How increasing global temperatures impact human health risks
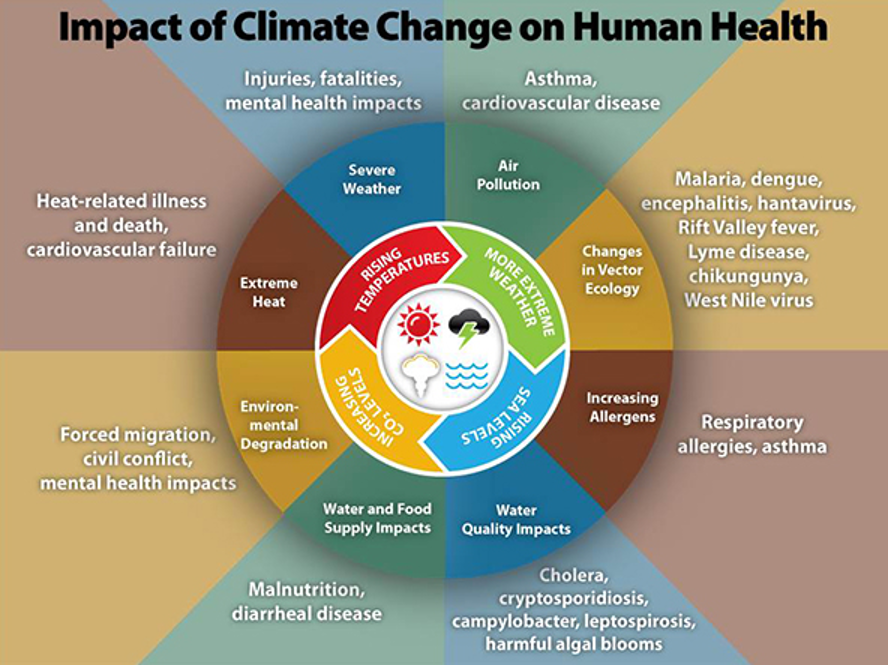
Rising global temperatures are having a profound impact on human health, with far-reaching consequences for individuals and communities worldwide. As the planet continues to warm, the risks associated with heat-related illnesses, cardiovascular disease, and other health problems are escalating. The World Health Organization estimates that between 2030 and 2050, climate change will cause approximately 250,000 additional deaths per year, mainly due to malnutrition, malaria, diarrheal diseases, and heat stress. Understanding the links between global temperatures and human health is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate these risks and protect vulnerable populations.
- Rising Temperatures and Human Health: Understanding the Risks
-
Rising Global Temperatures and Associated Human Health Risks: Understanding the Connection
- 'How do rising global temperatures affect human health outcomes?'
- Heat-Related Illnesses and Mortality
- Expansion of Disease Vectors
- Exacerbation of Existing Health Conditions
- 'Rising global temperatures: what are the top health risks to humans?'
- Heat-Related Illnesses
- Disease Vectors and Rising Temperatures
- Mental Health Impacts
- What are the health consequences of rising global temperatures on human populations?
- Heat-Related Illnesses
- Vector-Borne Diseases
- Mental Health Impacts
- Frequently Asked Questions
Rising Temperatures and Human Health: Understanding the Risks
The increasing global temperatures are having a profound impact on human health, with far-reaching consequences for individuals, communities, and health systems around the world. As the planet continues to warm, the risks associated with heat-related illnesses, cardiovascular disease, and other health problems are on the rise.
As global temperatures continue to rise, the incidence of heat-related illnesses is increasing, particularly among vulnerable populations such as the elderly, young children, and those with pre-existing medical conditions. Heat stress and heatstroke are becoming more common, with severe cases often requiring hospitalization. The World Health Organization (WHO) has estimated that between 2030 and 2050, climate change will cause approximately 250,000 additional deaths per year, mainly due to malnutrition, malaria, diarrheal diseases, and heat stress.
Cardiovascular Disease and Other Health Impacts
Rising temperatures are also linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, as the body's ability to regulate its temperature is impaired. This can lead to a range of health problems, including heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular conditions. Furthermore, the changing climate is altering the distribution of disease-carrying insects, such as mosquitoes, which can lead to an increased risk of vector-borne diseases like malaria and dengue fever.
