How chemical pollutants interact with climate change stressors
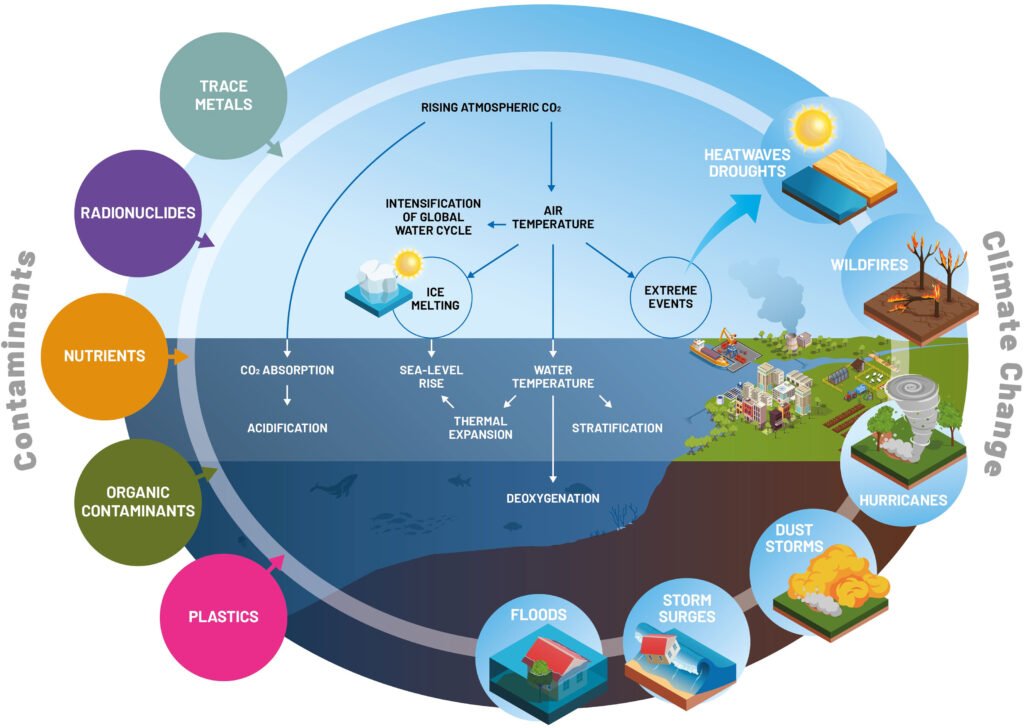
The escalating issue of climate change has brought to the forefront a complex interplay of environmental stressors, among which chemical pollutants play a significant yet often understated role. As global temperatures continue to rise and weather patterns become increasingly erratic, understanding the interactions between climate change stressors and chemical pollutants is crucial. This interaction can exacerbate the adverse effects on ecosystems, human health, and the planet as a whole. Examining these dynamics is essential for developing effective mitigation and adaptation strategies to address the compounded challenges posed by pollution and a changing climate.
- Chemical Pollutants and Climate Change: Understanding the Complex Interactions
-
Understanding the Complex Interplay Between Chemical Pollutants and Climate Change Drivers
- What role do chemical contaminants play in exacerbating climate change impacts?
- Impact on Ecosystems
- Effects on Human Health
- Feedback Loops and Amplification
- What is the impact of chemical pollutants on the climate system?
- Impact on Atmospheric Chemistry
- Influence on Climate Feedback Loops
- Effects on Ecosystems and Human Health
- How do chemical pollutants exacerbate the impacts of climate change stressors?
- Chemical Pollutants and Temperature Increase
- Impact on Water Resources
- Effects on Ecosystems and Biodiversity
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the primary chemical pollutants that interact with climate change stressors?
- How does climate change affect the fate and transport of chemical pollutants?
- Can climate change stressors increase the toxicity of chemical pollutants?
- What are the implications of the interactions between chemical pollutants and climate change stressors for policy and management?
Chemical Pollutants and Climate Change: Understanding the Complex Interactions
The interaction between chemical pollutants and climate change stressors is a complex and multifaceted issue. Climate change is not only altering ecosystems and disrupting biodiversity, but it is also affecting the fate and transport of chemical pollutants in the environment. As a result, it is essential to understand how these two factors interact and impact the health of our planet.
