How transportation emissions influence urban air quality and warming
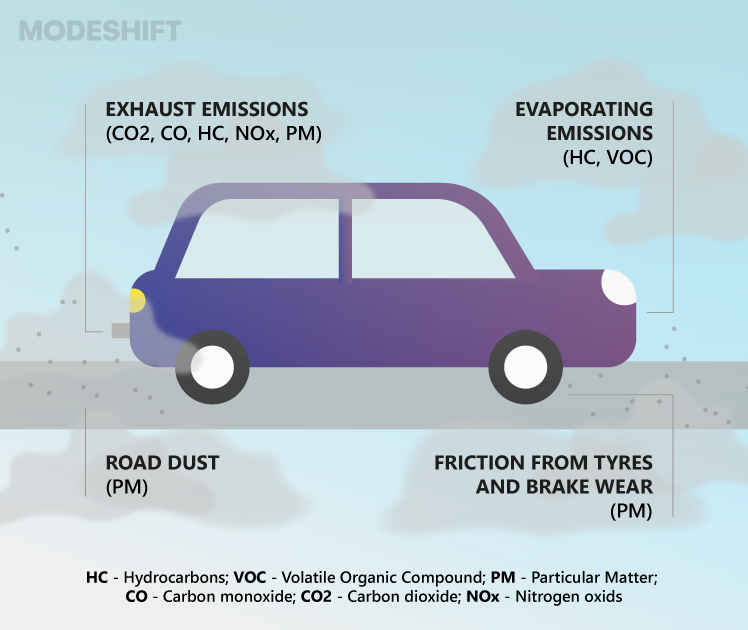
The rapid urbanization and increasing demand for transportation have led to a significant rise in emissions from vehicles, affecting both air quality and the urban climate. Transportation emissions release a multitude of pollutants, including particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and greenhouse gases, which contribute to air pollution and global warming. Understanding the impact of these emissions on urban environments is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate their harmful effects and create more sustainable cities. The relationship between transportation emissions, air quality, and urban warming will be explored, highlighting the need for cleaner transportation solutions.
- Impact of Transportation Emissions on Urban Air Quality and Global Warming
-
The Impact of Transportation Emissions on Urban Air Quality and Climate Change
- What impact do vehicle emissions have on air quality in cities?
- Impact on Urban Air Quality
- Effects on Human Health
- Mitigation Strategies
- What is the impact of transportation emissions on urban air quality?
- Impact on Human Health
- Effects on Urban Environment
- Strategies for Reducing Emissions
- What is the impact of transportation on urban air quality and environmental warming?
- Emissions from Transportation
- Impact on Environmental Warming
- Strategies for Mitigation
- What role do transportation emissions play in deteriorating urban air quality and exacerbating global warming?
- Impact on Urban Air Quality
- Contribution to Global Warming
- Potential Mitigation Strategies
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the primary emissions from transportation that affect urban air quality?
- How do transportation emissions contribute to urban warming?
- What is the impact of transportation emissions on urban air quality indices?
- Can reducing transportation emissions improve urban air quality and mitigate warming?
Impact of Transportation Emissions on Urban Air Quality and Global Warming
The influence of transportation emissions on urban air quality and global warming is a multifaceted issue that has garnered significant attention in recent years. As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change and air pollution, understanding the role that transportation emissions play in exacerbating these problems is crucial. Transportation emissions, which include pollutants and greenhouse gases emitted by vehicles, airplanes, and other forms of transportation, contribute significantly to both urban air pollution and global warming.
Effects on Urban Air Quality
Transportation emissions are a major contributor to urban air pollution, releasing harmful pollutants such as particulate matter (PM), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere. These pollutants can have severe health impacts on urban populations, including increased rates of respiratory diseases and cardiovascular conditions. The concentration of these pollutants in urban areas is often high due to the density of vehicles and other emission sources.
| Pollutant | Health Impact | Primary Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Particulate Matter (PM) | Respiratory and cardiovascular diseases | Diesel engines, construction, industrial activities |
| Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) | Respiratory problems, contributes to ground-level ozone formation | Vehicles, industrial processes, fossil fuel combustion |
| Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) | Respiratory issues, cancer risk | Vehicles, industrial processes, solvent use |
Contribution to Global Warming
Transportation is also a significant contributor to global warming, primarily through the emission of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases. The burning of fossil fuels in vehicles and other forms of transportation releases large amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere, contributing to the greenhouse effect and global warming. The impact of these emissions is felt not just locally but globally, as CO2 concentrations influence climate patterns worldwide.