Vulnerable Populations and Health Disparities
The impact of rising temperatures on human health is not evenly distributed, with certain populations facing greater risks than others. Low-income communities, indigenous populations, and those living in urban heat islands are often disproportionately affected, due to factors such as limited access to healthcare, inadequate housing, and lack of green spaces. The following table highlights some of the key health risks associated with rising temperatures:
| Health Risk | Vulnerable Population | Projected Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Heat-related illnesses | Elderly, young children, and those with pre-existing medical conditions | Increased hospitalizations and mortality |
| Cardiovascular disease | Individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions | Increased risk of heart attacks and strokes |
| Vector-borne diseases | Communities in areas with high mosquito densities | Increased risk of malaria, dengue fever, and other diseases |
Rising Global Temperatures and Associated Human Health Risks: Understanding the Connection
'How do rising global temperatures affect human health outcomes?'

Rising global temperatures are having a profound impact on human health outcomes. As the planet continues to warm due to climate change, the consequences for human health are becoming increasingly evident. The effects of rising temperatures are far-reaching, from increased mortality rates during heatwaves to the expansion of disease vectors and the exacerbation of existing health conditions.
Rising global temperatures are leading to an increase in heat-related illnesses and mortality, particularly among vulnerable populations such as the elderly, young children, and those with pre-existing medical conditions. The impact of heatwaves can be devastating, with high temperatures overwhelming the human body's ability to regulate its internal temperature, leading to heat exhaustion and heatstroke. Some of the key factors contributing to heat-related illnesses include:
- Prolonged exposure to high temperatures, especially in urban areas with heat islands
- Lack of access to air conditioning and other cooling measures
- Pre-existing medical conditions that impair the body's ability to regulate temperature
Expansion of Disease Vectors
As global temperatures rise, the habitats and ranges of disease vectors such as mosquitoes and ticks are expanding, increasing the risk of vector-borne diseases. Warmer temperatures allow these vectors to thrive in new regions, putting previously unaffected populations at risk. The expansion of disease vectors is a significant concern, with diseases such as malaria, dengue fever, and Lyme disease becoming increasingly prevalent. Some of the key factors contributing to the expansion of disease vectors include:
- Rising temperatures allowing vectors to survive and thrive in new regions
- Changes in precipitation patterns creating ideal breeding conditions for vectors
- Increased mobility and global travel facilitating the spread of disease
Exacerbation of Existing Health Conditions
