How frequent extreme weather events disrupt food security
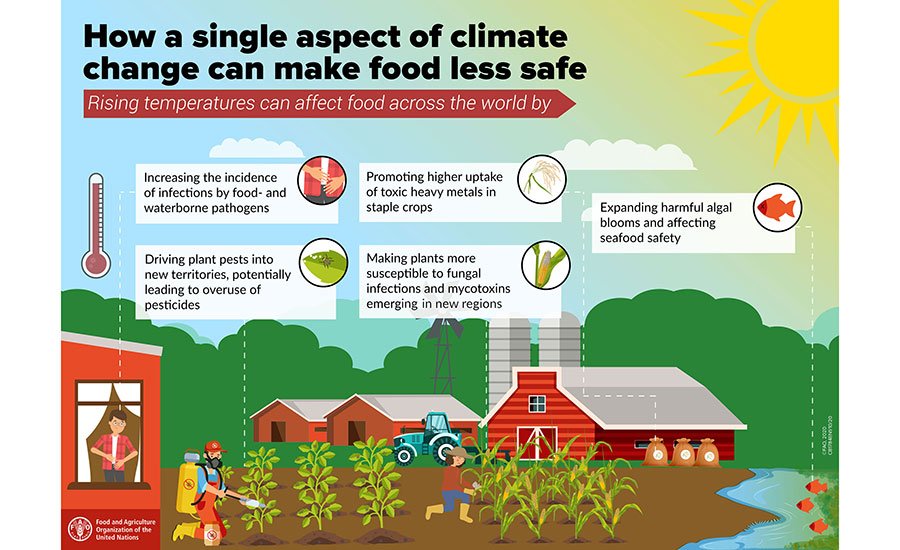
The increasing frequency and severity of extreme weather events have become a pressing concern globally. As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change, the impact on food security has emerged as a critical issue. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and intensified weather extremes are disrupting agricultural systems, affecting crop yields, and compromising food availability. The consequences of these disruptions can be far-reaching, influencing food prices, access to nutrition, and the overall well-being of communities. Understanding the complex relationships between extreme weather events and food security is essential.
- Impact of Extreme Weather Events on Global Food Security
-
Understanding the Impact of Recurring Extreme Weather on Global Food Stability
- What is the impact of extreme weather events on global food security?
- Impacts on Crop Yields
- Effects on Food Availability and Accessibility
- Long-term Consequences for Food Systems
- What is the impact of extreme weather events on global food security?
- Impacts on Crop Yields
- Effects on Food Prices and Availability
- Consequences for Food Systems and Livelihoods
- 'How do extreme weather events impact global food security?'
- Impacts on Crop Production
- Effects on Food Distribution and Access
- Consequences for Food Stability and Utilization
- 'How do extreme weather events impact global food stability?'
- Impact on Crop Yields and Quality
- Consequences for Food Distribution and Access
- Long-term Implications for Food Security
- Frequently Asked Questions
Impact of Extreme Weather Events on Global Food Security
The increasing frequency of extreme weather events such as droughts, floods, and heatwaves has become a significant concern for global food security. These events can have devastating effects on crop yields, food availability, and access to nutrition, ultimately threatening the well-being of communities worldwide. The disruption caused by extreme weather events can be far-reaching, affecting not only the immediate food supply but also the livelihoods of farmers and the stability of food systems.
Effects on Crop Yields and Production
Extreme weather events can significantly impact crop yields and production, leading to food shortages and economic losses. For instance, droughts can cause crop failures, while floods can destroy entire harvests. The resulting decrease in food production can lead to price volatility, making it difficult for vulnerable populations to access nutritious food. Furthermore, the loss of crops can also affect the livelihoods of farmers, who may struggle to recover from the losses.
| Weather Event | Impact on Crops | Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Drought | Crop failure, reduced yields | Food shortages, price increase |
| Floods | Crop destruction, soil erosion | Loss of livelihoods, food insecurity |
| Heatwaves | Reduced crop quality, yield loss | Decreased food availability, economic losses |
Disruption to Food Systems and Access to Nutrition
Extreme weather events can disrupt food systems, affecting not only the availability of food but also access to nutrition. Food distribution networks can be damaged or destroyed, making it difficult to transport food to affected areas. Moreover, the loss of infrastructure, such as roads and storage facilities, can further exacerbate the problem. As a result, communities may be left without access to nutritious food, leading to malnutrition and related health issues.
