How greenhouse gas emissions drive atmospheric warming patterns
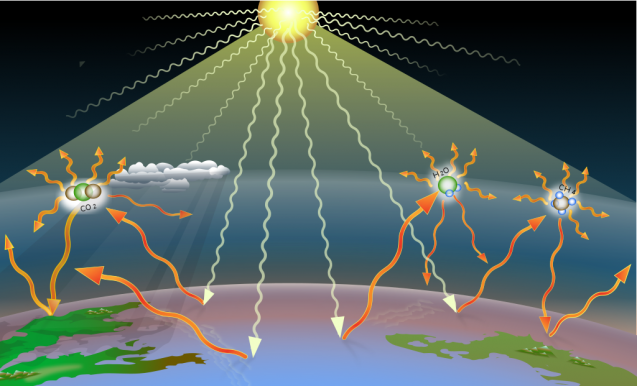
The increasing levels of greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere have been a pressing concern for decades, as they play a crucial role in driving global climate change. The rising concentrations of these gases, primarily carbon dioxide and methane, are fundamentally altering the planet's energy balance. Understanding how greenhouse gas emissions influence atmospheric warming patterns is essential for developing effective strategies to mitigate the worst impacts of climate change. Research into the complex interactions between greenhouse gases and the atmosphere is ongoing. This article examines the key mechanisms by which greenhouse gas emissions drive atmospheric warming patterns and their implications for the planet.
- Understanding the Impact of Greenhouse Gas Emissions on Atmospheric Warming
-
Understanding the Impact: How Greenhouse Gas Emissions Influence Global Atmospheric Warming Trends
- What is the impact of greenhouse gas emissions on atmospheric warming trends?
- Mechanisms of Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- Effects on Global Temperature Trends
- Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
- What drives atmospheric warming through the greenhouse effect?
- Greenhouse Gases
- Atmospheric Warming Process
- Impact on Climate
- What is the most significant greenhouse gas contributor to global warming?
- Sources of CO2 Emissions
- Impact of CO2 on Global Warming
- Reducing CO2 Emissions
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are greenhouse gas emissions and how do they contribute to atmospheric warming?
- How do different greenhouse gases affect atmospheric warming?
- What role do human activities play in increasing greenhouse gas emissions?
- Can natural factors influence greenhouse gas emissions and atmospheric warming?
Understanding the Impact of Greenhouse Gas Emissions on Atmospheric Warming
Greenhouse gas emissions play a crucial role in driving atmospheric warming patterns. The increasing levels of these gases in the Earth's atmosphere, primarily due to human activities such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes, trap more heat from the sun, leading to a global rise in temperatures. This phenomenon is known as the greenhouse effect. The main greenhouse gases responsible for this effect are carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and fluorinated gases. Understanding how these emissions influence atmospheric warming is essential for developing strategies to mitigate climate change.
The Role of CO2 in Atmospheric Warming
Carbon dioxide is the most prevalent greenhouse gas emitted by human activities, with the largest share coming from the burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas. The concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere has significantly increased since the Industrial Revolution, leading to an enhancement of the natural greenhouse effect and an increase in global temperatures. The warming effect of CO2 is well-documented and is a major driver of climate change, influencing weather patterns, sea-level rise, and ecosystems around the world.
Methane's Contribution to Atmospheric Warming
Methane is another potent greenhouse gas, with a global warming potential about 28 times higher than CO2 over a 100-year time frame. Methane emissions come from various sources, including agriculture (especially rice paddies and cattle), natural gas production and transport, and landfills. Reducing methane emissions is considered a critical strategy for slowing down the rate of global warming in the short term because of its significant impact on the climate.
Strategies for Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
To combat atmospheric warming, it is crucial to implement strategies that reduce greenhouse gas emissions. This can be achieved through a transition to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and adopting sustainable land use practices. For example, shifting from fossil fuels to solar and wind energy can significantly decrease CO2 emissions. Similarly, practices like reforestation and sustainable agriculture can help sequester carbon from the atmosphere.
| Greenhouse Gas | Global Warming Potential (100-year) | Major Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Dioxide (CO2) | 1 | Fossil fuel combustion, deforestation |
| Methane (CH4) | 28 | Agriculture, natural gas production and transport |
| Nitrous Oxide (N2O) | 265-298 | Agriculture, industrial processes |
| Fluorinated Gases | varies | Industrial processes, air conditioning |
Understanding the Impact: How Greenhouse Gas Emissions Influence Global Atmospheric Warming Trends
What is the impact of greenhouse gas emissions on atmospheric warming trends?