| Greenhouse Gas | Global Warming Potential | Primary Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Dioxide (CO2) | 1 (reference) | Fossil fuel combustion in vehicles and industry |
| Methane (CH4) | 28-36 over 100 years | Leakage from natural gas systems, landfills |
| Nitrous Oxide (N2O) | 265-298 over 100 years | Agriculture, industrial processes, vehicles |
Mitigation Strategies
To mitigate the impacts of transportation emissions on both urban air quality and global warming, various strategies can be employed. These include transitioning to cleaner energy sources for transportation, such as electricity or hydrogen, improving the fuel efficiency of vehicles, and promoting the use of public transportation and non-motorized forms of transport like cycling and walking. Implementing policies to encourage these changes, such as emission standards and incentives for cleaner vehicles, can significantly reduce the negative impacts of transportation emissions.
| Strategy | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Electrification of Vehicles | Transitioning vehicles to electric power | Significant reduction in CO2 and air pollutant emissions |
| Improving Fuel Efficiency | Enhancing the fuel economy of conventional vehicles | Reduction in CO2 emissions and fuel consumption |
| Promoting Public and Non-Motorized Transport | Encouraging the use of buses, trains, cycling, and walking | Decrease in the number of private vehicles on the road, reducing emissions |
The Impact of Transportation Emissions on Urban Air Quality and Climate Change
What impact do vehicle emissions have on air quality in cities?

Vehicle emissions significantly impact air quality in cities, contributing to a decline in the overall health and well-being of urban residents. The release of pollutants such as particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, and volatile organic compounds from vehicles can lead to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog, exacerbating respiratory conditions like asthma and other cardiovascular diseases.
Impact on Urban Air Quality
The concentration of vehicle emissions in urban areas deteriorates air quality, particularly in cities with high population densities and heavy traffic. This results in increased levels of air pollutants, which can have severe health implications for residents. Some of the key effects include:
- increased respiratory problems due to particulate matter and ozone
- long-term exposure to poor air quality, leading to cardiovascular diseases
- reduced visibility and increased smog formation, affecting daily life and urban aesthetics
Effects on Human Health
The health impacts of vehicle emissions are multifaceted, ranging from respiratory issues to cardiovascular problems. Prolonged exposure to poor air quality can lead to a range of health issues, including:
- increased incidence of respiratory diseases such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes, due to long-term exposure to pollutants
- vulnerable populations, such as children, the elderly, and those with pre-existing health conditions, are disproportionately affected
Mitigation Strategies
To alleviate the negative impacts of vehicle emissions on urban air quality, various strategies can be employed. These include:
- implementing stricter emissions standards for vehicles and promoting the use of cleaner fuels
- investing in public transportation and encouraging the adoption of electric or hybrid vehicles
- implementing congestion charges or low-emission zones to reduce the number of polluting vehicles in urban areas
What is the impact of transportation emissions on urban air quality?

Transportation emissions have a significant impact on urban air quality, as they release a large amount of pollutants into the atmosphere, including particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, volatile organic compounds, and carbon monoxide. These pollutants can cause a range of health problems, including respiratory diseases, cardiovascular disease, and even premature death. The impact of transportation emissions on urban air quality is particularly significant in densely populated cities, where the concentration of vehicles and other sources of emissions is high.
Impact on Human Health
The emissions from transportation can have serious consequences for human health, particularly in urban areas where the population is exposed to high levels of air pollution. The pollutants released by vehicles can cause a range of health problems, from mild irritation of the eyes and throat to serious conditions such as asthma and lung cancer. Some of the specific health impacts of transportation emissions include:
- Respiratory problems, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Cardiovascular disease, including heart attacks and strokes
- Cancer, particularly lung cancer
Effects on Urban Environment
Transportation emissions not only affect human health but also have a significant impact on the urban environment. The pollutants released by vehicles can damage buildings and infrastructure, reduce visibility, and alter ecosystems. Some of the specific effects of transportation emissions on the urban environment include:
- Damage to buildings and infrastructure through acid rain and particulate matter deposition
- Reduced visibility due to particulate matter and other pollutants
- Changes to urban ecosystems, including impacts on plant and animal species
Strategies for Reducing Emissions
There are a range of strategies that can be implemented to reduce the impact of transportation emissions on urban air quality. These include improving vehicle emissions standards, promoting alternative modes of transportation, and implementing congestion pricing schemes. Some specific strategies for reducing transportation emissions include:
- Improving fuel efficiency and promoting the use of cleaner fuels
- Encouraging the use of public transportation, walking, and cycling
- Implementing congestion pricing schemes to reduce traffic volume
What is the impact of transportation on urban air quality and environmental warming?