| Food System Component | Impact of Extreme Weather | Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Food distribution | Disruption to transportation networks | Delayed or blocked food deliveries |
| Infrastructure | Damage to roads, storage facilities | Loss of food, increased costs |
| Nutrition access | Reduced access to nutritious food | Malnutrition, related health issues |
Long-term Consequences and Resilience Building
The long-term consequences of extreme weather events on food security can be significant, with potential lasting impacts on the resilience of food systems. Repeated exposure to extreme weather events can lead to soil degradation, water scarcity, and loss of biodiversity, making it more challenging for communities to recover. To build resilience, it is essential to adopt climate-resilient agriculture practices, such as agroforestry and conservation agriculture, and to invest in disaster risk reduction measures.
| Resilience Building Measure | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Climate-resilient agriculture | Adoption of practices like agroforestry | Improved crop resilience, reduced losses |
| Disaster risk reduction | Investment in early warning systems, infrastructure | Reduced risk of damage, loss |
| Soil conservation | Implementation of conservation agriculture practices | Soil health improvement, reduced erosion |
Understanding the Impact of Recurring Extreme Weather on Global Food Stability
What is the impact of extreme weather events on global food security?
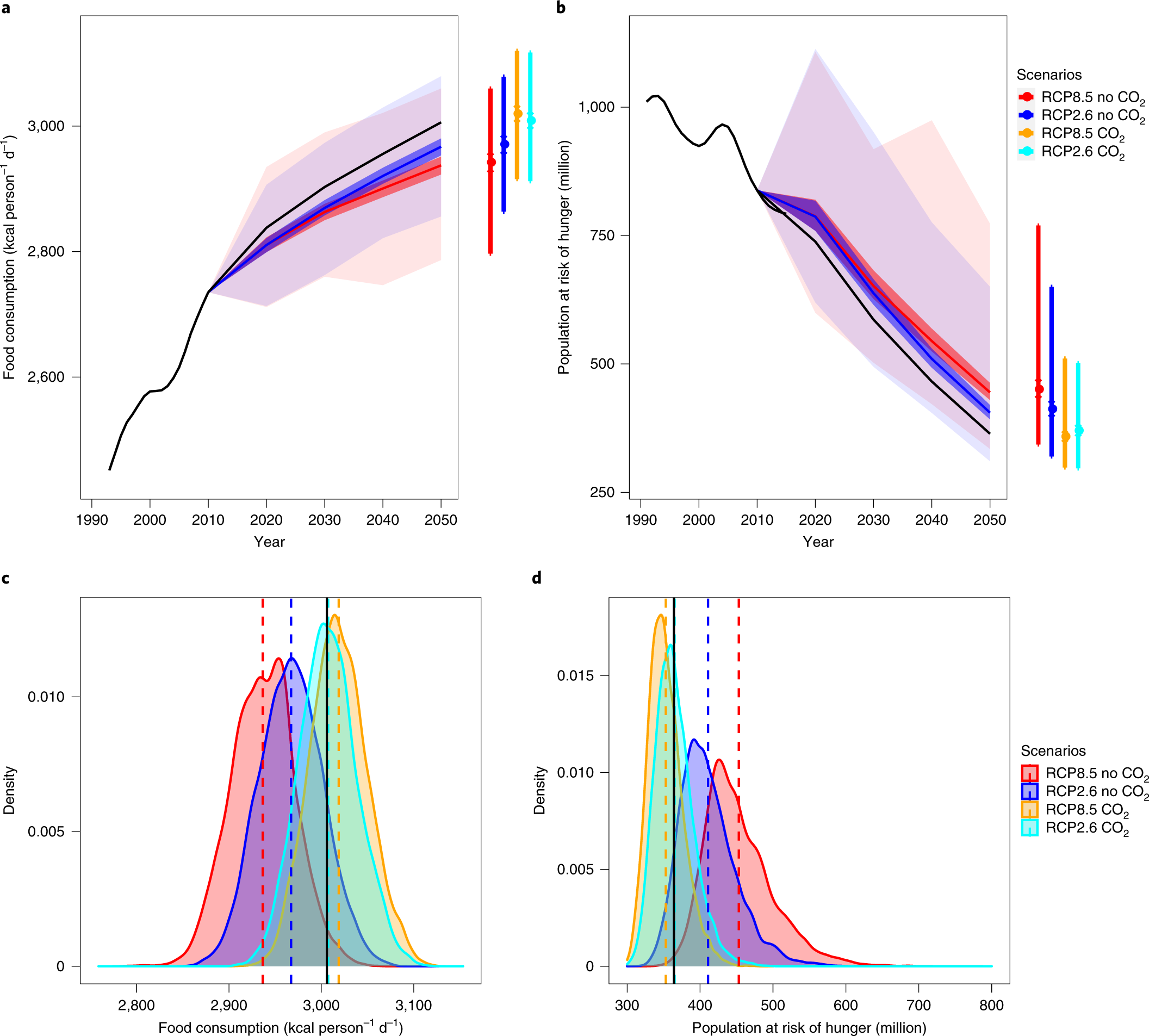
The impact of extreme weather events on global food security is a pressing concern as it can lead to crop failures, reduced yields, and changed growing seasons, ultimately affecting the availability and accessibility of food. Extreme weather events such as droughts, floods, heatwaves, and storms can have devastating effects on agricultural production, leading to food shortages and price increases. The consequences of these events can be far-reaching, impacting not only local communities but also global food systems.
