How energy inefficient buildings contribute climate change burden
The built environment plays a significant role in the global effort to mitigate climate change, with buildings accounting for a substantial portion of greenhouse gas emissions. Energy inefficient buildings, in particular, contribute to the climate change burden by consuming excessive amounts of energy, primarily generated from fossil fuels. This results in increased carbon emissions, further exacerbating the problem. As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change, it is essential to examine the impact of energy inefficient buildings and explore strategies to reduce their carbon footprint, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable future. Energy efficiency is a critical aspect.
- The Impact of Energy Inefficient Buildings on Climate Change
-
The Impact of Energy Inefficient Buildings on Climate Change: Understanding the Burden
- What role does energy efficiency play in mitigating the impact of climate change caused by inefficient buildings?
- Reducing Energy Consumption
- Economic and Environmental Benefits
- Implementing Energy Efficiency Measures
- 'What role do energy-inefficient buildings play in exacerbating climate change?'
- Energy Consumption Patterns
- Environmental Impacts
- Potential Solutions
- What role do energy-inefficient buildings play in exacerbating climate change through infrastructure?
- Energy Consumption Patterns
- Infrastructure Implications
- Potential Mitigation Strategies
- What role does electricity waste play in exacerbating climate change through energy inefficiency?
- Sources of Electricity Waste
- Impact of Electricity Waste on Climate Change
- Strategies to Mitigate Electricity Waste
- Frequently Asked Questions
The Impact of Energy Inefficient Buildings on Climate Change
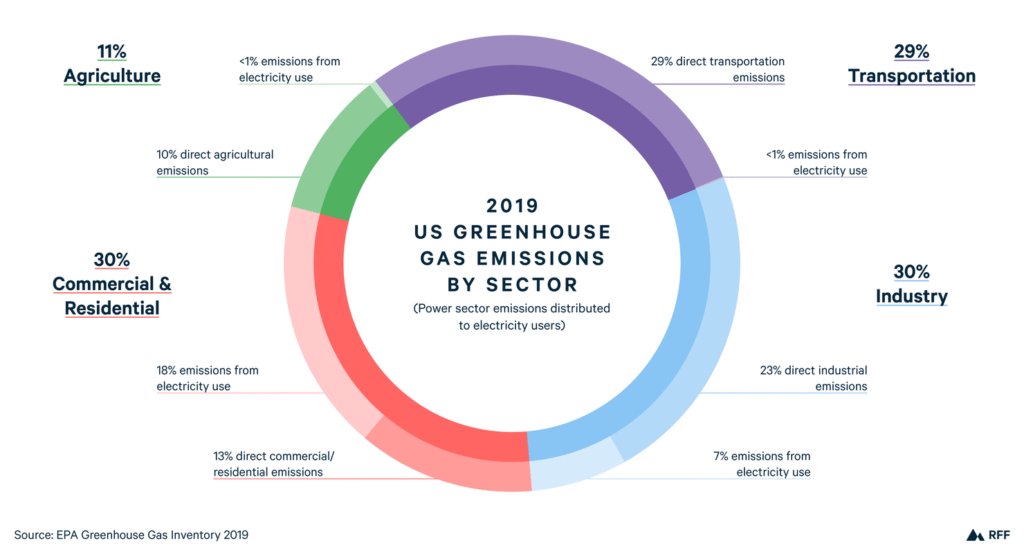
Energy inefficient buildings play a significant role in exacerbating the climate change burden. The construction and operation of buildings are among the largest consumers of energy worldwide, and when these buildings are not designed or retrofitted with energy efficiency in mind, they contribute substantially to greenhouse gas emissions. The energy used in buildings comes primarily from fossil fuels, which release carbon dioxide (CO2) and other harmful pollutants into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming and climate change.
Energy Consumption and Emissions
Buildings account for a significant portion of global energy consumption and associated emissions. In many countries, the building sector is responsible for nearly 40% of total energy use and a substantial share of CO2 emissions. The primary sources of these emissions are heating, cooling, and powering buildings. When buildings are energy inefficient, they require more energy to maintain comfortable temperatures and provide necessary services, leading to increased emissions of CO2 and other greenhouse gases.
Consequences of Inefficiency
The consequences of energy inefficiency in buildings extend beyond the environmental impact. Inefficient buildings also have higher operating costs due to increased energy consumption. This not only affects the building owners and occupants but also strains the energy grid, particularly during peak usage periods. Furthermore, energy inefficiency can lead to reduced indoor air quality and comfort, negatively impacting the health and productivity of occupants.
Pathways to Improvement
Improving energy efficiency in buildings can significantly mitigate their contribution to climate change. This can be achieved through various measures, including enhancing building insulation, installing energy-efficient lighting and HVAC systems, and incorporating renewable energy sources. Retrofitting existing buildings with energy-efficient technologies and designing new buildings with energy efficiency in mind are critical strategies for reducing the sector's carbon footprint.
| Building Component | Energy Inefficiency Impact | Improvement Measure |
|---|---|---|
| Building Envelope | Poor insulation leads to heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer. | Enhanced Insulation and Window Upgrades. |
| Lighting Systems | Inefficient lighting consumes more electricity. | LED Lighting and Smart Lighting Controls. |
| HVAC Systems | Inefficient systems increase energy consumption for heating and cooling. | High-Efficiency HVAC Units and Regular Maintenance. |
The Impact of Energy Inefficient Buildings on Climate Change: Understanding the Burden
What role does energy efficiency play in mitigating the impact of climate change caused by inefficient buildings?