Impact of Climate Change on Chemical Pollutant Fate and Transport
Climate change is altering the way chemical pollutants move through the environment. Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns are affecting the volatilization, degradation, and transport of pollutants, potentially leading to increased exposure to toxic substances. For example, warmer temperatures can increase the rate of chemical reactions, leading to the formation of more toxic compounds.
Effects of Chemical Pollutants on Climate Change Vulnerability
Chemical pollutants can also exacerbate the impacts of climate change on ecosystems and human health. Exposure to pollutants can weaken the resilience of organisms and ecosystems, making them more vulnerable to the effects of climate-related stressors such as droughts, heatwaves, and storms. This can have cascading effects on ecosystem services and human well-being.
Synergistic Effects of Chemical Pollutants and Climate Change
The combined effects of chemical pollutants and climate change can be more than the sum of their individual impacts. Synergistic interactions between pollutants and climate-related stressors can lead to non-linear effects, where the presence of one stressor amplifies the impact of the other. Understanding these interactions is critical to predicting and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
| Climate Change Stressor | Chemical Pollutant Interaction | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Rising Temperatures | Increased volatilization of pollutants | Increased exposure to toxic substances |
| Changing Precipitation Patterns | Altered transport and deposition of pollutants | Increased contamination of water sources |
| Increased Extreme Weather Events | Release of pollutants from damaged infrastructure | Increased exposure to hazardous substances |
Understanding the Complex Interplay Between Chemical Pollutants and Climate Change Drivers
What role do chemical contaminants play in exacerbating climate change impacts?

Chemical contaminants play a significant role in exacerbating climate change impacts. The release of various pollutants into the environment, such as greenhouse gases, particulate matter, and toxic chemicals, contributes to the acceleration of global warming and its associated effects. These contaminants can come from a range of sources, including industrial activities, agricultural practices, and the burning of fossil fuels.
Impact on Ecosystems
Chemical contaminants can have devastating effects on ecosystems, which in turn can exacerbate the impacts of climate change. For example, pollutants such as pesticides and heavy metals can alter the composition of ecosystems, leading to changes in species populations and potentially even extinctions.
- The release of pollutants can reduce the resilience of ecosystems to climate change.
- Changes in species populations can have cascading effects on ecosystem functioning.
- Loss of biodiversity can reduce the ability of ecosystems to sequester carbon.
Effects on Human Health
Climate change can increase the spread of chemical contaminants, posing significant risks to human health. Warmer temperatures and changing precipitation patterns can lead to the release of stored pollutants, contaminating water and air.
- Increased frequency of extreme weather events can lead to the release of pollutants from industrial facilities.
- Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can increase the spread of waterborne diseases.
- Air pollution can exacerbate respiratory problems, particularly in vulnerable populations.
Feedback Loops and Amplification
Chemical contaminants can create feedback loops that amplify the impacts of climate change. For example, the release of methane from thawing permafrost can accelerate global warming, which in turn can lead to further thawing and methane release.
- The release of greenhouse gases from natural systems can accelerate global warming.
- Chemical contaminants can alter the Earth's energy balance, leading to further warming.
- The degradation of natural systems can reduce their ability to mitigate the effects of climate change.
What is the impact of chemical pollutants on the climate system?