Impacts on Crop Yields
Extreme weather events can significantly impact crop yields, leading to reduced productivity and lower quality crops. For instance, droughts can cause crop stress, while floods can damage or destroy crops. The effects of these events can be long-lasting, with some crops taking years to recover. Some of the key impacts on crop yields include:
- Reduced crop productivity due to drought or excessive rainfall
- Loss of crops due to extreme weather events such as floods or storms
- Changes in growing seasons and shifts in pest and disease dynamics
Effects on Food Availability and Accessibility
The impact of extreme weather events on global food security is also felt through changes in food availability and accessibility. When crops fail or are destroyed, food availability decreases, leading to price increases. This can make food less accessible to vulnerable populations, exacerbating existing food insecurity. Some of the key effects on food availability and accessibility include:
- Price increases due to shortages and supply chain disruptions
- Changes in food trade patterns and impacts on global markets
- Increased food insecurity among vulnerable populations
Long-term Consequences for Food Systems
The long-term consequences of extreme weather events on global food security can be severe, with potential lasting impacts on food systems. Repeated exposure to extreme weather events can lead to soil degradation, loss of biodiversity, and changes in water availability, making it more challenging to maintain productive and resilient food systems. Some of the key long-term consequences include:
- Soil degradation and loss of fertile land
- Changes in water availability and quality
- Loss of biodiversity and ecosystem services
What is the impact of extreme weather events on global food security?
The impact of extreme weather events on global food security is multifaceted and far-reaching, affecting agricultural productivity, food availability, and access to food. Extreme weather events such as droughts, floods, and heatwaves can lead to crop failures, livestock deaths, and damage to agricultural infrastructure, ultimately resulting in food shortages and price increases.
Impacts on Crop Yields
Extreme weather events can significantly impact crop yields, leading to reduced food availability and economic losses for farmers. Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns can alter the growing conditions for crops, making them more susceptible to pests and diseases.
- Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can disrupt the delicate balance of ecosystems, leading to an increase in pest and disease pressure.
- Extreme weather events can also damage or destroy crops, resulting in yield losses and reduced quality.
- The impacts of extreme weather events on crop yields can be particularly severe in regions with limited agricultural infrastructure and resources.
Effects on Food Prices and Availability
The impacts of extreme weather events on crop yields and livestock productivity can have significant effects on food prices and availability. When crops fail or are damaged, food supplies can become scarce, leading to price increases.
- Price increases can make food less accessible to vulnerable populations, particularly those living in poverty.
- Food price volatility can also have broader economic impacts, affecting not only consumers but also farmers and other stakeholders in the food system.
- The impacts of extreme weather events on food prices and availability can be particularly severe in regions with limited social safety nets and emergency response systems.
Consequences for Food Systems and Livelihoods
The impacts of extreme weather events on global food security can have significant consequences for food systems and livelihoods. When food systems are disrupted, the livelihoods of farmers, herders, and other stakeholders can be severely affected.
- The loss of crops or livestock can lead to significant economic losses for farmers and herders.
- The impacts of extreme weather events on food systems can also have broader social impacts, affecting the cultural and social fabric of communities.
- The resilience of food systems to extreme weather events can be improved through the adoption of climate-resilient agricultural practices and technologies.
'How do extreme weather events impact global food security?'