Energy efficiency plays a crucial role in mitigating the impact of climate change caused by inefficient buildings. Buildings are among the largest consumers of energy worldwide, accounting for a significant portion of greenhouse gas emissions. Inefficient buildings waste energy, leading to increased energy consumption, higher energy costs, and a larger carbon footprint. By improving energy efficiency in buildings, we can reduce the demand for energy, lower emissions, and help combat climate change.
Reducing Energy Consumption
Improving energy efficiency in buildings involves various measures that reduce the amount of energy required to power them. This can be achieved through the use of energy-efficient technologies and practices, such as installing LED lighting, optimizing HVAC systems, and enhancing building insulation.
- Upgrading to energy-efficient windows to minimize heat loss and gain
- Implementing smart building technologies to optimize energy usage
- Using renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, to reduce dependence on fossil fuels
Economic and Environmental Benefits
Energy-efficient buildings offer numerous economic and environmental benefits. By reducing energy consumption, building owners and occupants can save on energy costs, while also contributing to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions.
- Lower energy bills due to reduced energy consumption
- Reduced maintenance costs through the use of durable and efficient systems
- Enhanced property values due to the appeal of energy-efficient buildings
Implementing Energy Efficiency Measures
Implementing energy efficiency measures in buildings requires a comprehensive approach that involves various stakeholders, including building owners, architects, engineers, and policymakers. Governments can play a crucial role by establishing and enforcing energy efficiency standards and providing incentives for building owners to adopt energy-efficient practices.
- Conducting energy audits to identify areas of inefficiency
- Developing and implementing energy-efficient building codes and standards
- Providing financial incentives for energy-efficient retrofits and new constructions
'What role do energy-inefficient buildings play in exacerbating climate change?'

Energy-inefficient buildings play a significant role in exacerbating climate change by consuming large amounts of energy, primarily in the form of electricity and heating fuels. This energy consumption is often associated with the burning of fossil fuels, which releases greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming. The inefficient use of energy in buildings not only increases the demand for energy but also results in higher emissions of pollutants.
Energy Consumption Patterns
The energy consumption patterns in energy-inefficient buildings are characterized by high levels of energy waste. This is often due to outdated or poorly maintained building systems, inadequate insulation, and inefficient lighting and appliances. As a result, these buildings require more energy to maintain a comfortable temperature and provide necessary services.
- Inadequate building envelope design leads to heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer.
- Inefficient HVAC systems consume more energy than necessary.
- Outdated lighting systems, such as incandescent bulbs, waste a significant amount of energy.
Environmental Impacts
The environmental impacts of energy-inefficient buildings are multifaceted. The increased energy consumption not only contributes to climate change but also results in air pollution, water pollution, and habitat destruction. The extraction, processing, and transportation of fossil fuels required to meet the energy demands of these buildings can lead to environmental degradation.
- Greenhouse gas emissions from energy-inefficient buildings contribute to climate change.
- Air pollutants from fossil fuel combustion affect local air quality and public health.
- The demand for water and other resources in energy production can strain local resources.
Potential Solutions
To mitigate the role of energy-inefficient buildings in exacerbating climate change, several solutions can be implemented. These include retrofitting existing buildings with energy-efficient technologies and designing new buildings with energy efficiency in mind.
- Upgrading to energy-efficient HVAC systems and appliances can significantly reduce energy consumption.
- Improving building insulation and envelope design can minimize heat loss and gain.
- Implementing smart building technologies can optimize energy use based on occupancy and need.
What role do energy-inefficient buildings play in exacerbating climate change through infrastructure?

Energy-inefficient buildings play a significant role in exacerbating climate change through infrastructure. These buildings are characterized by their high consumption of energy for heating, cooling, and powering various appliances, largely due to poor insulation, outdated HVAC systems, and inefficient lighting. The high energy demand of these buildings results in increased greenhouse gas emissions, primarily carbon dioxide, which is a major contributor to global warming. The infrastructure supporting these buildings, including power generation and transmission systems, also contributes to environmental degradation.
Energy Consumption Patterns
Energy consumption patterns in inefficient buildings are a critical factor in understanding their impact on climate change. These buildings often rely heavily on non-renewable energy sources, which are major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions. The energy is used for various purposes, including heating, cooling, lighting, and powering appliances.
- High energy consumption for heating and cooling due to poor insulation and inefficient HVAC systems.
- Increased reliance on non-renewable energy sources for power generation.
- Use of outdated and inefficient lighting and appliances.