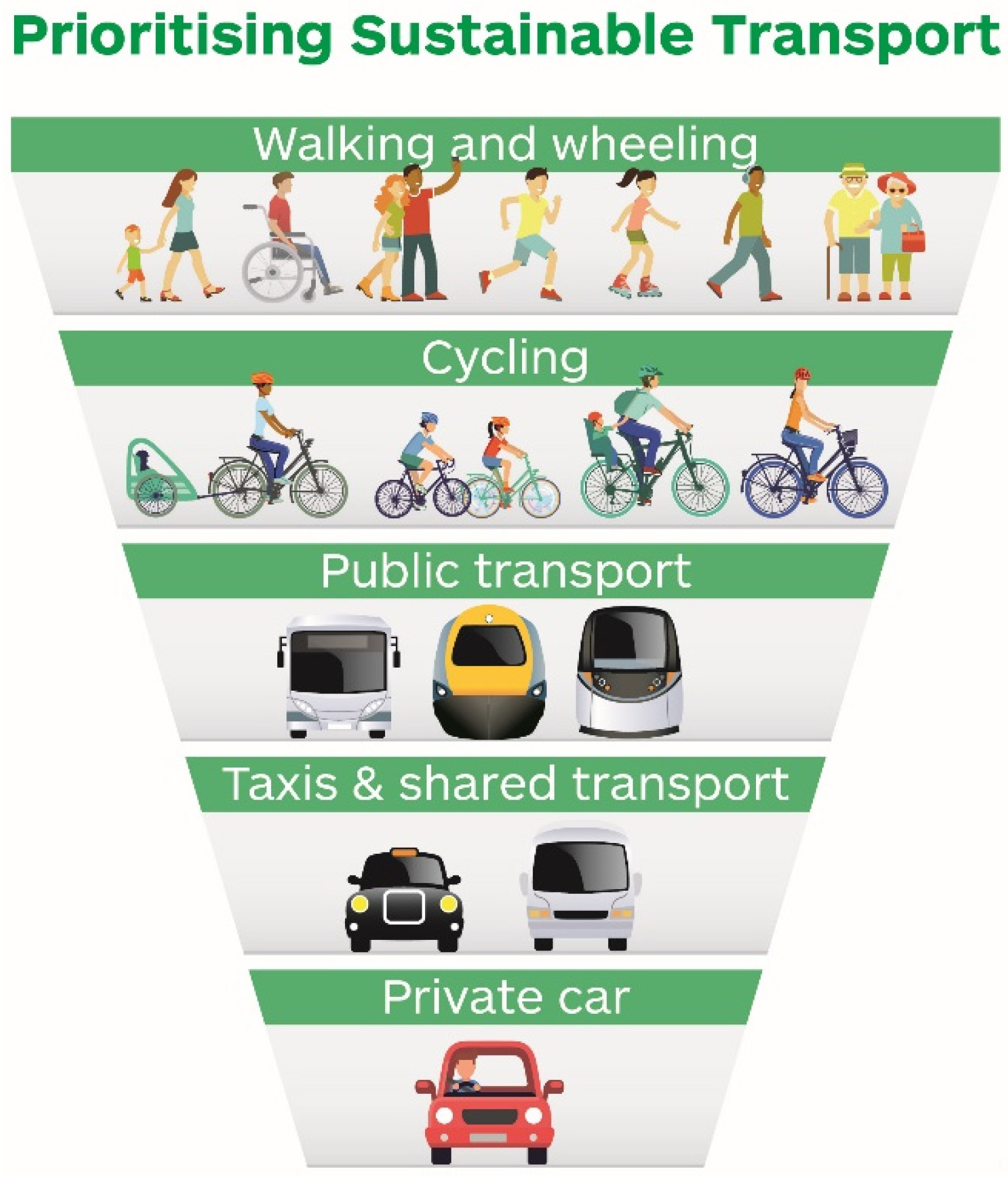
The impact of transportation on urban air quality and environmental warming is a significant concern worldwide. The increasing number of vehicles on the road has led to a rise in air pollutants, contributing to poor air quality and environmental degradation.
Emissions from Transportation
The primary source of air pollution from transportation is the emission of pollutants from vehicles, including particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, and volatile organic compounds. These pollutants can have severe health impacts, including respiratory problems and cardiovascular disease. The emissions from transportation also contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog, further exacerbating air quality issues.
- Particulate matter, including PM2.5 and PM10, can cause respiratory problems and cardiovascular disease.
- Nitrogen oxides can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog.