Extreme weather events have a significant impact on global food security, affecting the availability, access, utilization, and stability of food supplies. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events such as droughts, floods, and heatwaves alter the conditions under which crops are grown, livestock are raised, and food is distributed. This can lead to crop failures, reduced yields, and changed growing seasons, ultimately affecting the global food supply.
Impacts on Crop Production
Extreme weather events directly impact crop production by damaging or destroying crops, altering the growing conditions, and disrupting the delicate balance of ecosystems. For instance, droughts can lead to water scarcity, while floods can cause soil erosion and nutrient loss. The effects on crop production can be far-reaching, with some of the key consequences including:
- Reduced crop yields due to unfavorable weather conditions
- Loss of biodiversity as certain crops are more vulnerable to extreme weather events
- Shifts in growing seasons and areas, potentially leading to changes in pest and disease dynamics
Effects on Food Distribution and Access
Extreme weather events not only affect food production but also the distribution and access to food. Infrastructure damage from events like floods and storms can disrupt transportation networks, making it difficult to get food from farms to markets. Additionally, price volatility can occur as supply chains are disrupted, affecting the affordability of food for consumers. Some of the key effects on food distribution and access include:
- Disruption of transportation networks due to infrastructure damage
- Increased food prices due to supply chain disruptions and reduced availability
- Reduced access to food for vulnerable populations, exacerbating food insecurity
Consequences for Food Stability and Utilization
The stability and utilization of food supplies are also significantly impacted by extreme weather events. Changes in food availability and access can lead to malnutrition, particularly in communities that are already vulnerable. Furthermore, the nutritional quality of food can be affected by the conditions under which it is produced and stored. Some of the key consequences for food stability and utilization include:
- Increased risk of malnutrition due to reduced access to diverse and nutritious food
- Potential for increased food waste as spoilage occurs due to improper storage conditions
- Long-term health impacts on communities due to changes in dietary patterns and nutritional quality
'How do extreme weather events impact global food stability?'
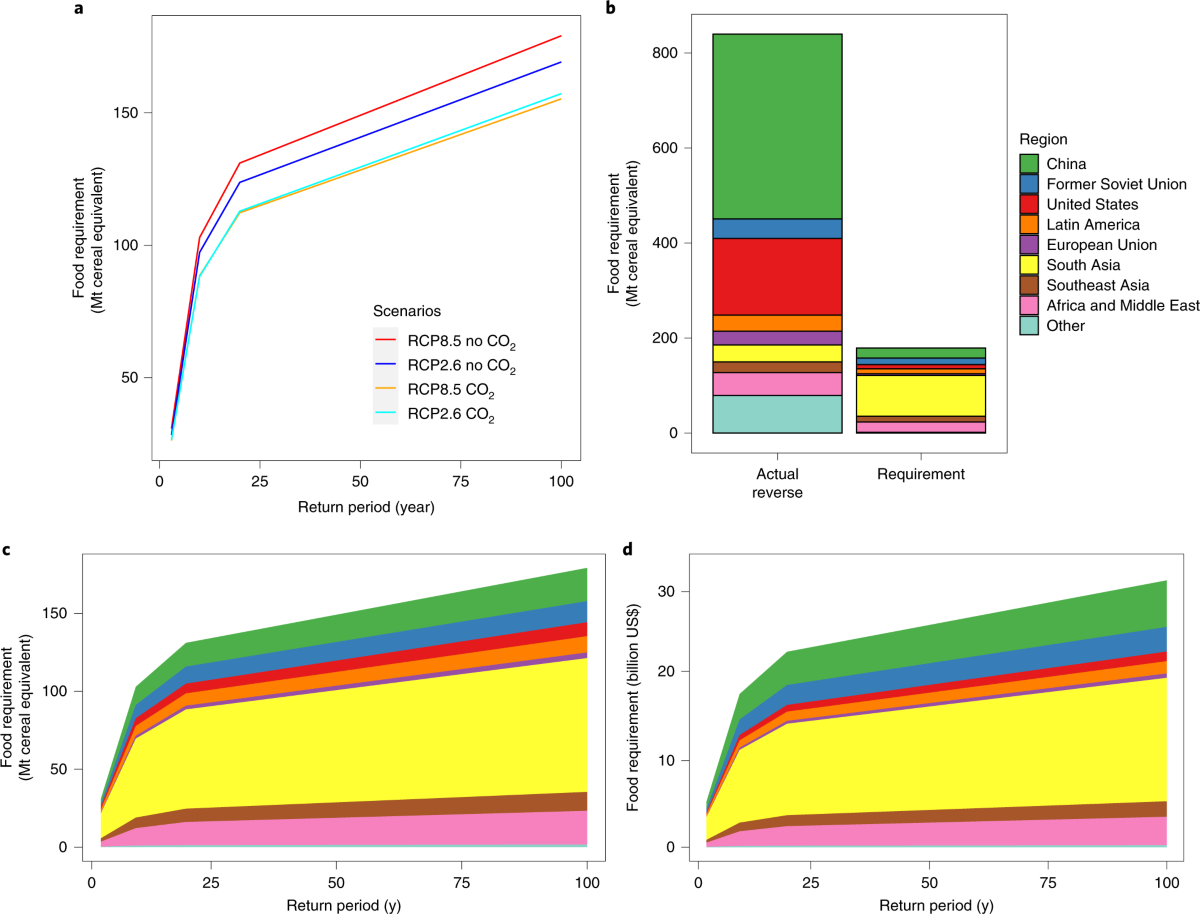
Extreme weather events significantly impact global food stability by affecting crop yields, food distribution, and access to nutritious food. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events such as droughts, floods, and heatwaves alter the conditions under which crops are grown, leading to reduced productivity and lower quality produce.
Impact on Crop Yields and Quality
The impact of extreme weather events on crop yields and quality is multifaceted. Extreme temperatures can directly damage crops, while altered precipitation patterns can lead to either drought or excessive moisture, both of which are detrimental to crop health.
- Temperature fluctuations can disrupt the delicate timing of plant flowering and pollination, leading to reduced seed set and lower yields.
- Excessive rainfall can cause soil erosion, nutrient leaching, and waterlogged soils that hinder root growth and promote disease.