The impact of greenhouse gas emissions on atmospheric warming trends is a pressing concern in the context of climate change. Greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, trap heat in the atmosphere, leading to a warming effect on the planet. As the concentration of these gases increases, the atmosphere retains more heat, resulting in rising global temperatures.
Mechanisms of Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The primary mechanism through which greenhouse gas emissions affect atmospheric warming is the greenhouse effect. When greenhouse gases are released into the atmosphere, they absorb and re-emit infrared radiation, trapping heat and contributing to global warming. The main sources of these emissions include fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and industrial processes. Some key factors influencing the impact of greenhouse gas emissions include:
- The concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere
- The type of greenhouse gas emitted, as different gases have varying global warming potentials
- The rate at which these gases are emitted
Effects on Global Temperature Trends
The increased concentration of greenhouse gases has led to a significant rise in global temperatures over the past century. The average global temperature has been increasing at an unprecedented rate, with the last decade being the warmest on record. This warming trend is not uniform and varies by region, with polar regions experiencing more rapid warming than other areas. Key aspects of this trend include:
- An increase in extreme weather events such as heatwaves and droughts
- Melting of glaciers and ice sheets, contributing to sea-level rise
- Shifts in the distribution and prevalence of certain ecosystems and species
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
To combat the impacts of greenhouse gas emissions on atmospheric warming, various mitigation and adaptation strategies are being implemented. Mitigation efforts focus on reducing emissions through the transition to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and promoting sustainable land use practices. Adaptation strategies, on the other hand, aim to enhance resilience to the impacts of climate change. Some critical components of these strategies include:
- Transitioning to cleaner energy sources to reduce dependence on fossil fuels
- Implementing policies to protect and restore natural carbon sinks like forests
- Developing and deploying climate-resilient infrastructure and technologies
What drives atmospheric warming through the greenhouse effect?
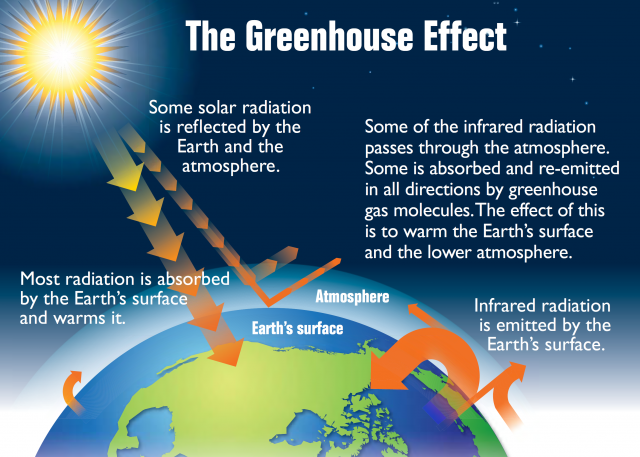
The greenhouse effect is a natural process that occurs when certain gases in the Earth's atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor, trap heat from the sun, leading to a warming effect on the planet.
Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gases play a crucial role in the Earth's energy balance. They allow short-wave radiation from the sun to pass through the atmosphere and reach the Earth's surface, where it is absorbed and converted into long-wave radiation. This long-wave radiation is then trapped by the greenhouse gases, preventing it from escaping back into space.
- Carbon dioxide is one of the most significant greenhouse gases, responsible for around 65% of the warming attributable to all greenhouse gases.
- Methane is another potent greenhouse gas, with a global warming potential around 28 times higher than carbon dioxide over a 100-year time frame.
- Water vapor is also an important greenhouse gas, as it is the most abundant greenhouse gas in the atmosphere and has a significant impact on the Earth's energy balance.
Atmospheric Warming Process
The atmospheric warming process is complex and involves the interaction of various factors, including the concentration of greenhouse gases, the amount of solar radiation received by the Earth, and the properties of the atmosphere itself. As the concentration of greenhouse gases increases, more long-wave radiation is trapped, leading to an increase in the Earth's average temperature.
- The increased concentration of greenhouse gases enhances the natural greenhouse effect, leading to an increase in the amount of heat trapped in the atmosphere.
- The warming of the atmosphere is not uniform, with some regions experiencing more significant warming than others due to factors such as changes in ocean currents and the distribution of land and sea.
- The atmospheric warming process is also influenced by other factors, including aerosols and changes in the Earth's orbit.
Impact on Climate
The greenhouse effect has a significant impact on the Earth's climate, influencing temperature, precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events. As the planet warms, it can lead to more frequent and severe heatwaves, droughts, and storms.
