How equitable development ensures climate justice outcomes
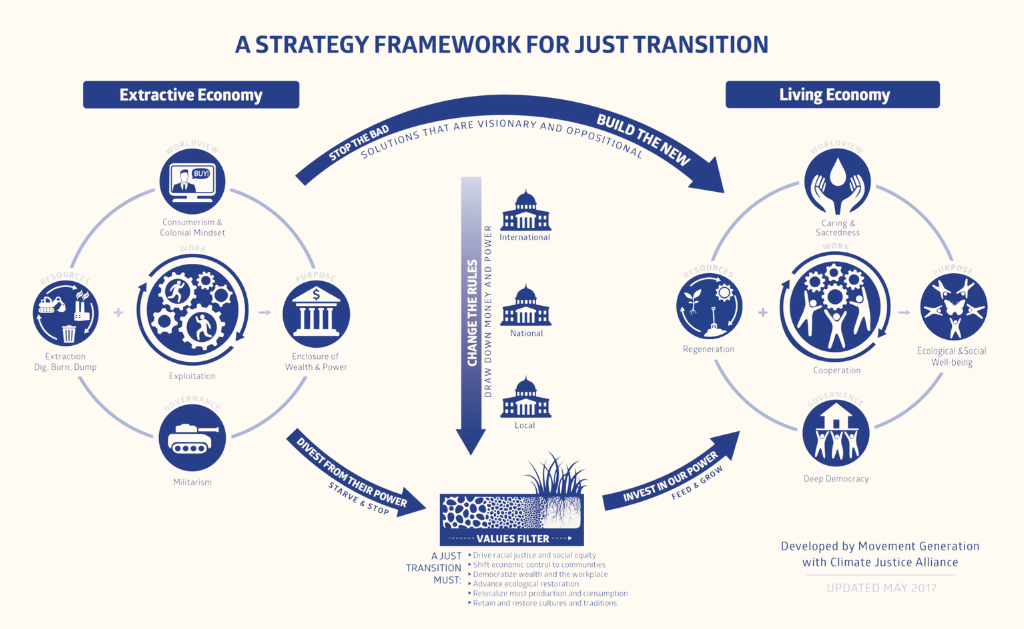
The escalating climate crisis has underscored the need for a more nuanced understanding of its far-reaching impacts, particularly on vulnerable populations. As the world grapples with rising temperatures and associated disasters, the concept of climate justice has gained prominence. At its core, climate justice seeks to address the disproportionate effects of climate change on marginalized communities. Equitable development is increasingly seen as a crucial strategy for achieving climate justice outcomes by ensuring that the benefits and burdens of development are shared fairly, thereby fostering resilience and adaptive capacity among the most vulnerable.
- Ensuring Climate Justice through Equitable Development
-
Achieving Climate Justice through Equitable Development Strategies
- 'What role does equitable development play in achieving climate justice through climate action?'
- Addressing Existing Inequalities
- Promoting Inclusive Decision-Making
- Fostering Climate-Resilient Economies
- What role does equitable development play in achieving climate justice?
- Addressing Disproportionate Impacts on Vulnerable Populations
- Promoting Climate-Resilient Development Pathways
- Fostering International Cooperation and Climate Governance
- What role do equitability and environmental justice play in achieving sustainable development and climate justice outcomes?
- Integration with Sustainable Development Goals
- Addressing Climate Change through Environmental Justice
- Promoting Equitability in Climate Finance
- What role does climate justice play in addressing global inequality?
- Disproportionate Impact on Vulnerable Populations
- Addressing Historical Injustices
- Promoting Equitable Climate Action
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is equitable development and how does it relate to climate justice?
- How does equitable development ensure climate justice outcomes?
- What are the key elements of equitable development in the context of climate justice?
- Why is equitable development critical for achieving long-term climate justice?