- Conversely, drought conditions can lead to water stress, reducing plant growth and increasing susceptibility to pests and diseases.
Consequences for Food Distribution and Access
Extreme weather events not only affect the production of food but also its distribution and access. Infrastructure damage from events like floods and storms can disrupt transportation networks, leading to food spoilage and shortages in affected areas.
- Damage to roads and bridges can isolate communities, making it difficult to deliver food aid or supplies.
- Power outages resulting from extreme weather can compromise cold storage facilities, leading to the spoilage of perishable goods.
- Additionally, the economic impacts of extreme weather events can reduce consumers' purchasing power, further limiting access to food.
Long-term Implications for Food Security
The long-term implications of extreme weather events on global food stability are concerning. Repeated exposure to such events can lead to chronic food insecurity, particularly in vulnerable communities.
- Soil degradation resulting from erosion or salinization can reduce the long-term productivity of agricultural land.
- Loss of biodiversity, both in terms of crop varieties and pollinators, can make agricultural systems more vulnerable to future shocks.
- Migration and displacement caused by extreme weather events can strain the resources of receiving communities, potentially leading to social and economic tensions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are extreme weather events and how do they impact food security?
Extreme weather events include droughts, floods, heatwaves, and storms that disrupt food availability and access. These events damage crops, destroy infrastructure, and affect agricultural productivity, leading to food shortages and price increases. Vulnerable populations, especially in developing countries, are most affected, experiencing decreased food security and increased malnutrition.
How do droughts specifically affect food security?
Droughts significantly impact food security by reducing crop yields and water availability for irrigation. This leads to decreased food production, increased food prices, and reduced incomes for farmers. Prolonged droughts can also deplete water sources, further exacerbating the issue. Droughts can have long-term effects on agricultural productivity and food availability, making recovery challenging.
Can extreme weather events lead to long-term food insecurity?
Yes, extreme weather events can lead to long-term food insecurity, especially if they recur frequently or are particularly severe. Repeated exposure to such events can erode the resilience of communities, making it difficult for them to recover. This can lead to chronic food insecurity, where populations struggle to access sufficient and nutritious food over an extended period.
What measures can be taken to mitigate the impact of extreme weather on food security?
Implementing climate-resilient agricultural practices, such as using drought-tolerant crop varieties and improving irrigation systems, can help mitigate the effects of extreme weather. Enhancing early warning systems and supporting climate information services can also enable farmers to make informed decisions. Additionally, investing in social protection programs and disaster risk reduction measures can help protect vulnerable populations from the impacts of extreme weather events.

Leave a Reply