- Volatile organic compounds can react with other pollutants to form ground-level ozone and secondary particulate matter.
Impact on Environmental Warming
Transportation is also a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, primarily carbon dioxide, which contribute to environmental warming. The burning of fossil fuels in vehicles releases large amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, leading to global warming and climate change. This can have far-reaching consequences, including rising sea levels, more frequent natural disasters, and changes in weather patterns.
- The transportation sector is one of the largest contributors to greenhouse gas emissions globally.
- The burning of fossil fuels in vehicles releases carbon dioxide, a potent greenhouse gas.
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions from transportation will require a shift to alternative fuels and more efficient vehicles.
Strategies for Mitigation
To mitigate the impact of transportation on urban air quality and environmental warming, several strategies can be employed. These include improving vehicle efficiency, promoting the use of alternative fuels, and encouraging the use of public transportation and non-motorized modes of transportation. Additionally, implementing policies such as congestion pricing and low-emission zones can help reduce emissions and improve air quality.
- Improving vehicle efficiency can reduce emissions and improve air quality.
- Promoting the use of alternative fuels, such as electricity and biofuels, can reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
- Encouraging the use of public transportation and non-motorized modes of transportation can reduce the number of vehicles on the road.
What role do transportation emissions play in deteriorating urban air quality and exacerbating global warming?

Transportation emissions significantly contribute to the deterioration of urban air quality and the exacerbation of global warming. The combustion of fossil fuels in vehicles releases a multitude of pollutants, including particulate matter (PM), nitrogen oxides (NOx), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and carbon dioxide (CO2), into the atmosphere. These emissions not only harm human health by increasing the incidence of respiratory and cardiovascular diseases but also play a crucial role in climate change.
Impact on Urban Air Quality
The emissions from transportation, particularly in urban areas, lead to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog, which are major components of air pollution. This not only affects the health and wellbeing of urban populations but also damages crops and buildings. The key factors contributing to poor air quality due to transportation emissions include:
- The large number of vehicles on the road, especially in densely populated cities.
- The age and condition of vehicles, with older vehicles typically emitting more pollutants.
- The type of fuel used, with diesel engines often producing more NOx and PM than gasoline engines.
Contribution to Global Warming
Transportation is one of the significant contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, primarily CO2, which is a potent greenhouse gas that traps heat in the atmosphere, leading to global warming. The continuous increase in the number of vehicles on the road worldwide exacerbates this issue. Factors influencing the contribution of transportation to global warming include:
- The reliance on fossil fuels as the primary energy source for transportation.
- The growth in demand for transportation, driven by economic development and urbanization.
- The lack of stringent emissions regulations and enforcement in many parts of the world.
Potential Mitigation Strategies
To address the issues of urban air quality and global warming caused by transportation emissions, various strategies can be employed. These include improving vehicle fuel efficiency, promoting the use of cleaner energy sources such as electricity or hydrogen for transportation, and enhancing public transportation systems to reduce the reliance on personal vehicles. Effective measures could involve:
- Implementing stricter emissions standards for new vehicles.
- Encouraging the adoption of electric or hybrid vehicles through incentives.
- Investing in public transportation infrastructure to make it more appealing and efficient.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary emissions from transportation that affect urban air quality?
The primary emissions from transportation that affect urban air quality are particulate matter (PM), nitrogen oxides (NOx), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and carbon monoxide (CO). These pollutants come from vehicles such as cars, trucks, buses, and motorcycles, and can react to form ground-level ozone and secondary PM, exacerbating respiratory issues and other health problems.
How do transportation emissions contribute to urban warming?
Transportation emissions contribute to urban warming by releasing greenhouse gases, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2) and black carbon, which absorb solar radiation and trap heat. These emissions enhance the urban heat island effect, where built-up areas are warmer than surrounding rural areas due to the concentration of heat-absorbing surfaces and human activities.
What is the impact of transportation emissions on urban air quality indices?
Transportation emissions significantly impact urban air quality indices, as they are a major source of pollutants that contribute to poor air quality. Cities with high transportation emissions often experience elevated levels of air pollution, negatively affecting the air quality index and posing health risks to residents, particularly those with pre-existing respiratory conditions.
Can reducing transportation emissions improve urban air quality and mitigate warming?
Reducing transportation emissions can significantly improve urban air quality and mitigate warming. By transitioning to cleaner transportation modes, such as electric or hybrid vehicles, and promoting non-motorized transportation, cities can decrease pollutant emissions and lower greenhouse gas emissions, resulting in better air quality and a reduced urban heat island effect.

Leave a Reply