Ensuring Climate Justice through Equitable Development
Equitable development is crucial in achieving climate justice outcomes as it addresses the disproportionate impact of climate change on vulnerable populations. By prioritizing equity, development efforts can reduce the gap between the haves and have-nots, ensuring that everyone has access to resources and opportunities necessary to adapt to the changing climate. This approach not only promotes social justice but also fosters resilience and sustainability in the face of climate-related challenges. Climate justice is about recognizing the historical and ongoing injustices that have led to the current climate crisis and taking corrective measures to address them.
Addressing Disproportionate Impacts
The effects of climate change are not evenly distributed, with the poor and marginalized communities bearing the brunt of its impacts. Equitable development seeks to address these disparities by focusing on the needs of the most vulnerable populations. This includes investing in climate-resilient infrastructure, supporting climate-resilient agriculture, and providing access to climate information and early warning systems. By doing so, equitable development helps to reduce the vulnerability of communities to climate-related shocks and stresses.
Promoting Inclusive Decision-Making
Equitable development also involves promoting inclusive decision-making processes that give a voice to all stakeholders, particularly those who are often marginalized or excluded. This includes ensuring that the needs and concerns of local communities are taken into account in the development of climate policies and projects. By doing so, equitable development helps to build trust and foster cooperation among different stakeholders, leading to more effective and sustainable climate outcomes. Inclusive decision-making is critical in ensuring that climate actions are equitable and just.
Fostering Climate-Resilient Economies
Equitable development can also contribute to the creation of climate-resilient economies by promoting sustainable livelihoods and supporting economic diversification. This includes investing in renewable energy, green infrastructure, and climate-resilient industries. By doing so, equitable development helps to reduce the economic vulnerability of communities to climate-related shocks and stresses, while also promoting sustainable economic growth.
| Key Strategies | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Investing in climate-resilient infrastructure | Reduces vulnerability to climate-related shocks |
| Supporting climate-resilient agriculture | Enhances food security and promotes sustainable livelihoods |
| Promoting inclusive decision-making | Fosters cooperation and trust among stakeholders |
Achieving Climate Justice through Equitable Development Strategies
'What role does equitable development play in achieving climate justice through climate action?'

Equitable development is crucial in achieving climate justice through climate action as it ensures that the benefits and burdens of climate change mitigation and adaptation efforts are distributed fairly among different populations. This involves addressing the existing social, economic, and environmental inequalities that make certain groups more vulnerable to the impacts of climate change.
Addressing Existing Inequalities
Equitable development plays a vital role in addressing the existing inequalities that exacerbate the impacts of climate change on vulnerable populations. This involves identifying and addressing the systemic barriers that prevent marginalized communities from accessing resources, services, and opportunities that can help them adapt to climate change.
- Providing climate-resilient infrastructure in marginalized communities
- Supporting climate-resilient agriculture practices among smallholder farmers
- Enhancing access to climate information and early warning systems for vulnerable populations
Promoting Inclusive Decision-Making
Equitable development promotes inclusive decision-making processes that involve the participation of diverse stakeholders, including marginalized communities, in the development and implementation of climate action plans. This ensures that the needs and concerns of all stakeholders are taken into account, and that climate action plans are responsive to the needs of the most vulnerable populations.
- Establishing participatory budgeting processes for climate change adaptation and mitigation projects
- Creating platforms for marginalized communities to engage with policymakers and other stakeholders
- Supporting capacity-building initiatives for local communities to take ownership of climate action plans
Fostering Climate-Resilient Economies
Equitable development fosters climate-resilient economies by promoting sustainable livelihoods and economic opportunities that are resilient to the impacts of climate change. This involves supporting climate-resilient infrastructure, promoting sustainable agriculture practices, and enhancing access to climate-resilient technologies and finance.
- Supporting the development of climate-resilient infrastructure, such as sea walls and green roofs
- Promoting sustainable agriculture practices, such as agroforestry and permaculture
- Enhancing access to climate-resilient technologies, such as climate-resilient crops and irrigation systems
What role does equitable development play in achieving climate justice?