Infrastructure Implications
The infrastructure supporting energy-inefficient buildings has significant implications for the environment. The demand for energy to power these buildings drives the need for additional power generation and transmission infrastructure, much of which is based on fossil fuels. This not only contributes to greenhouse gas emissions but also results in environmental degradation due to the extraction, processing, and transportation of these fuels.
- Expansion of fossil fuel-based power generation to meet high energy demands.
- Development of transmission infrastructure, which can lead to habitat destruction and other environmental impacts.
- Increased strain on existing grid infrastructure, potentially leading to inefficiencies and reliability issues.
Potential Mitigation Strategies
Addressing the role of energy-inefficient buildings in exacerbating climate change requires the implementation of effective mitigation strategies. These can include retrofitting buildings with energy-efficient technologies, adopting renewable energy sources, and implementing policies to encourage sustainable building practices.
- Retrofitting buildings with energy-efficient HVAC systems and insulation.
- Adopting on-site renewable energy generation, such as solar or wind power.
- Implementing building codes and standards that promote energy efficiency.
What role does electricity waste play in exacerbating climate change through energy inefficiency?
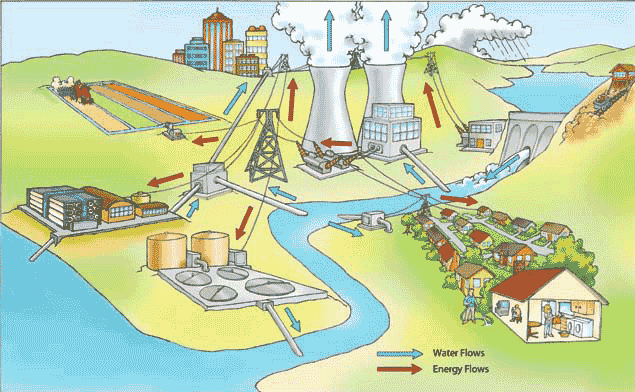
Electricity waste plays a significant role in exacerbating climate change through energy inefficiency. The generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity result in substantial energy losses, primarily in the form of heat. This inefficiency not only wastes energy but also leads to increased greenhouse gas emissions, as more fuel is burned to meet the demand for electricity. As a result, the environmental impact of electricity waste is substantial, contributing to climate change and air pollution.
Sources of Electricity Waste
Electricity waste occurs at various stages of the electricity supply chain, including generation, transmission, and distribution. Inefficient power plants, outdated infrastructure, and poor energy management practices all contribute to electricity waste. Some of the key sources of electricity waste include:
- inefficient appliances and lighting
- outdated or poorly maintained electrical infrastructure
- overconsumption of electricity due to lack of energy-efficient practices
Impact of Electricity Waste on Climate Change
The impact of electricity waste on climate change is multifaceted. Not only does it lead to increased greenhouse gas emissions, but it also perpetuates energy inefficiency. As the demand for electricity continues to grow, the environmental consequences of electricity waste will only intensify. Some of the key effects of electricity waste on climate change include:
- enhanced greenhouse gas emissions due to increased energy consumption
- accelerated climate change through the release of carbon dioxide and other pollutants
- increased air pollution, negatively affecting public health and environmental quality
Strategies to Mitigate Electricity Waste
To mitigate the effects of electricity waste, various strategies can be implemented. These include improving energy efficiency, promoting the use of renewable energy sources, and adopting smart grid technologies. Some effective strategies to reduce electricity waste include:
- upgrading to energy-efficient appliances and lighting
- investing in smart grid infrastructure to optimize energy distribution
- promoting energy conservation practices through education and awareness campaigns
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of energy inefficient buildings in climate change?
Energy inefficient buildings significantly contribute to climate change by consuming more energy than necessary, resulting in increased greenhouse gas emissions. These emissions, primarily carbon dioxide, trap heat in the atmosphere, accelerating global warming. Inefficient buildings rely heavily on fossil fuels for heating, cooling, and power, further exacerbating the problem and increasing the overall carbon footprint.
How do energy inefficient buildings impact the environment?
Energy inefficient buildings harm the environment by wasting energy, increasing energy demand, and relying on non-renewable energy sources. This leads to higher emissions of greenhouse gases and other pollutants, contributing to climate change, air pollution, and negative impacts on ecosystems and biodiversity. The environmental impact is further compounded by the resources required to construct and maintain these buildings.
Can retrofitting buildings reduce their contribution to climate change?
Retrofitting buildings with energy-efficient technologies can significantly reduce their contribution to climate change. Upgrades such as improved insulation, energy-efficient lighting and HVAC systems, and smart building technologies can decrease energy consumption and lower greenhouse gas emissions. Retrofitting can also enhance occupant comfort and reduce operational costs, making it a beneficial strategy for both the environment and building owners.
Are there economic benefits to improving energy efficiency in buildings?
Improving energy efficiency in buildings offers substantial economic benefits, including reduced energy costs and lower operational expenses. Energy-efficient buildings also tend to have higher property values and can command higher rental rates. Additionally, governments often provide incentives for energy-efficient retrofits, such as tax credits and grants, further offsetting the costs and enhancing the economic viability of such projects.

Leave a Reply