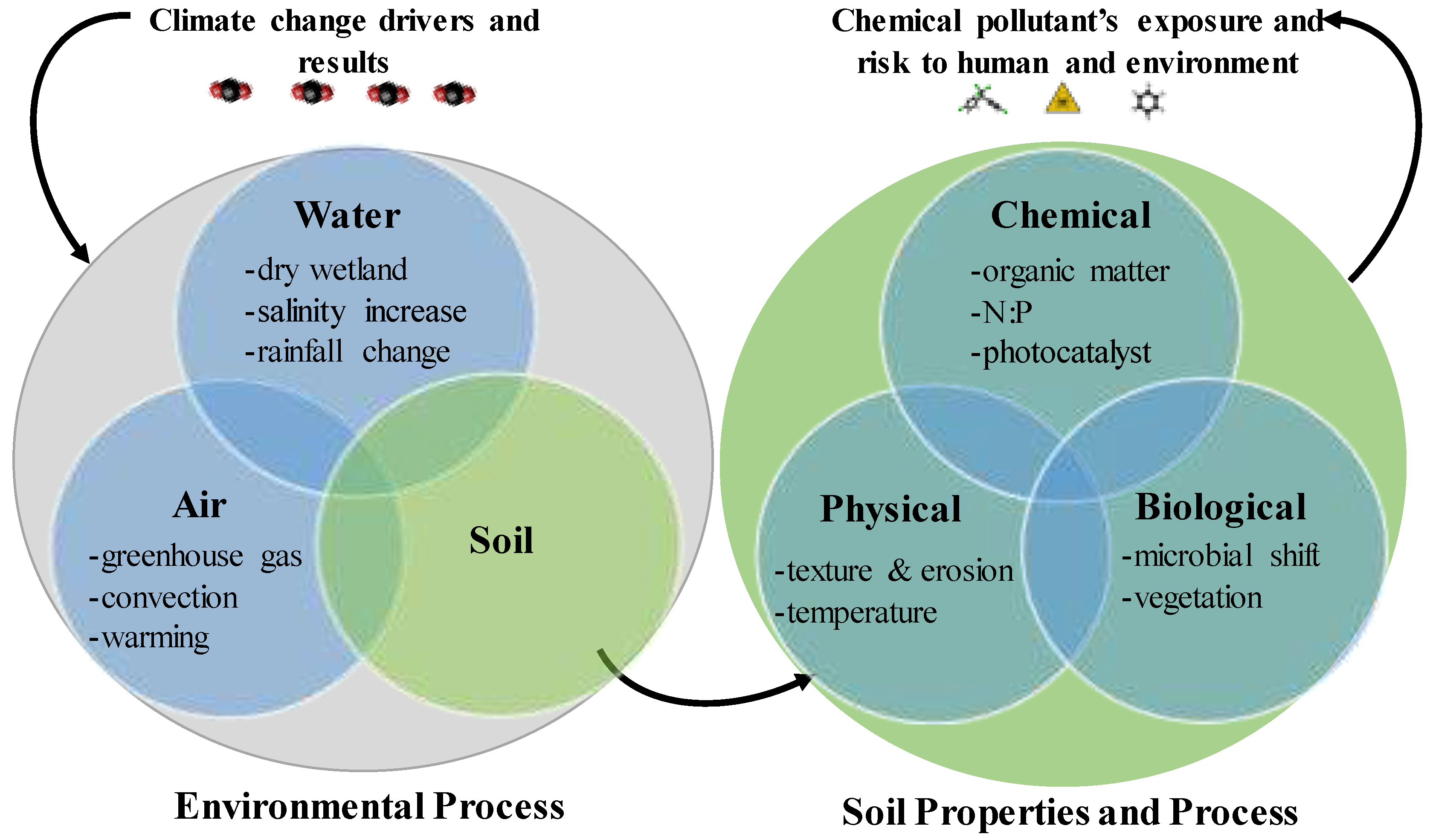
The impact of chemical pollutants on the climate system is multifaceted and far-reaching, involving various pathways through which these pollutants can influence climate change. Chemical pollutants, including greenhouse gases, aerosols, and other substances, can alter the Earth's energy balance, affect atmospheric circulation patterns, and influence the formation of clouds and precipitation.
Impact on Atmospheric Chemistry
Chemical pollutants can significantly impact atmospheric chemistry by altering the concentration of key species that influence the climate. For instance, pollutants such as nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds can lead to the formation of ground-level ozone and aerosols, which in turn affect the atmospheric radiative balance. The effects of these changes can be seen in several areas, including:
- Changes in atmospheric oxidation capacity, which can influence the lifetime of greenhouse gases and other pollutants.
- Alterations in the formation of secondary pollutants, such as particulate matter and ozone, which have significant health and environmental impacts.
- Impacts on the stratospheric ozone layer, which protects the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation.
Influence on Climate Feedback Loops
Chemical pollutants can also influence climate feedback loops, which are critical in determining the overall response of the climate system to external perturbations. For example, the release of certain pollutants can enhance or dampen feedback mechanisms such as the ice-albedo feedback or the water vapor feedback. Key aspects of this influence include:
- The role of aerosols in modifying cloud properties and thus influencing the Earth's albedo.