Equitable development is crucial in achieving climate justice as it ensures that the benefits and burdens of climate change mitigation and adaptation efforts are distributed fairly among different populations. This involves addressing the existing social, economic, and environmental inequalities that make certain groups more vulnerable to the impacts of climate change. By promoting equitable development, we can reduce the disparities in access to resources, opportunities, and decision-making processes that exacerbate climate injustices.
Addressing Disproportionate Impacts on Vulnerable Populations
Equitable development plays a vital role in addressing the disproportionate impacts of climate change on vulnerable populations, such as low-income communities, indigenous peoples, and small-island developing states. These groups often lack the resources and capacity to adapt to climate change, making them more susceptible to its adverse effects.
- Providing climate-resilient infrastructure to protect vulnerable communities from the impacts of climate-related disasters
- Supporting climate-resilient agriculture and livelihoods to enhance the resilience of vulnerable populations
- Promoting inclusive decision-making processes to ensure that the needs and concerns of vulnerable populations are taken into account
Promoting Climate-Resilient Development Pathways
Equitable development involves promoting climate-resilient development pathways that prioritize the needs of vulnerable populations and the environment. This can be achieved by adopting policies and strategies that reduce greenhouse gas emissions, promote sustainable development, and enhance climate resilience.
- Investing in renewable energy and energy efficiency to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change
- Implementing sustainable land-use practices, such as reforestation and agroforestry, to sequester carbon and promote ecosystem resilience
- Supporting climate-resilient infrastructure development, such as sea walls and green roofs, to protect communities from climate-related hazards
Fostering International Cooperation and Climate Governance
Equitable development requires international cooperation and effective climate governance to address the global nature of climate change. This involves promoting collaborative approaches to climate change mitigation and adaptation, as well as ensuring that climate policies and programs are designed and implemented in a transparent, accountable, and participatory manner.
- Enhancing international climate finance mechanisms to support climate action in developing countries
- Promoting technology transfer and capacity-building to enhance the ability of developing countries to address climate change
- Supporting climate information and early warning systems to enhance climate resilience and reduce the risks associated with climate-related disasters
What role do equitability and environmental justice play in achieving sustainable development and climate justice outcomes?

Equitability and environmental justice play a crucial role in achieving sustainable development and climate justice outcomes. The concept of equitability refers to the fair distribution of resources, benefits, and burdens among different stakeholders, whereas environmental justice emphasizes the need to address the disproportionate impact of environmental degradation on vulnerable populations. The integration of equitability and environmental justice into sustainable development and climate justice outcomes ensures that the needs and rights of all individuals and communities are taken into account.
Integration with Sustainable Development Goals
The integration of equitability and environmental justice with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) is essential for achieving sustainable development outcomes. The SDGs provide a framework for addressing various development challenges, including poverty, inequality, and environmental degradation. By incorporating equitability and environmental justice into the SDGs, policymakers can ensure that the needs of marginalized communities are addressed, and that the benefits of development are shared fairly. Some key considerations for integrating equitability and environmental justice into the SDGs include:
- Ensuring that the needs and rights of vulnerable populations are taken into account in the development of SDG targets and indicators
- Promoting the participation of marginalized communities in the development and implementation of SDG-related policies and programs
- Addressing the root causes of inequality and environmental degradation, such as poverty, discrimination, and lack of access to resources
Addressing Climate Change through Environmental Justice
Environmental justice is critical in addressing climate change, as it highlights the need to address the disproportionate impact of climate change on vulnerable populations. Climate change exacerbates existing inequalities, as the poor and marginalized are often more vulnerable to its impacts, such as sea-level rise, droughts, and extreme weather events. By prioritizing environmental justice, policymakers can ensure that climate change policies and programs are designed to address the needs of vulnerable populations. Some key strategies for addressing climate change through environmental justice include:
- Supporting climate change adaptation and resilience-building initiatives in vulnerable communities
- Promoting the use of climate-resilient agriculture practices and technologies
- Enhancing access to climate information and early warning systems for vulnerable populations
Promoting Equitability in Climate Finance
Equitability is essential in climate finance, as it ensures that the benefits and burdens of climate finance are shared fairly among different stakeholders. Climate finance can be a powerful tool for promoting sustainable development and climate justice, but it can also exacerbate existing inequalities if not managed carefully. By prioritizing equitability in climate finance, policymakers can ensure that climate finance is used to support the needs of vulnerable populations. Some key considerations for promoting equitability in climate finance include:
- Ensuring that climate finance is allocated in a transparent and accountable manner
- Promoting the participation of vulnerable populations in the development and implementation of climate finance policies and programs
- Addressing the root causes of inequality and environmental degradation, such as poverty and lack of access to resources
What role does climate justice play in addressing global inequality?