Rising global temperatures are also exacerbating existing health conditions, particularly respiratory diseases such as asthma. Warmer temperatures increase the production of allergens and pollutants, exacerbating respiratory issues and reducing air quality. The impact of rising temperatures on existing health conditions is a significant concern, with increased hospitalizations and mortality rates. Some of the key factors contributing to the exacerbation of existing health conditions include:
- Increased production of allergens and pollutants due to warmer temperatures
- Changes in air quality and increased particulate matter
- Increased frequency and severity of extreme weather events
'Rising global temperatures: what are the top health risks to humans?'
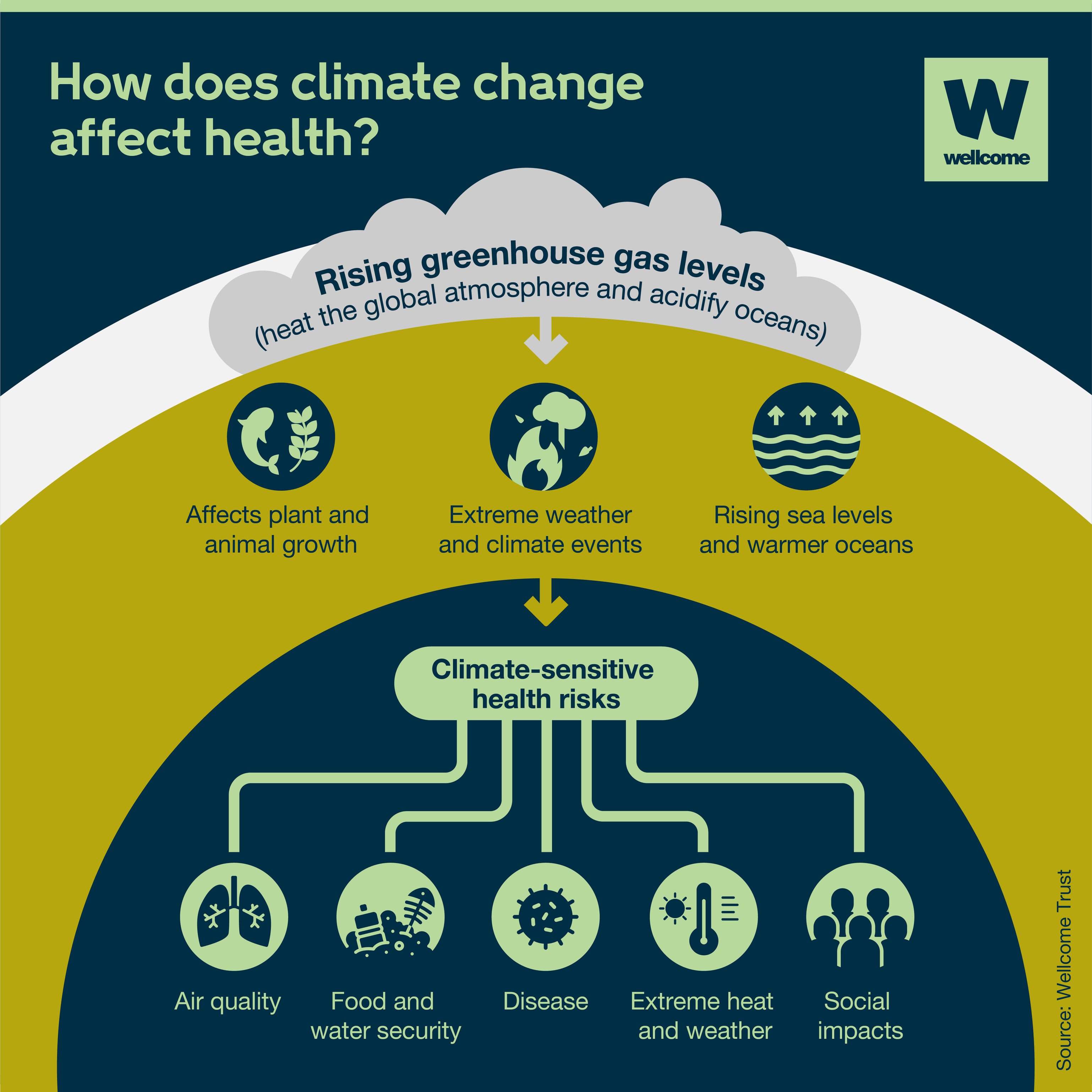
Rising global temperatures pose significant health risks to humans, affecting various aspects of well-being and increasing the likelihood of certain diseases. The top health risks associated with rising global temperatures include increased mortality due to heat stress, the spread of disease vectors, and mental health impacts. The impact of rising temperatures on human health is multifaceted, involving direct and indirect effects that can be devastating. One of the most immediate effects is the increase in heat-related illnesses and deaths. As temperatures rise, the body's ability to regulate its internal temperature is challenged, leading to conditions such as heat exhaustion and heatstroke.
Heat-related illnesses occur when the body is unable to cool itself properly, often due to excessive heat and humidity. This can lead to a range of health issues, from mild heat cramps and exhaustion to life-threatening heatstroke. Vulnerable populations such as the elderly, young children, and those with pre-existing medical conditions are at a higher risk.
- The elderly are more susceptible due to decreased mobility and the presence of chronic health conditions.
- Young children are at risk because their bodies are less able to regulate temperature effectively.
- People with pre-existing medical conditions may have impaired bodily responses to heat stress.
Disease Vectors and Rising Temperatures
Rising global temperatures are altering ecosystems and facilitating the spread of disease vectors such as mosquitoes and ticks. Warmer temperatures can expand the habitats of these vectors, increasing the incidence of diseases they carry.
- Expanded geographic ranges for mosquitoes can lead to increased transmission of diseases like malaria and dengue fever.
- Warmer temperatures can accelerate the life cycles of disease vectors, potentially increasing disease transmission rates.
- Changes in precipitation patterns can create ideal breeding conditions for mosquitoes and other vectors.
Mental Health Impacts
The mental health impacts of rising global temperatures should not be underestimated. Extreme weather events and changing environmental conditions can have profound psychological effects on individuals and communities.
- Trauma from extreme weather events can lead to anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
- Loss of livelihoods and homes due to climate-related disasters can exacerbate mental health issues.
- The stress of adapting to a changing climate can have long-term effects on mental well-being.
What are the health consequences of rising global temperatures on human populations?