- Rising temperatures can alter the distribution and prevalence of certain climate-sensitive diseases and pests.
- Changes in precipitation patterns can impact agriculture, water resources, and ecosystems.
- The increased frequency and severity of extreme weather events can have significant social, economic, and environmental impacts.
What is the most significant greenhouse gas contributor to global warming?
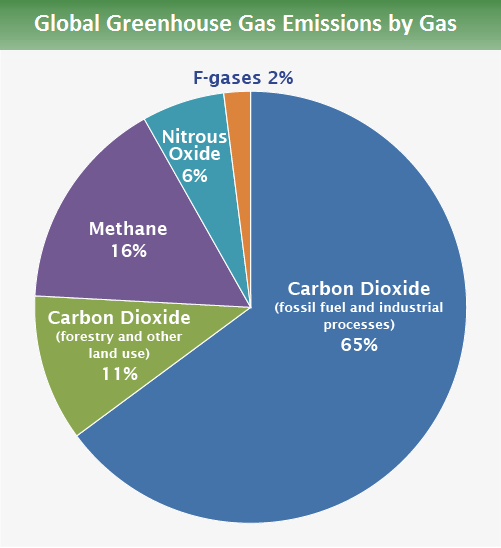
The most significant greenhouse gas contributor to global warming is carbon dioxide (CO2). CO2 is released through human activities such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and land-use changes, leading to a significant increase in its concentration in the atmosphere. This increase in CO2 concentration enhances the natural greenhouse effect, trapping more heat and leading to global warming.
Sources of CO2 Emissions
CO2 emissions come from various human activities that involve the combustion of fossil fuels, industrial processes, and changes in land use. The primary sources include the burning of coal, oil, and natural gas for energy and transportation, as well as deforestation and land degradation. Some of the key sectors responsible for CO2 emissions are:
- Energy production and consumption, including electricity generation and industrial processes
- Transportation, including cars, trucks, airplanes, and other vehicles
- Land-use changes, such as deforestation and degradation of forests
Impact of CO2 on Global Warming
The increased concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere has a profound impact on global warming. As CO2 is a potent greenhouse gas, it traps heat from the sun, preventing it from being released back into space. This trapped heat leads to an increase in global temperatures, contributing to climate change. Some of the effects of CO2 on global warming include:
- Rising global temperatures, leading to more frequent and severe heatwaves
- Changes in precipitation patterns, resulting in droughts and floods
- Melting of polar ice caps and glaciers, contributing to sea-level rise
Reducing CO2 Emissions
To mitigate the effects of global warming, it is essential to reduce CO2 emissions. This can be achieved through a range of measures, including increasing energy efficiency, transitioning to renewable energy sources, and protecting natural carbon sinks like forests. Some strategies for reducing CO2 emissions include:
- Improving energy efficiency in buildings and industry
- Promoting the use of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power
- Implementing policies to protect and restore forests, which absorb CO2 from the atmosphere
Frequently Asked Questions
What are greenhouse gas emissions and how do they contribute to atmospheric warming?
Greenhouse gas emissions refer to the release of gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide into the atmosphere, primarily through human activities like burning fossil fuels and deforestation. These gases trap heat from the sun, leading to a warming effect on the atmosphere, known as the greenhouse effect. This warming is a key driver of climate change, with significant impacts on global temperatures and weather patterns.
How do different greenhouse gases affect atmospheric warming?
Different greenhouse gases have varying levels of impact on atmospheric warming due to their distinct global warming potentials and atmospheric lifetimes. For example, carbon dioxide is the most prevalent long-lived greenhouse gas, while methane has a higher warming potential but a shorter atmospheric lifetime. Understanding the specific effects of each gas is crucial to developing effective strategies for mitigating climate change.
What role do human activities play in increasing greenhouse gas emissions?
Human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels for energy and transportation, are the primary drivers of increased greenhouse gas emissions. Deforestation, agriculture, and industrial processes also contribute significantly. The extraction, processing, and consumption of fossil fuels release large amounts of carbon dioxide, while agriculture and land-use changes lead to emissions of methane and nitrous oxide.
Can natural factors influence greenhouse gas emissions and atmospheric warming?
Yes, natural factors can influence greenhouse gas emissions and atmospheric warming. Volcanic eruptions, for instance, can release large amounts of sulfur dioxide, which can reflect sunlight and cool the atmosphere. However, human activities remain the dominant cause of the current increase in greenhouse gas emissions, and natural factors do not offset the warming caused by human-induced emissions. Understanding the interplay between natural and human factors is essential to predicting future climate change.

Leave a Reply