
- Alterations in the topography and habitat characteristics of migration routes, such as changes in sea level and vegetation cover.
Consequences for Ecosystems
The changes in wildlife migration patterns have significant consequences for ecosystems. As migratory species shift their migration routes and schedules, they can alter the dynamics of the ecosystems they interact with. This can lead to changes in population sizes, community composition, and ecosystem processes. Some potential consequences of changes in wildlife migration patterns for ecosystems include:
- Changes in nutrient cycling and seed dispersal patterns, as migratory species play important roles in these processes.
- Shifts in predator-prey dynamics, as changes in migration patterns can affect the availability of prey species.
- Alterations in the structure and function of ecosystems, as migratory species play important roles in shaping their environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are wildlife migration shifts?
Wildlife migration shifts refer to changes in the timing, route, or distance of animal migrations in response to environmental cues. As climate zones change, many species are altering their migration patterns to adapt to new temperature and precipitation regimes. This can be seen in changes to bird migration routes, fish migration timing, and the movement patterns of terrestrial animals.
How do wildlife migration shifts indicate changing climate zones?
Wildlife migration shifts can serve as indicators of changing climate zones because many species are sensitive to temperature and precipitation changes. As climate zones shift, animals may alter their migration patterns to track suitable habitats, food sources, or breeding grounds. By monitoring these changes, scientists can infer shifts in climate zones and assess the impacts on ecosystems.
What are the consequences of wildlife migration shifts?
The consequences of wildlife migration shifts can be far-reaching, affecting not only the migrating species but also the ecosystems they interact with. Changes to migration patterns can disrupt food webs, alter species interactions, and impact human livelihoods that depend on wildlife. For example, changes to bird migration patterns can affect pest control and pollination services.
Can wildlife migration shifts be used to predict future climate change impacts?
Yes, wildlife migration shifts can be used to predict future climate change impacts. By analyzing changes to migration patterns and linking them to climate drivers, scientists can develop models that forecast potential future changes. This information can be used to inform conservation efforts and develop strategies to mitigate the impacts of climate change on ecosystems and human communities.

Leave a Reply