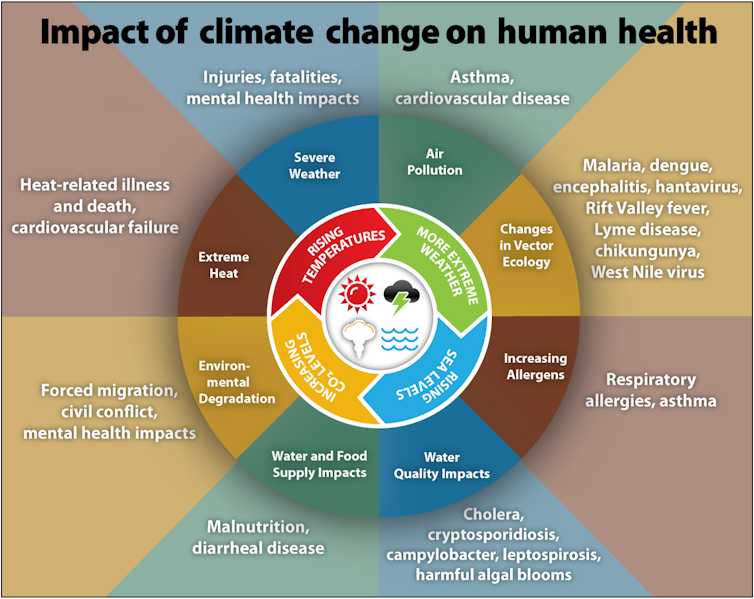
Rising global temperatures are having a profound impact on human health, with far-reaching consequences for populations around the world. As temperatures continue to rise, the effects on human health are becoming increasingly evident.
The most immediate consequence of rising global temperatures is an increase in heat-related illnesses. As temperatures soar, the human body's ability to regulate its internal temperature is put to the test, leading to a range of heat-related illnesses, from mild heat exhaustion to life-threatening heatstroke.
- Heat exhaustion is a condition that occurs when the body loses too much water and salt, usually due to excessive sweating.
- Heatstroke is a more severe condition that occurs when the body's temperature regulation system is overloaded, causing the body temperature to rise to dangerous levels.
- Vulnerable populations, such as the elderly, young children, and those with pre-existing medical conditions, are disproportionately affected by heat-related illnesses.
Vector-Borne Diseases
Rising global temperatures are also altering the distribution and prevalence of vector-borne diseases, such as malaria, dengue fever, and Zika virus. As temperatures rise, the habitats and behaviors of disease-carrying insects like mosquitoes and ticks are changing, increasing the risk of disease transmission.
- Warmer temperatures are allowing disease-carrying insects to survive and thrive in areas that were previously too cool for them.
- Changes in precipitation patterns and increased frequency of extreme weather events are also contributing to the spread of vector-borne diseases.
- The expansion of disease-carrying insects into new areas is putting previously unaffected populations at risk of infection.
Mental Health Impacts
In addition to the physical health consequences, rising global temperatures are also having a profound impact on mental health. The trauma and stress caused by extreme weather events, as well as the gradual changes in climate, are taking a toll on mental wellbeing.
- The displacement and migration caused by climate change are leading to increased stress, anxiety, and depression.
- The loss of livelihoods and cultural heritage due to climate change is also contributing to mental health impacts.
- The uncertainty and unpredictability of climate change are creating a sense of unease and insecurity, exacerbating existing mental health conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary health risks associated with rising global temperatures?
Rising global temperatures are linked to increased mortality and morbidity due to heat-related illnesses, cardiovascular diseases, and respiratory issues. Warmer temperatures also facilitate the spread of disease vectors like mosquitoes and ticks, elevating the risk of vector-borne diseases such as malaria and dengue fever. Extreme heat events can overwhelm healthcare systems, further complicating response efforts.
How do warmer temperatures affect the spread of disease?
Warmer temperatures can expand the geographical range and seasonality of disease vectors, increasing the potential for outbreaks. For example, ticks and mosquitoes thrive in warmer conditions, leading to a higher incidence of diseases they transmit. Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can also contaminate water sources, heightening the risk of waterborne diseases. This necessitates enhanced surveillance and preventive measures.
Can rising temperatures exacerbate existing health conditions?
Yes, rising temperatures can exacerbate existing health conditions, particularly cardiovascular and respiratory diseases. Heat stress can worsen conditions like asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), while increased air pollution from wildfires and heatwaves can further aggravate respiratory issues. Vulnerable populations, including the elderly and those with pre-existing medical conditions, are disproportionately affected by these changes.
What measures can be taken to mitigate the health impacts of global warming?
To mitigate the health impacts, strategies include enhancing heatwave early warning systems, promoting public awareness about heat-related illnesses, and implementing cooling measures in urban areas. Strengthening healthcare infrastructure and improving disease surveillance are also crucial. Additionally, reducing greenhouse gas emissions can slow the rate of global warming, decreasing the associated health risks over time.

Leave a Reply