Climate justice plays a crucial role in addressing global inequality by highlighting the disproportionate impact of climate change on vulnerable populations. The effects of climate change, such as rising sea levels, droughts, and extreme weather events, are felt more severely by communities that have contributed the least to greenhouse gas emissions. These communities often lack the resources and infrastructure to adapt to climate change, making them more susceptible to its negative impacts.
Disproportionate Impact on Vulnerable Populations
The concept of climate justice recognizes that certain groups, such as low-income communities, indigenous peoples, and small-island developing states, are more vulnerable to the impacts of climate change. These groups often rely heavily on natural resources for their livelihoods and have limited capacity to respond to climate-related disasters. The disproportionate impact of climate change on these populations is a result of historical and ongoing inequalities, including lack of access to education, healthcare, and economic opportunities.
- Limited access to climate-resilient infrastructure and technology
- Increased exposure to climate-related hazards and stressors
- Reduced ability to adapt to changing environmental conditions
Addressing Historical Injustices
Climate justice seeks to address the historical injustices that have contributed to the current state of climate change. This includes recognizing the role of colonialism, imperialism, and other forms of exploitation in perpetuating environmental degradation and social inequality. By acknowledging these historical injustices, climate justice advocates can work towards a more equitable distribution of resources and opportunities, and promote more sustainable and just development pathways.
- Recognition of historical emissions and their ongoing impacts
- Redress for past injustices and ongoing inequalities
- Support for climate-resilient development and adaptation efforts
Promoting Equitable Climate Action
Climate justice is essential for promoting equitable climate action that prioritizes the needs and perspectives of vulnerable populations. This includes supporting climate change adaptation and mitigation efforts that are led by local communities and prioritize their needs and concerns. By promoting equitable climate action, we can work towards a more just and sustainable future that addresses the root causes of climate change and promotes human well-being for all.
- Supporting community-led climate change initiatives
- Promoting inclusive and participatory decision-making processes
- Prioritizing the needs and perspectives of vulnerable populations in climate policy and action
Frequently Asked Questions
What is equitable development and how does it relate to climate justice?
Equitable development refers to the fair distribution of resources and benefits, ensuring that all individuals and communities have equal access to opportunities and services. It is crucial for achieving climate justice as it addresses the disproportionate impact of climate change on vulnerable populations, promoting a more just and inclusive response to climate challenges.
How does equitable development ensure climate justice outcomes?
Equitable development ensures climate justice outcomes by prioritizing the needs and perspectives of marginalized communities, who are often the most affected by climate change. By doing so, it helps to reduce existing social and economic inequalities, promoting a more just and resilient response to climate-related challenges and fostering sustainable development that benefits all.
What are the key elements of equitable development in the context of climate justice?
Key elements include inclusive decision-making processes, fair distribution of climate finance and benefits, and addressing the specific needs of vulnerable populations. It also involves promoting sustainable livelihoods, enhancing climate resilience, and supporting human rights, ultimately contributing to a more equitable and just climate governance framework that leaves no one behind.
Why is equitable development critical for achieving long-term climate justice?
Equitable development is critical for achieving long-term climate justice because it addresses the root causes of vulnerability and inequality, ensuring that climate actions are sustainable, effective, and just. By prioritizing equity, it helps to build trust, foster cooperation, and promote a more durable and resilient response to the climate crisis, ultimately leading to more sustainable and equitable outcomes.

Leave a Reply