- The impact of pollutants on the formation of ice nuclei, which can affect cloud formation and precipitation patterns.
- The effects of climate change on the distribution and impact of chemical pollutants, creating a feedback loop between climate change and air quality.
Effects on Ecosystems and Human Health
The impact of chemical pollutants on ecosystems and human health is another critical dimension of their influence on the climate system. Pollutants can damage ecosystems, reduce biodiversity, and have direct and indirect effects on human health, all of which can be exacerbated by climate change. Important considerations include:
- The impact of pollutants on crop yields and food security, which can be further stressed by changing climate conditions.
- The effects of air pollution on human health, including increased mortality and morbidity due to cardiovascular and respiratory diseases.
- The potential for climate change to alter the distribution of disease vectors and the prevalence of certain health issues.
How do chemical pollutants exacerbate the impacts of climate change stressors?

Chemical pollutants can exacerbate the impacts of climate change stressors by interacting with and amplifying the effects of rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and increased extreme weather events. These interactions can have devastating consequences for ecosystems, human health, and the economy. For instance, chemical pollutants can alter the distribution, behavior, and physiology of organisms, making them more vulnerable to climate change stressors. This can lead to changes in species composition, reduced biodiversity, and disruptions to ecosystem services.
Chemical Pollutants and Temperature Increase
The increase in global temperatures due to climate change can react with chemical pollutants in the environment, such as ozone and particulate matter, to form more toxic compounds. This can lead to increased air pollution, negatively impacting human health, particularly for vulnerable populations such as the elderly and young children. Some of the effects include:
- Increased formation of ground-level ozone due to rising temperatures, exacerbating respiratory issues
- Release of stored pollutants in thawing permafrost, potentially contaminating water sources
- Enhanced toxicity of pollutants due to increased temperatures, affecting aquatic life
Impact on Water Resources
Climate change alters precipitation patterns, leading to droughts and floods, which can significantly impact the distribution and concentration of chemical pollutants in water bodies. This can result in the degradation of water quality, affecting both human consumption and ecosystems. Key aspects include:
- Increased runoff from heavy rainfall events, carrying pollutants into water bodies
- Concentration of pollutants in water sources during droughts due to reduced water volumes
- Changes in water temperature and chemistry affecting the bioavailability and toxicity of pollutants
Effects on Ecosystems and Biodiversity
The combination of chemical pollutants and climate change stressors can have synergistic effects on ecosystems, leading to loss of biodiversity and ecosystem disruption. This can compromise essential ecosystem services such as pollination, pest control, and nutrient cycling. Notable impacts are:
- Altered species distribution and extinction risk due to combined stressors
- Disruption of nutrient cycles and primary production affecting the food chain
- Loss of ecosystem resilience and ability to recover from disturbances
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary chemical pollutants that interact with climate change stressors?
Chemical pollutants such as particulate matter, ozone, and nitrogen dioxide can interact with climate change stressors like temperature and precipitation patterns. These interactions can exacerbate air quality issues and have negative impacts on human health and ecosystems. The primary pollutants involved are those emitted from fossil fuel combustion, industrial processes, and agricultural activities.
How does climate change affect the fate and transport of chemical pollutants?
Climate change alters environmental conditions, influencing the fate and transport of chemical pollutants. Changes in temperature, precipitation, and atmospheric circulation patterns can increase the mobility and persistence of pollutants, affecting their distribution and exposure to humans and wildlife. This can lead to increased contamination of air, water, and soil, with associated risks to ecosystems and human health.
Can climate change stressors increase the toxicity of chemical pollutants?
Yes, climate change stressors can increase the toxicity of chemical pollutants. For example, warmer temperatures can enhance the bioavailability and toxicity of certain pollutants, while changes in water chemistry can alter the speciation and toxicity of metals. This can lead to increased risks to aquatic life and human health, particularly for vulnerable populations.
What are the implications of the interactions between chemical pollutants and climate change stressors for policy and management?
The interactions between chemical pollutants and climate change stressors have significant implications for policy and management. Integrated approaches are needed to mitigate the combined impacts of pollution and climate change, including reducing greenhouse gas emissions and pollutant releases. This requires coordinated policies and strategies that address the interconnectedness of environmental stressors and their impacts on human health and ecosystems.

Leave a Reply